Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2008; 14(13): 2037-2043
Published online Apr 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2037
Published online Apr 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.2037
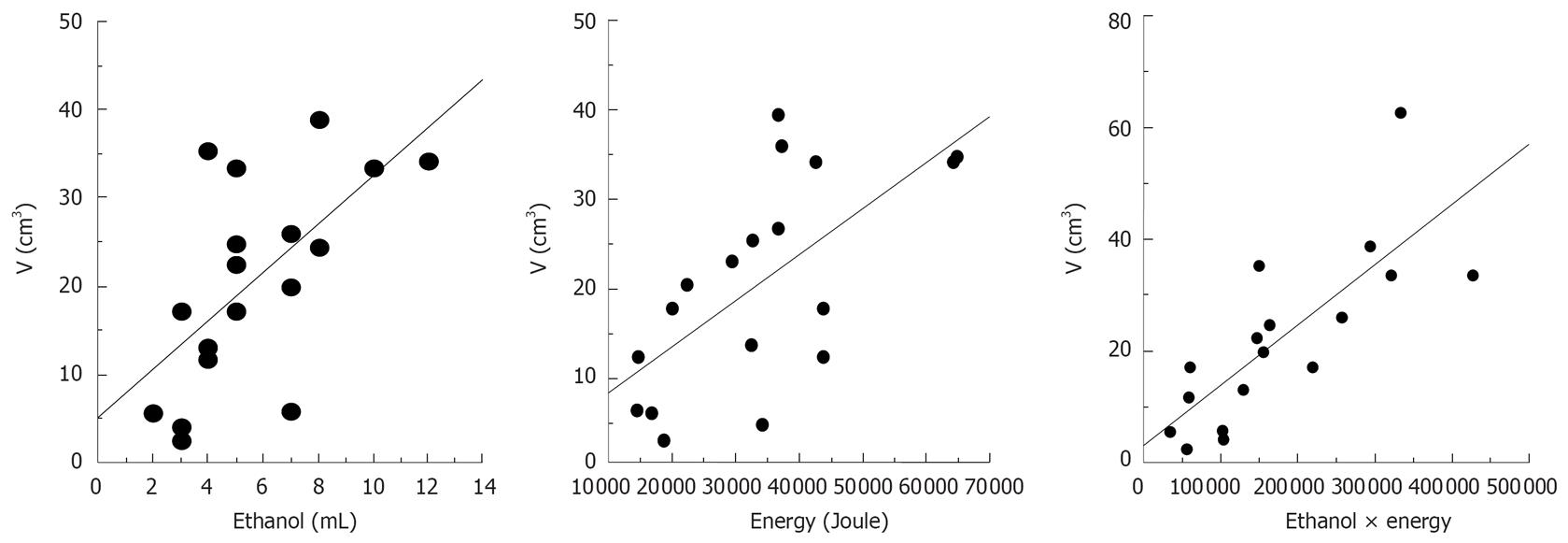
Figure 1 Relationship between the volume of coagulated necrosis induced and the amounts of ethanol injected or total applied energy or the product of the amounts of ethanol and the total applied energy.
All the amounts of ethanol, total applied energy, or the products of the amount of ethanol and total applied energy showed a significant positive correlation with the volume of coagulated necrosis. (Ethanol vs volume, r = 0.54, P = 0.018; energy vs volume, r = 0.61, P = 0.0057; ethanol × energy vs volume, r = 0.61, P = 0.0078).
