Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2007; 13(5): 657-670
Published online Feb 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.657
Published online Feb 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.657
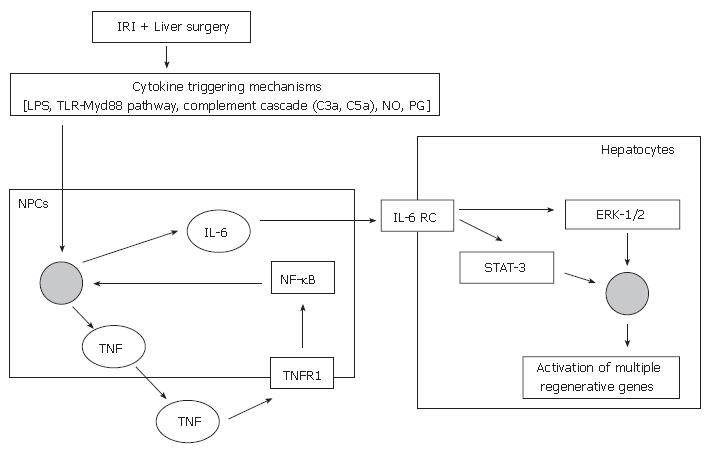
Figure 1 Current proposed mechanisms of the priming pathway of liver regeneration.
IRI: Ischaemic reperfusion injury; LPS: Lipo-polysaccharide; TLR: Toll-like receptor; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation factor 88; NO: Nitric oxide; PG: Prostaglandins; NPCs: Non-parenchymal cells; TNF: Tumour necrosis factor; TNFR1: TNF receptor type I; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappaB; IL-6: Interleukin-6; IL-6 RC: IL-6 receptor complex; ERK-1/2: Extracellular regulated kinases 1/2; STAT-3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3.
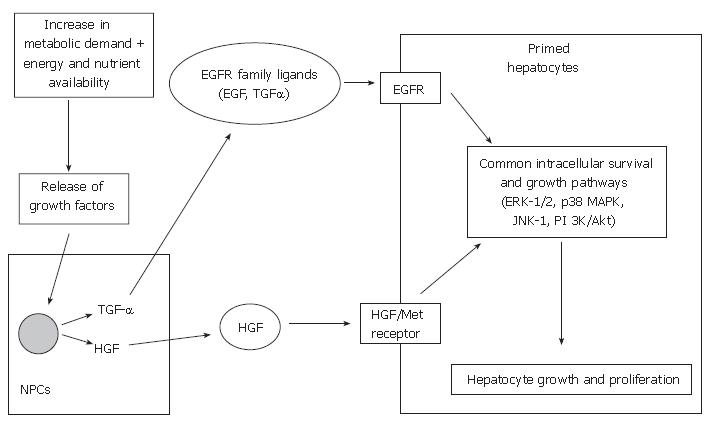
Figure 2 Potentiation of growth factor signaling pathways involved in cell cycle progression in liver regeneration.
NPCs: Non-parenchymal cells; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; TGF-α: Transforming growth factor-α; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK-1/2: Extracellular regulated kinases 1/2; JNK: c-jun-NH2-terminal kinase; PI 3K/Akt: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-signal pathway.
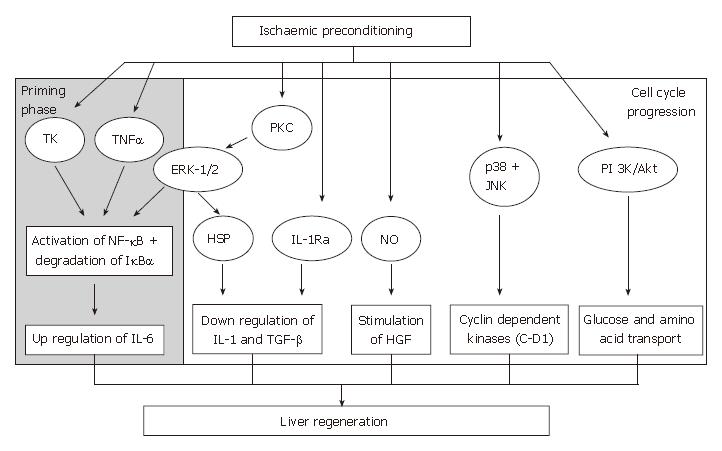
Figure 3 The effect of ischaemic preconditioning and its effectors on the signaling pathways of liver regeneration.
TK: Tyrosine kinase; PKC: Protein kinase C; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappaB; IκBα: Inhibitory binding protein for NF-κB; ERK-1/2: Extracellular regulated kinases 1/2; HSPs: Heat shock proteins; NO: Nitric oxide; IL1-RA: Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; PI 3K/Akt: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-signal pathway; JNK: c-jun-NH2-terminal kinase; C-D1: Cyclin D1; IL-1: Interleukin-1; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β.
- Citation: Gomez D, Homer-Vanniasinkam S, Graham A, Prasad K. Role of ischaemic preconditioning in liver regeneration following major liver resection and transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(5): 657-670
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i5/657.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i5.657