Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2008; 14(12): 1903-1907
Published online Mar 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1903
Published online Mar 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1903
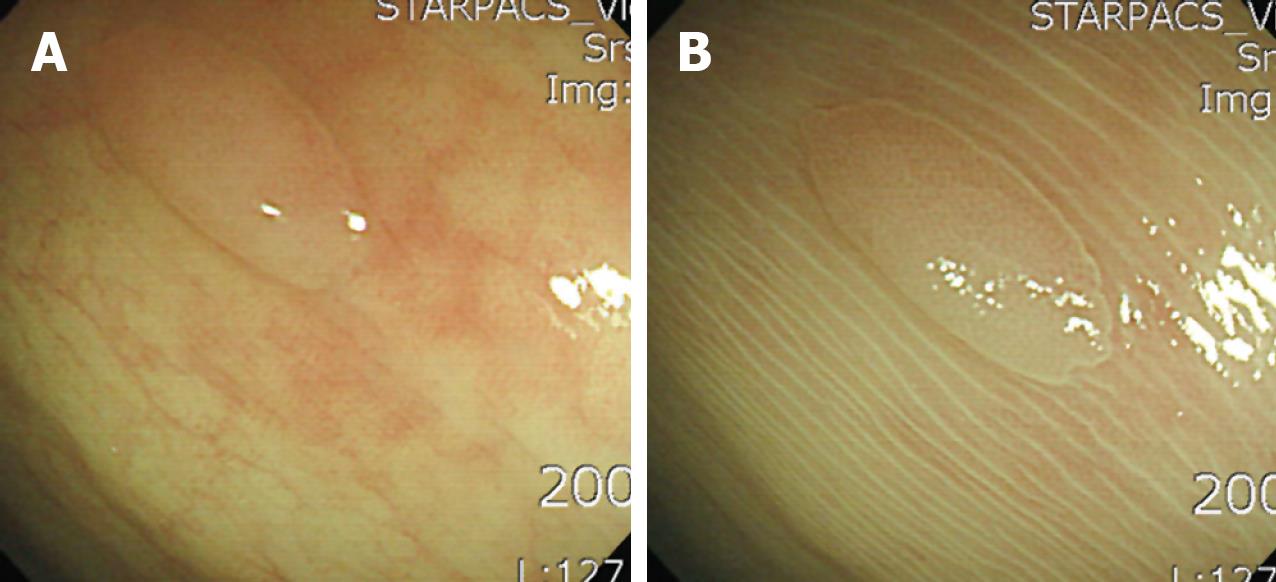
Figure 1 Linear and regularly patterned colonic mucosa surrounding a polyp.
On endoscopic removal, pathology revealed a hyperplastic colon polyp. A: Before spraying with acetic acid a sessile polyp is seen; B: After spraying with acetic acid the colonic mucosa surrounding the polyp has a linear and regular pattern.
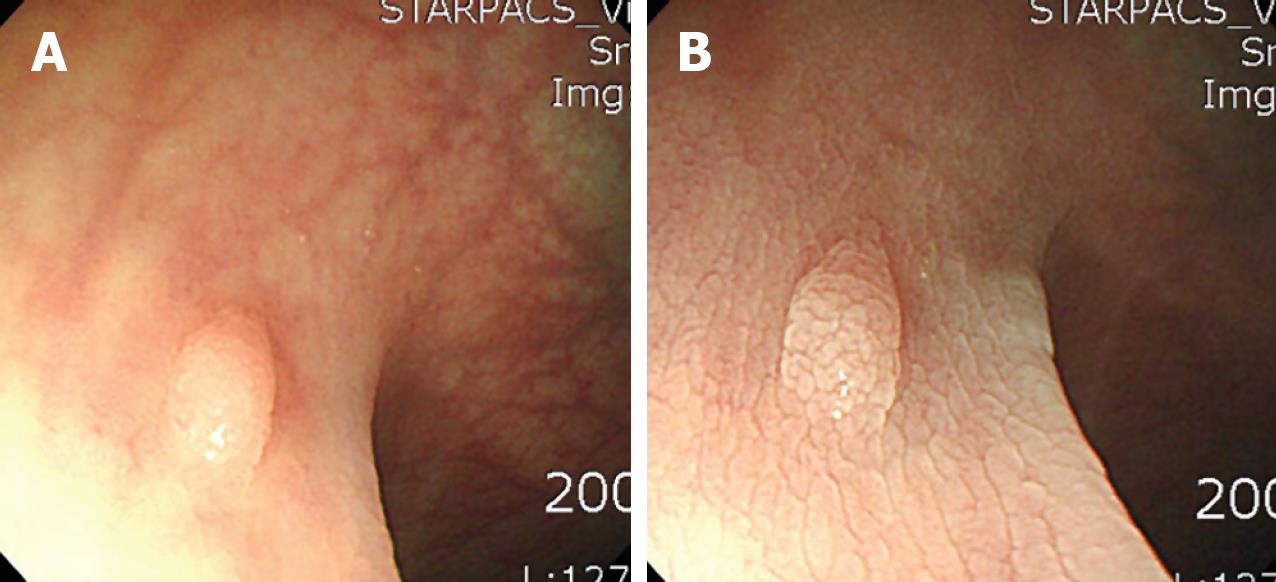
Figure 2 Nodular and irregularly patterned colonic mucosa surrounding a polyp.
