Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2008; 14(14): 2284-2287
Published online Apr 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2284
Published online Apr 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2284
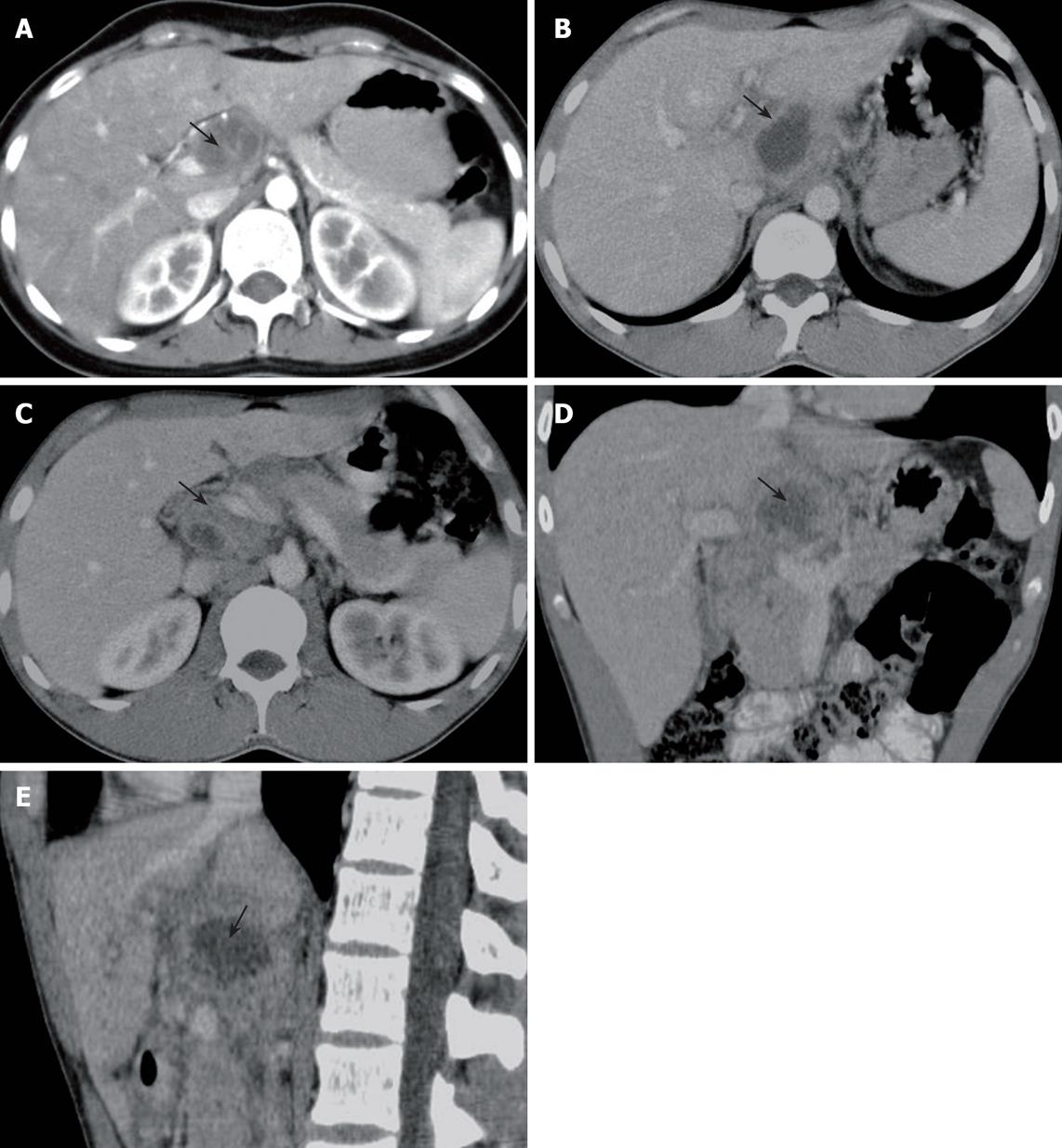
Figure 1 A 24-year-old man with tuberculous abscess in the hepatoduodenal ligament.
