Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2008; 14(1): 140-142
Published online Jan 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.140
Published online Jan 7, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.140
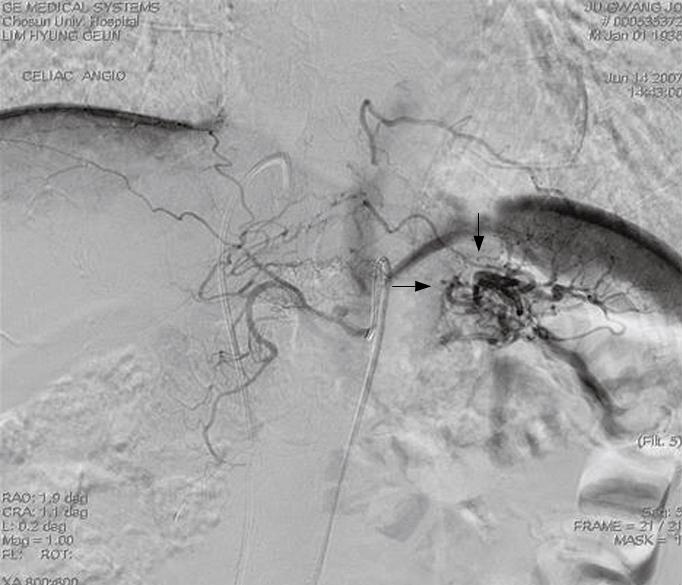
Figure 1 Celiac angiography showing a hypervascular mass-like lesion in the pancreatic tail area (arrows).
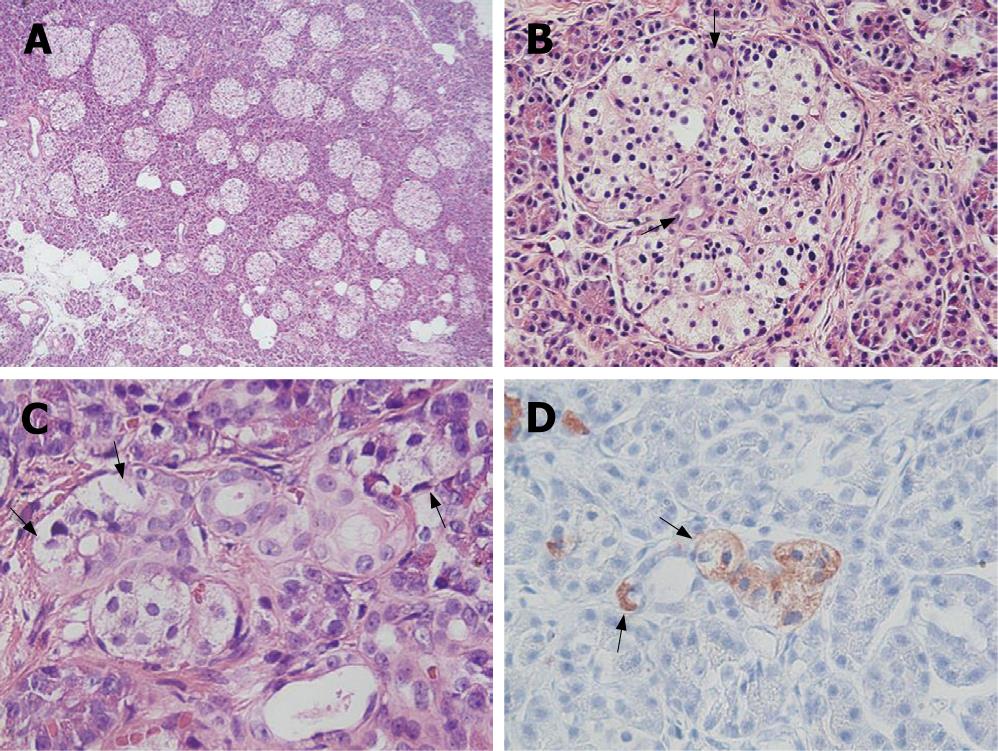
Figure 2 Irregularly sized-dysplastic islets scattering randomly throughout the pancreas (A), islets in intimate association with ducts forming a so-called ductulo-insular complex (arrows indicate ductules within the islet) (B), islet cells (arrows) budding off the duct epithelium (C), insulin-positive islet cells (arrows) budding off the duct epithelium (immunohistochemical stain for insulin) (D).
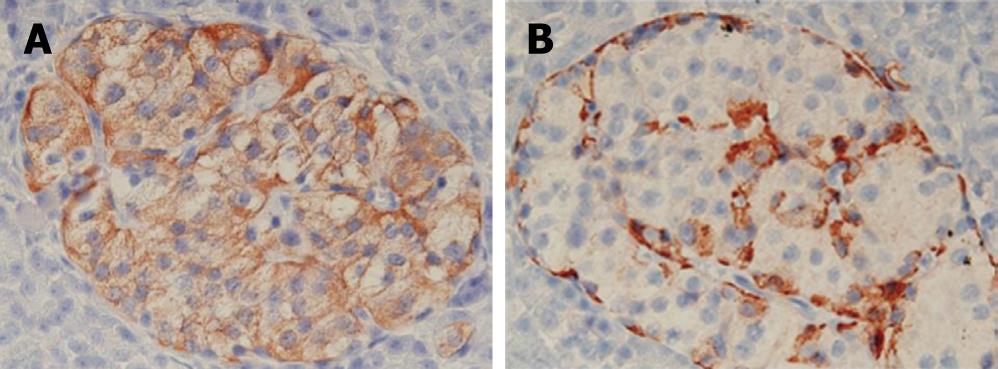
Figure 3 An immunohistochemical study showing increased insulin producing β-cells (A), glucagon producing α-cells (B).
- Citation: Hong R, Choi DY, Lim SC. Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia due to diffuse nesidioblastosis in adults: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(1): 140-142
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i1/140.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.140