Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2008; 14(19): 3101-3104
Published online May 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3101
Published online May 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3101
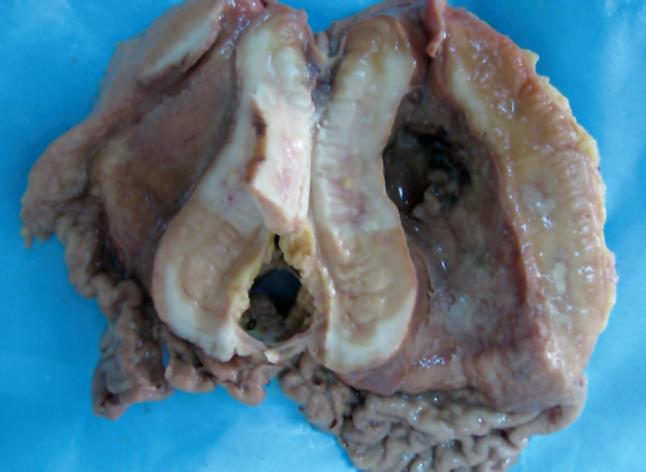
Figure 1 A large neoplastic ulcer in the stomach involving the whole gastric wall.
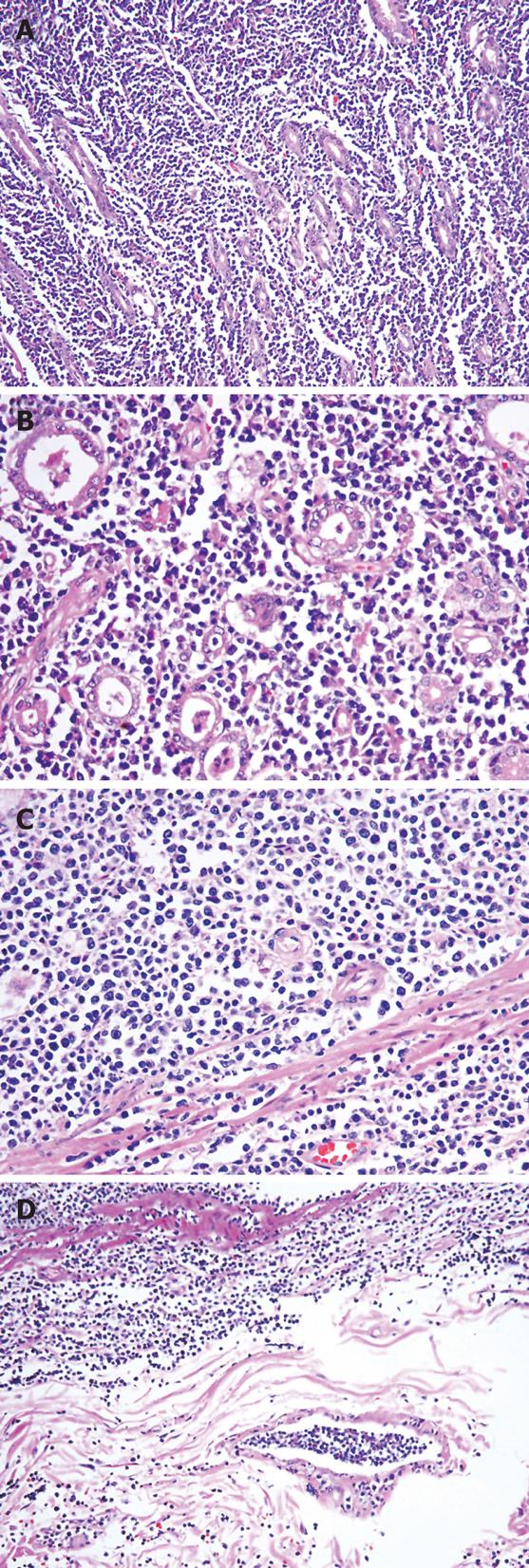
Figure 2 Diffuse proliferation of lymphoblastic cells between gastric glands of stomach B-LBL.
A: HE, × 100; B: HE, × 200; C: HE, × 200; D: Tumor emboli within lymphatic vessels of the gastric wall (HE, × 100).
