Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2008; 14(13): 2100-2105
Published online Apr 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2100
Published online Apr 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2100
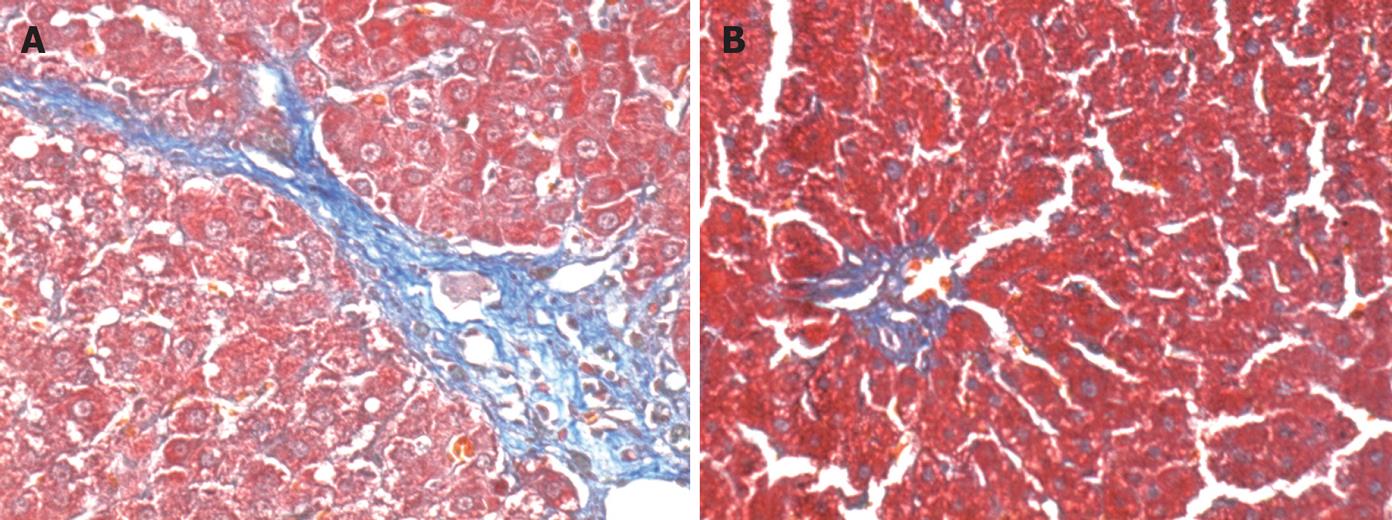
Figure 1 Subcutaneous injection of CCl4 caused severe hepatic injury such as significant hepatic cell necrosis and excessive collagen deposition.
With Masson staining, the collagen fiber was shown blue and hepatic cells were red. ( A: Masson, × 200). Oxymarine treated livers showed less hepatic cell necrosis and less collagen deposition ( B: Masson, × 200).
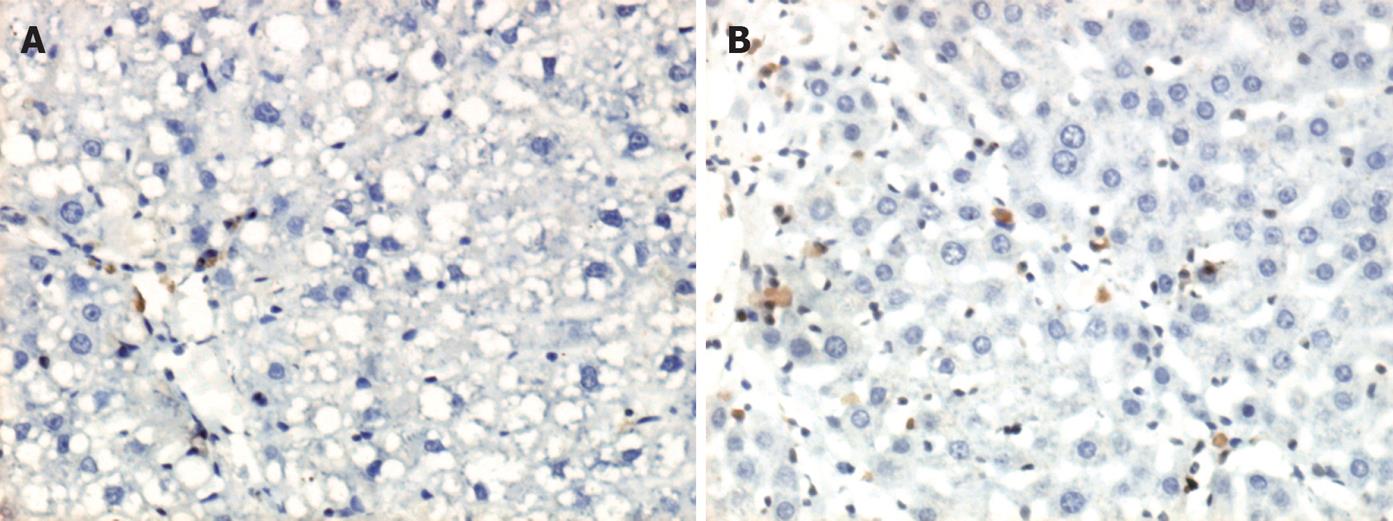
Figure 2 Expression of Smad 7 protein in liver tissue of model rats was increased when detected with immunohistochemistry ( A: IH, × 200) when compared to the control group.
