Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2008; 14(20): 3207-3211
Published online May 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3207
Published online May 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3207
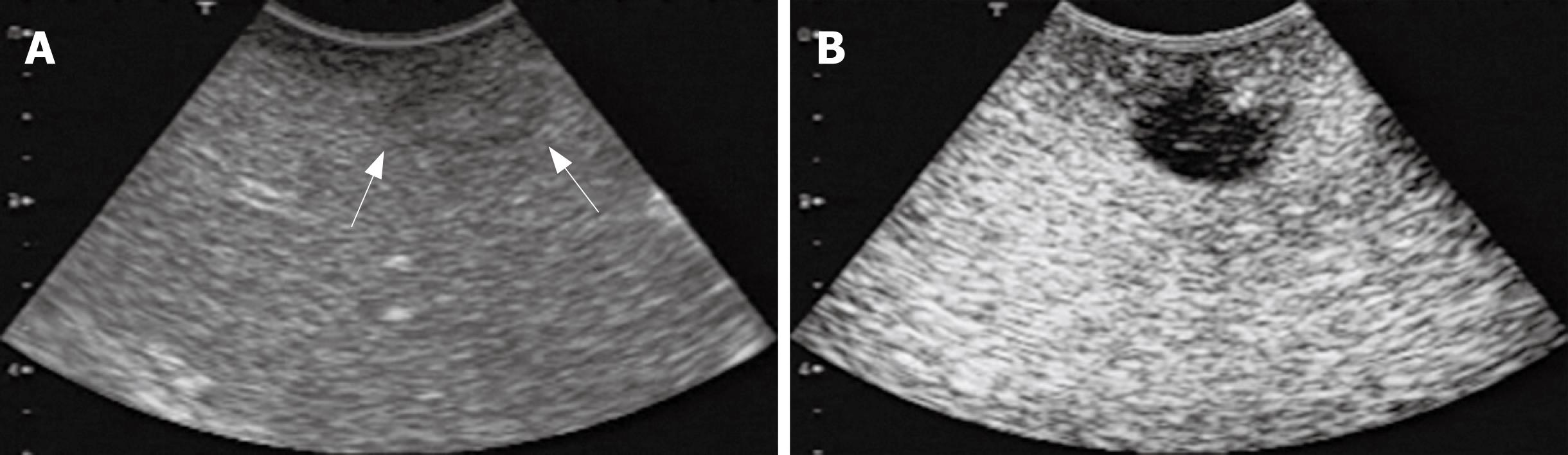
Figure 1 IOUS and CE-IOUS views of a metastasis at the Segment 8.
A: The metastatic lesion was unclearly detected as a slightly hypoechoic mass; B: CE-IOUS view of the same lesion. The metastatic lesion was shown as a distinct hypoechoic mass at the late Kupffer-phase.
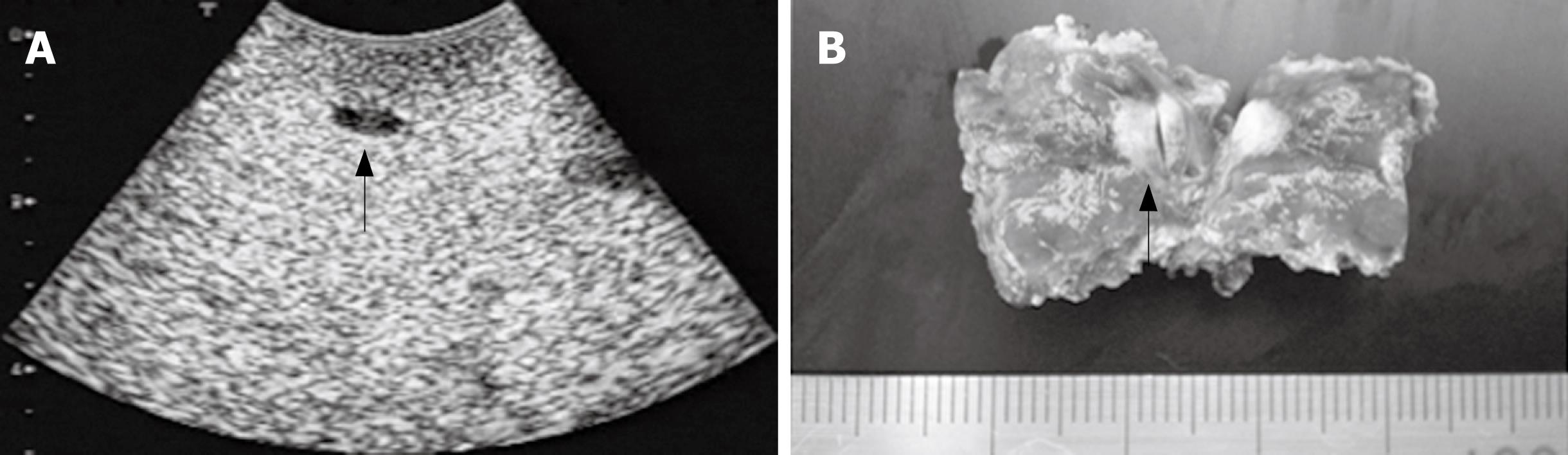
Figure 2 An occult metastasis.