A: Axial CT image (arterial phase) showing a low dense abscess measuring approximately 3.9 cm × 2.8 cm with a slightly contrast-enhanced wall in hepatoduodenal ligament (arrow); B: Axial CT image (venous phase) showing a low dense abscess with a contrast-enhanced wall in hepatoduodenal ligament (arrow); C: Axial CT image showing enlarged lymph nodes with peripheral and homogenerous enhancement in the portacaval space (arrow); D: Coronal CT image showing a low dense abscess with a contrast-enhanced wall in hepatoduodenal ligament (arrow); E: Sagittal CT image showing a low dense abscess with a contrast-enhanced wall in hepatoduodenal ligament (arrow).
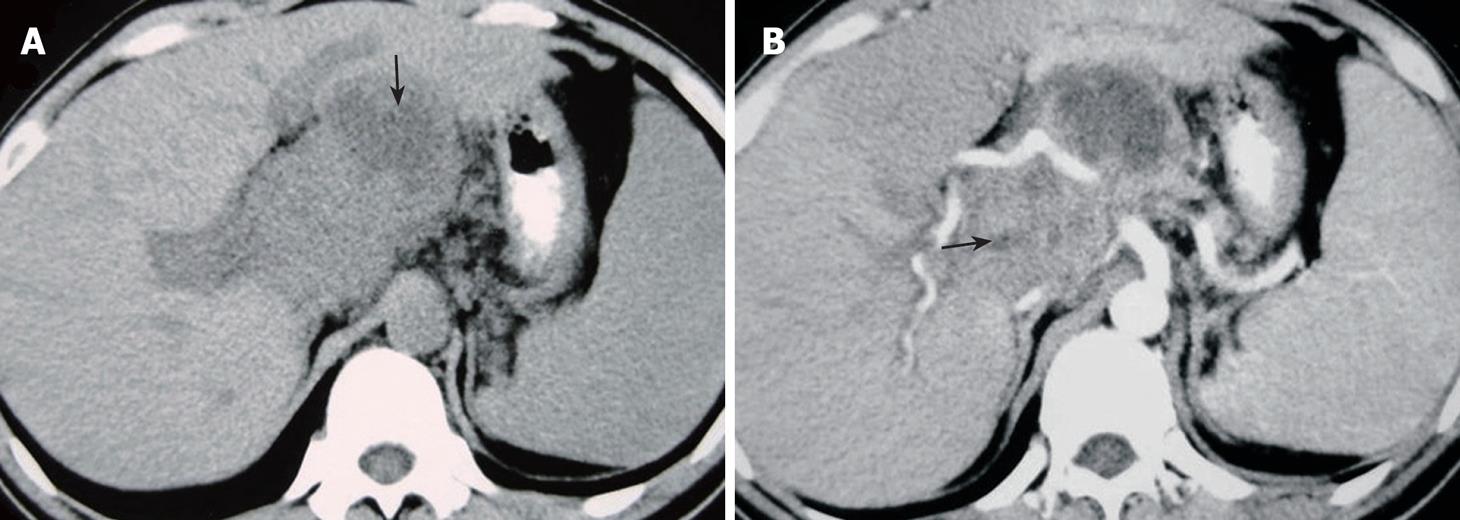
Figure 2 A 30-year-old man with a tuberculous abscess in the hepatoduodenal ligament.
A: Axial plain CT image showing a low dense abscess measuring approximately 4.1 cm × 2.7 cm in hepatoduodenal ligament (arrow); B: Axial contrast-enhanced CT image showing a low dense abscess with a contrast-enhanced wall and enlarged lymph nodes in hepatoduodenal ligament (arrow).
- Citation: Dong P, Wang B, Sun YQ. Tuberculous abscess in hepatoduodenal ligament: Evaluation with contrast-enhanced computed tomography. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(14): 2284-2287
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i14/2284.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2284