However, the expression of Smad 7 protein in the livers of the Oxymatrine-treated group was even more significantly increased ( B: IH, × 200). The positive rate of Smad 7 protein expression was 1.9% and 4.3% in the model group and the treated group, respectively (data obtained from statistical software, P < 0.05).
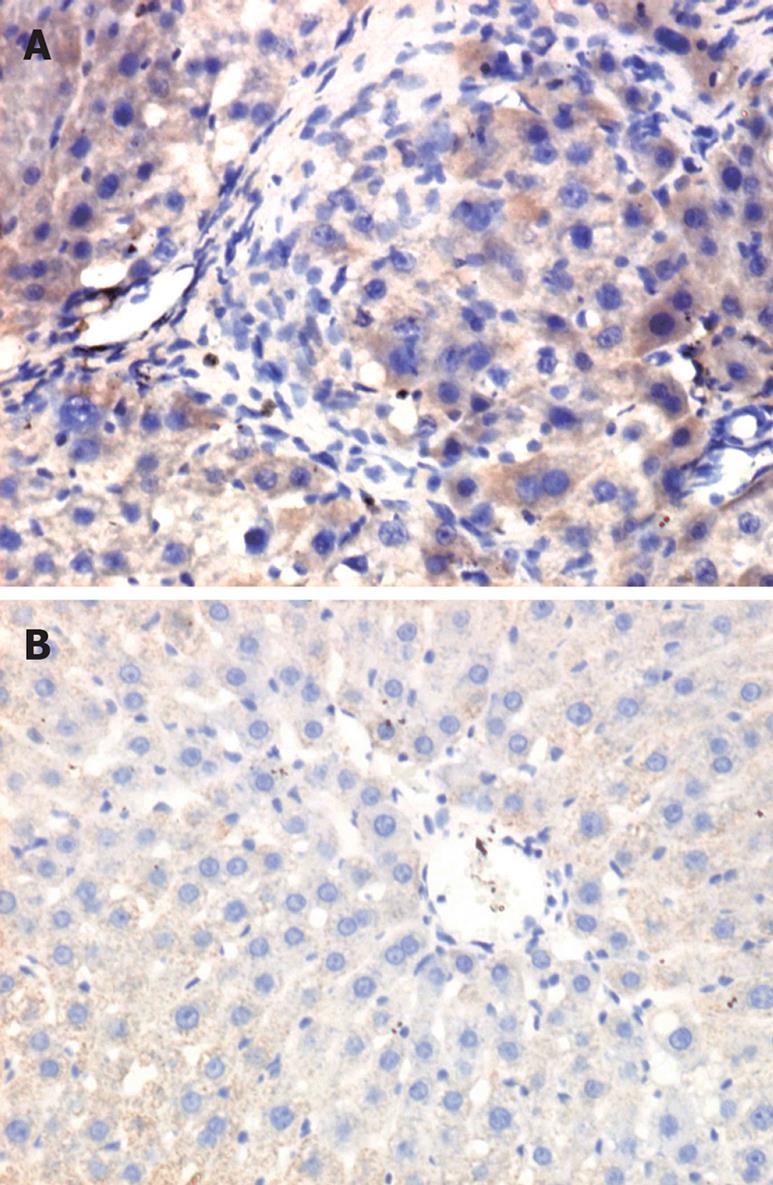
Figure 3 In the control group, the expression of CBP mRNA was at a very low level, the A (optical densit) value of it was nearly 0.
After CCl4 injection, the expression of CBP mRNA in the liver of fibrotic rats was significantly enhanced ( A: ISH, × 200). However, in the livers of the Oxymatrine-treated rats, the expression of CBP was also increased compared to the control group ( B: ISH, × 200), but it was significantly reduced compared to the model group. The A value of CBP mRNA in model group and treated group were 0.235 ± 0.025 and 0.065 ± 0.049, respectively (P < 0.05).
- Citation: Wu XL, Zeng WZ, Jiang MD, Qin JP, Xu H. Effect of Oxymatrine on the TGFbeta-Smad signaling pathway in rats with CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(13): 2100-2105
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i13/2100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2100