Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2008; 14(16): 2474-2486
Published online Apr 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2474
Published online Apr 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2474
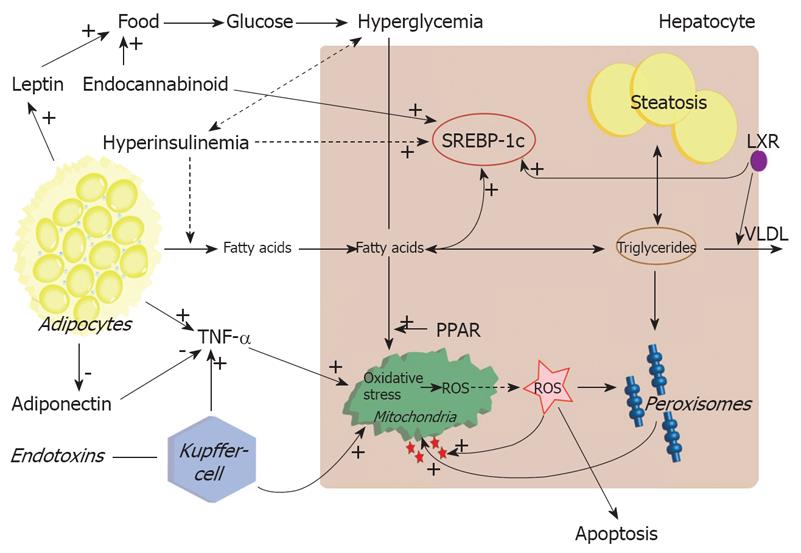
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis during insulin resistance.
FFA is supplied to the liver through dietary intake, and lipolysis in adipocytes via chylomicron remnants. Transcription of SREBP-1c is chronically up-regulated resulting in DNL. Simultaneous inhibition of VLDL synthesis results in disruption of triglycerides export. The surplus of fatty acids is stored in triglycerides or metabolized via peroxisomal and mitochondrial oxidation. The excessive oxidation will lead to production of ROS and oxidative stress. This will trigger the inflammatory response and apoptosis as well activation of stellate cells.
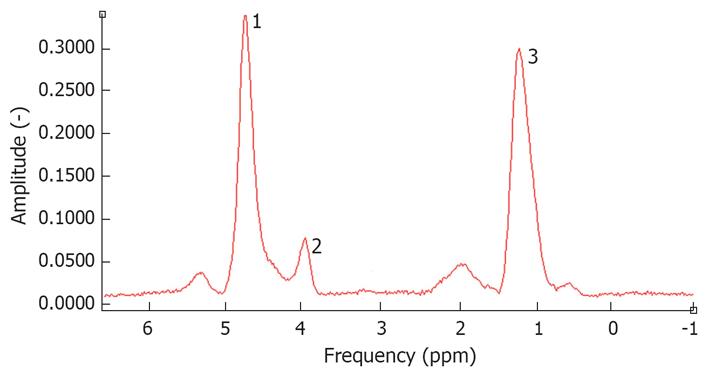
Figure 2 Spectrum of a fatty liver measured by 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
The water peak is at 4.3 ppm. 1: Residual water partially suppressed; 2: Glycerol/phospholipids; 3: (-CH2-)n of saturated fat.
- Citation: Schreuder TC, Verwer BJ, Nieuwkerk CMV, Mulder CJ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An overview of current insights in pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(16): 2474-2486
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i16/2474.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2474