On endoscopic removal, pathology revealed a hyperplastic colon polyp. A: Before spraying with acetic acid a sessile polyp is seen; B: After spraying with acetic acid the colonic mucosa surrounding the polyp has a nodular and irregular pattern.
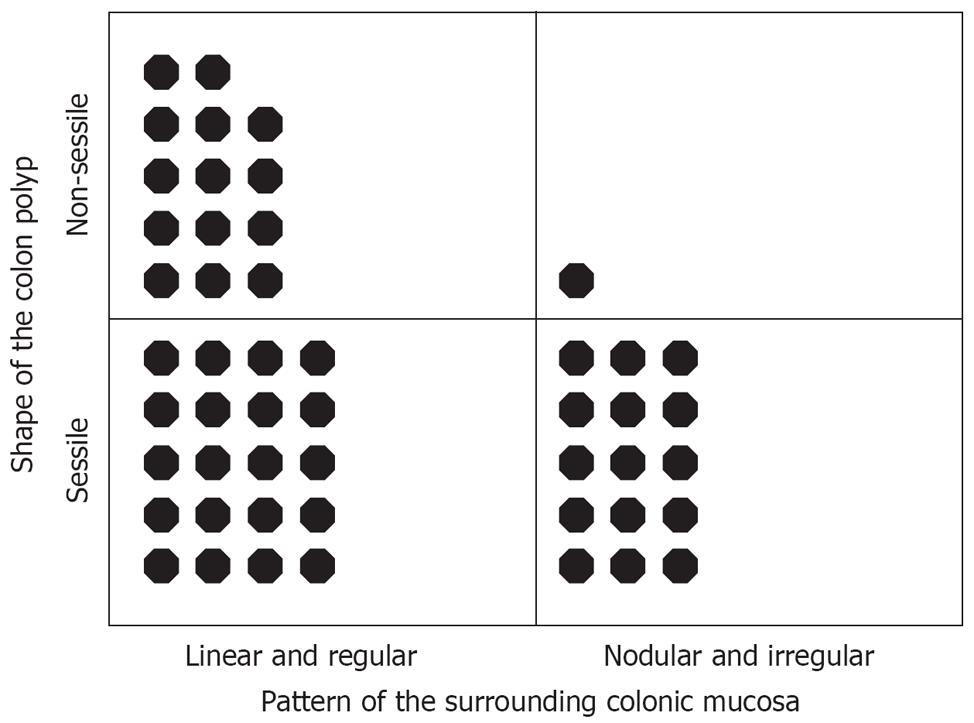
Figure 3 Diagnosis according to the shape of the colon polyp and the pattern of its surrounding colonic mucosa.
Each black dot indicates a polyp. Most of the non-sessile colon polyps revealed linear and regular patterned surrounding colonic mucosa (P = 0.02).
- Citation: Kim JH, Lee SY, Kim BK, Choe WH, Kwon SY, Sung IK, Park HS, Jin CJ. Importance of the surrounding colonic mucosa in distinguishing between hyperplastic and adenomatous polyps during acetic acid chromoendoscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(12): 1903-1907
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i12/1903.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.1903