Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2008; 14(16): 2596-2598
Published online Apr 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2596
Published online Apr 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2596
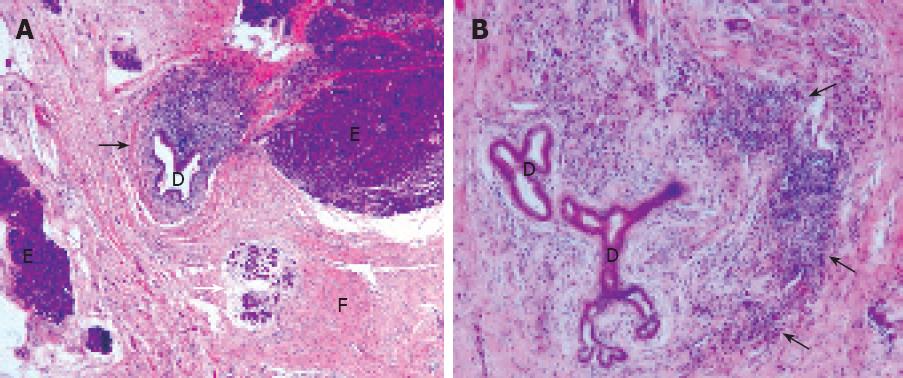
Figure 1 A: Pancreatic histological section showing the periductular infiltrate composed of lymphoplasmocytic inflammatory cells (black arrow), and areas of acinar cell necrosis (white arrow); B: High power field magnification section depicting the lymphoplasmocytic infiltrate around pancreatic ducts (black arrows), a typical feature of autoimmune pancreatitis.
D: Pancreatic duct; E: Acinar cells and; F: Area of diffuse fibrosis.
- Citation: Frossard JL, Dumonceau JM, Pastor C, Spahr L, Hadengue A. Concomitant autoimmune and genetic pancreatitis leads to severe inflammatory conditions. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(16): 2596-2598
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i16/2596.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2596