A: An occult metastasis at the segment 4 only detected by CE-IOUS. A clear hypoechoic mass (approximately 6 mm in diameter; black arrow) was newly detected at the delayed Kupffer phase. This metastatic lesion could not be found by CT, MRI, and IOUS. B: Macroscopic view of this metastasis (arrow).
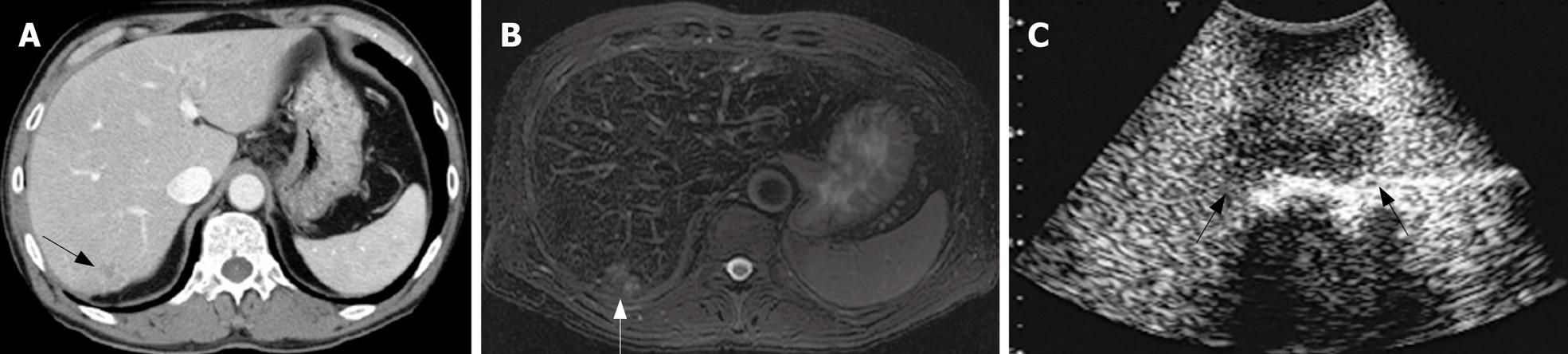
Figure 3 Preoperative CT and SPIO-MRI, and CE-IOUS.
A: An enhanced-CT view and an ill-defined low density mass was detected at the segment 7 (arrow); B: A SPIO MRI view and an ill-defined high intensity mass was detected at the segment 8 (arrow); C: CE-IOUS view at the delayed Kupffer phase and a well-demarcated hypoechoic mass was detected by CE-IOUS.
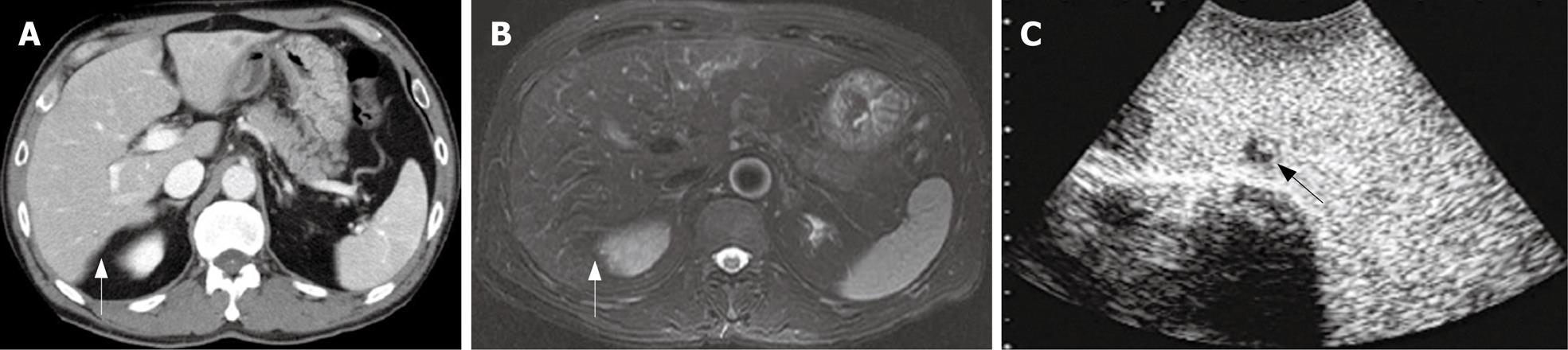
Figure 4 Preoperative CT and SPIO-MRI, and CE-IOUS.
A: An enhanced-CT could not detect any lesion at the Segment 6 (arrow); B: A SPIO MRI view could not detect any lesion at the Segment 6 (arrow); C: CE-IOUS view at the delayed Kupffer phase and a small hypoechoic mass partially containing a isoechoic lesion was detected by CE-IOUS.
- Citation: Nakano H, Ishida Y, Hatakeyama T, Sakuraba K, Hayashi M, Sakurai O, Hataya K. Contrast-enhanced intraoperative ultrasonography equipped with late Kupffer-phase image obtained by sonazoid in patients with colorectal liver metastases. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(20): 3207-3211
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i20/3207.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.3207