Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2007; 13(8): 1275-1278
Published online Feb 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i8.1275
Published online Feb 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i8.1275
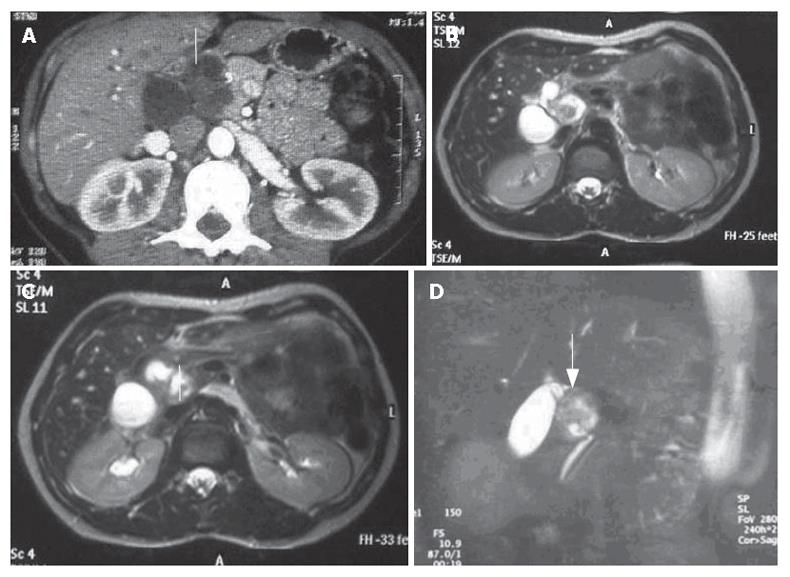
Figure 1 A: CT scan showing a very heterogeneous formation with a liquid content in close contiguity to the CBD (white arrow); B, C, D: Cholangio-MRI reveals a solid formation with a hypointensive signal in the weighted T1 sequences at the pancreatic isthmus (white arrows) with dilation of the upstream bile ducts.
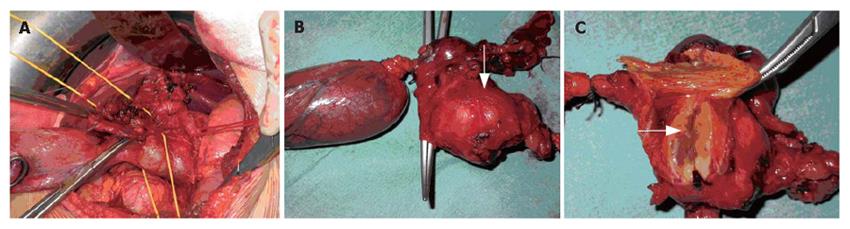
Figure 2 Intraoperative view of involvement of the intermediate tract of the common bile duct between its confluence with the cystic duct (A) and the prepancreatic tract (B) and (C) Gross inspection showing that the lesion (arrows) is solid and situated intramurally and below the mucosa in close contiguity with the CBD.
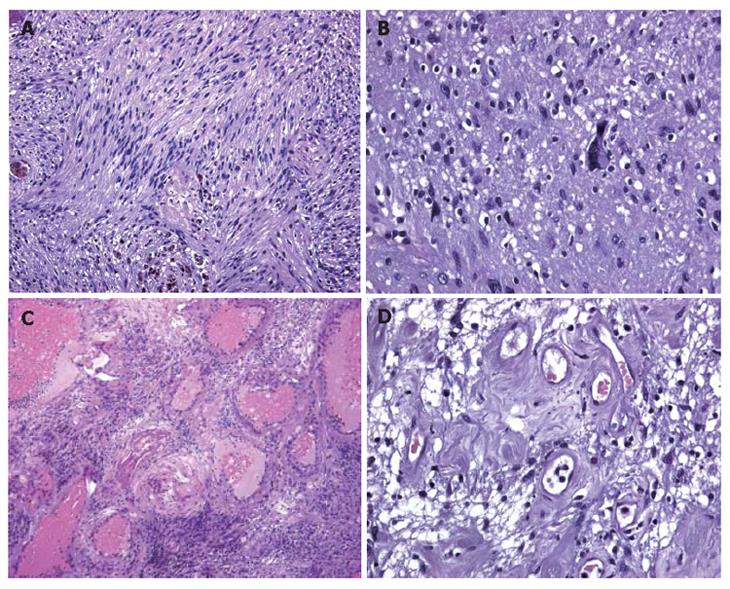
Figure 3 A: Histological examination showing that inter-woven bundles of fused cells separated by slacker, oedematous areas with a pseudocystic appearance (Antoni A schwannoma growth pattern); B: Histological examination showing a few cells with hyperchromic, atypical and bizarre nuclei.
Histological examination showing a few cells with hyperchromic, atypical and bizarre nuclei; C: Histological examination showing hyalinisation and ectatic and partially thrombosed vessels; D: Histological examination showing perivascular hyalinisation.
- Citation: Fenoglio L, Severini S, Cena P, Migliore E, Bracco C, Pomero F, Panzone S, Cavallero GB, Silvestri A, Brizio R, Borghi F. Common bile duct schwannoma: A case report and review of literature. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(8): 1275-1278
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i8/1275.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i8.1275