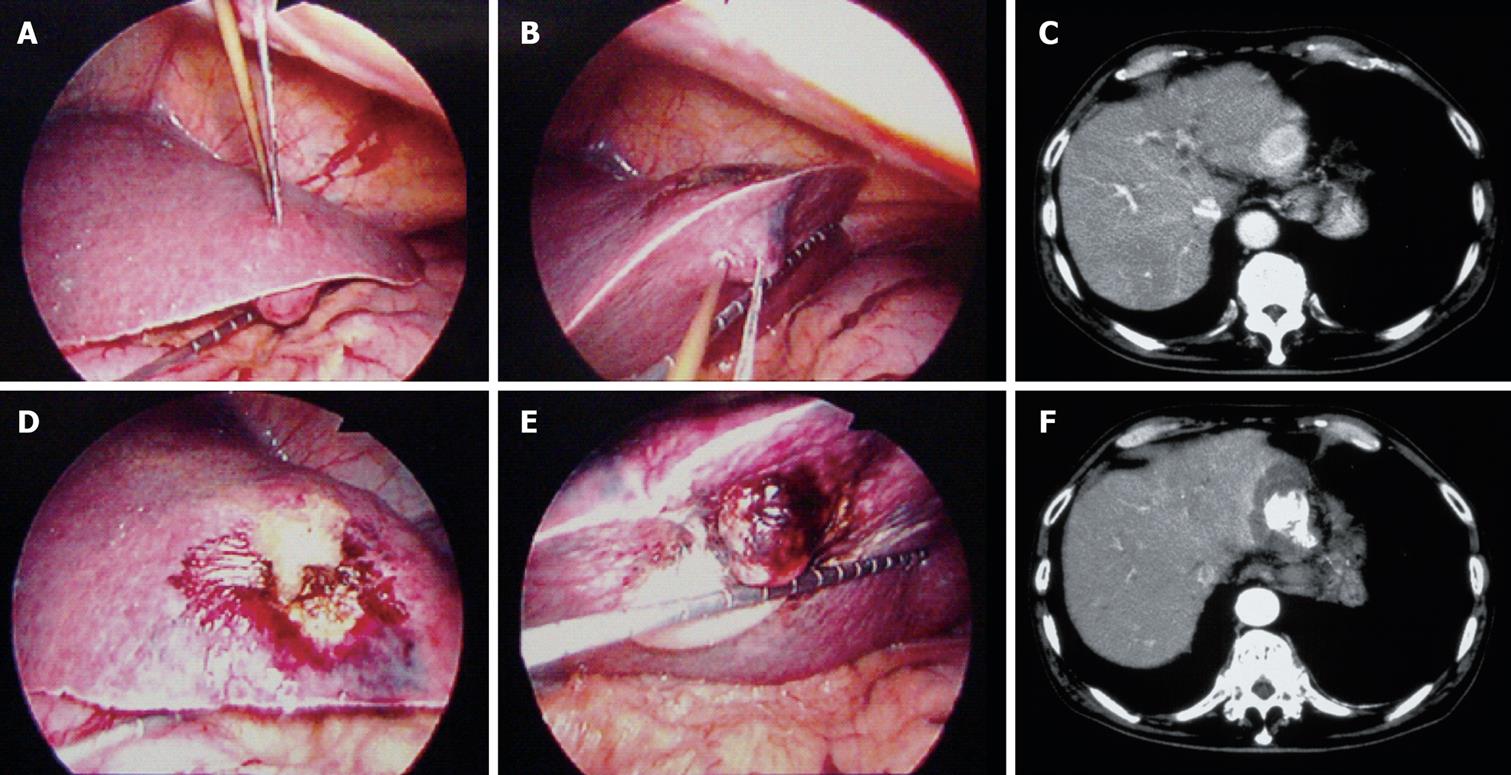
Figure 2 A case of HCC located on the reverse surface of the liver (S2 of the liver) treated with L-EI-RFA.
A HCC (2 cm in diameter) showed an enhancement in early vascular phase of helical dynamic CT (A); RFA electrode and PEI needle were firstly inserted from the surface of the liver (B) and secondly inserted from the reverse surface of the liver (C); After injecting the ethanol containing 15% lipiodol, RFA was performed. Dynamic CT after the treatment showed lipiodol deposit associated with the original tumor and low density area was observed around the tumor (D); Laparoscopic observation of the tumor from the surface (E) and from the reverse surface (F) of the liver after the treatment.
- Citation: Kurokohchi K, Watanabe S, Yoneyama H, Deguchi A, Masaki T, Himoto T, Miyoshi H, Mohammad HS, Kitanaka A, Taminato T, Kuriyama S. A combination therapy of ethanol injection and radiofrequency ablation under general anesthesia for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(13): 2037-2043
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i13/2037.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.2037