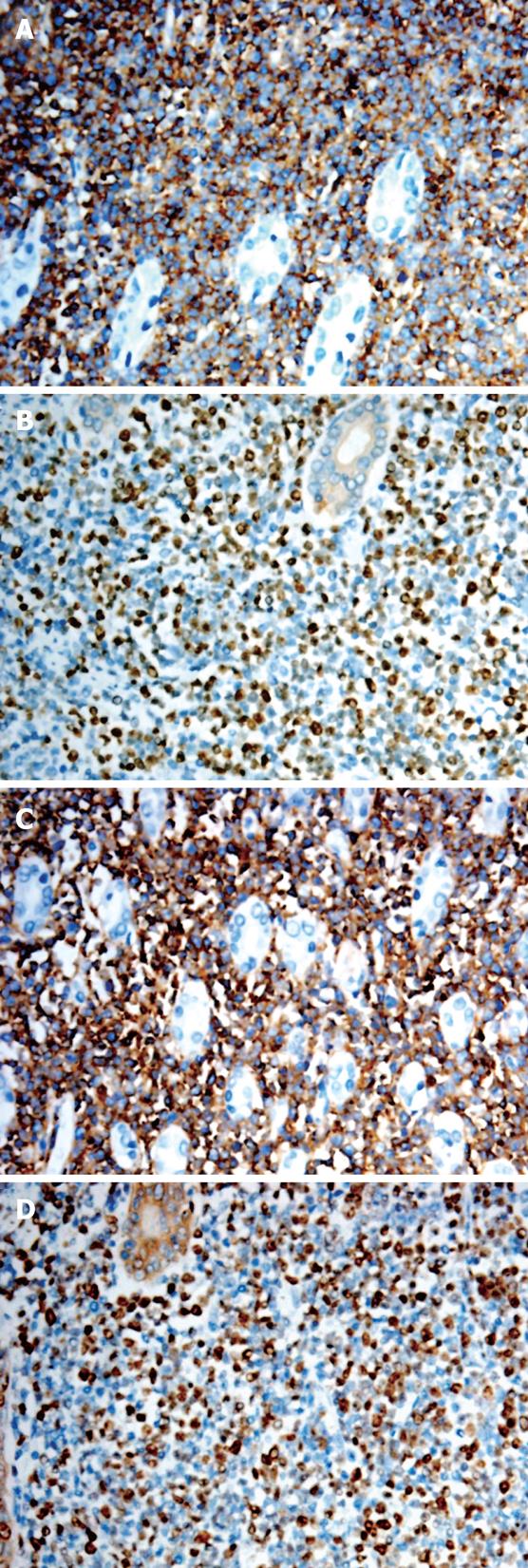
Figure 3 Stomach B-LBL (EnVision, × 200).
A: Lym-phoblasts diffusely stained with anti-CD79a; B: A large number of lymphoblasts positive for nuclear antigen TdT; C: Lymphoblasts diffusely stained with anti-CD10; D: A large number of lymphoblasts positive for Ki-67.
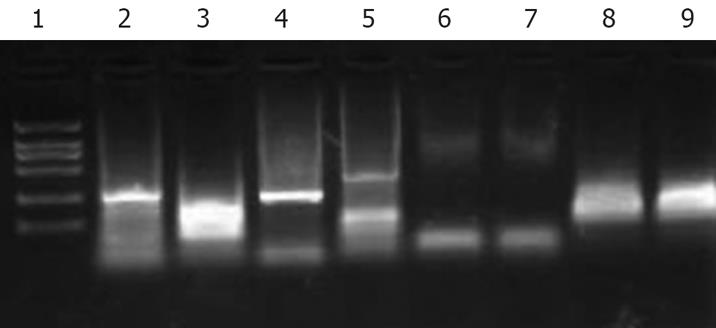
Figure 4 Polymerase chain reaction showing rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes.
Lane 1: Marker; lane 2: FR2, sample collected from stomach B cell lymphoblastic lymphoma showing monoclonal pattern; lane 3: FR3A, sample collected from stomach B cell lymphoblastic lymphoma showing a smear; lane 4: FR2, B cell lymphoma cell line Raja used as positive control; lane 5, FR3A, B cell lymphoma cell line Raja used as positive control. Lane 6, JVI, sample collected from stomach B cell lymphoblastic lymphoma showing a negative pattern; lane 7: JVII, sample collected from stomach B cell lymphoblastic lymphoma showing a negative pattern; lane 8: JVI, T cell lymphoma cell line Jurkat used as a positive control; lane 9: JVII, T cell lymphoma cell line Jurkat used as a positive control.
- Citation: He MX, Zhu MH, Liu WQ, Wu LL, Zhu XZ. Primary lymphoblastic B-cell lymphoma of the stomach: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(19): 3101-3104
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i19/3101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.3101