Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2007; 13(47): 6425-6432
Published online Dec 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i47.6425
Published online Dec 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i47.6425
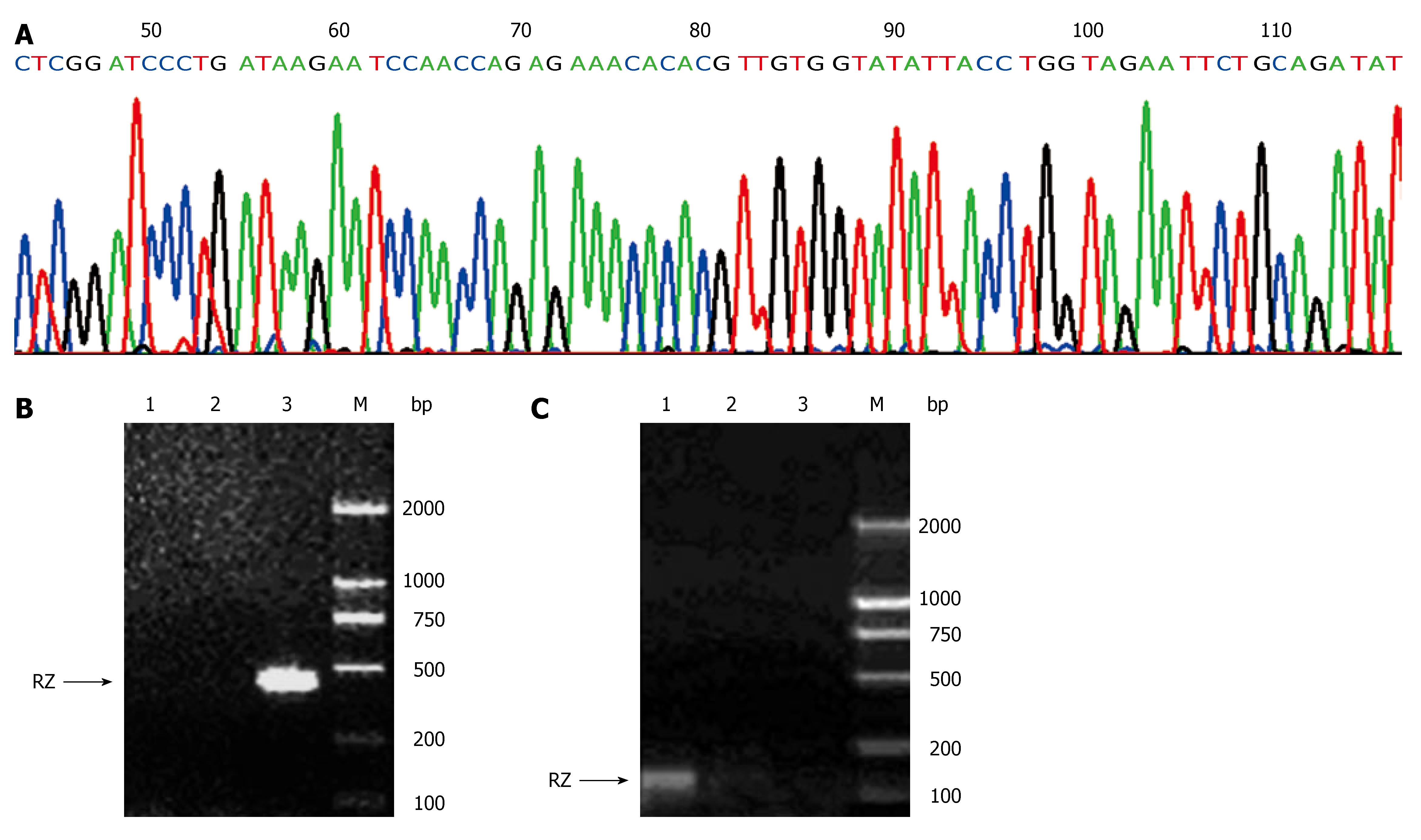
Figure 1 Construction and identification of recombinant eukaryotic expression plasmid pcDNA3.
1+/RZ. A: Sequencing result of the anti-hVEGF hairpin ribozyme gene subcloned into pcDNA3.1+; B: Integration of the ribozyme gene detected by PCR (1: SMMC-7721 cells; 2: SMMC-7721/pcDNA3.1+cells; 3: SMMC-7721/RZ cells; M: DL2000 marker); C: Transcription of the ribozyme gene detected by RT-PCR (1: SMMC-7721/RZ cells; 2: SMMC-772 cells; 3: SMMC-7721/ pcDNA3.1+ cells; M: DL2000 marker).
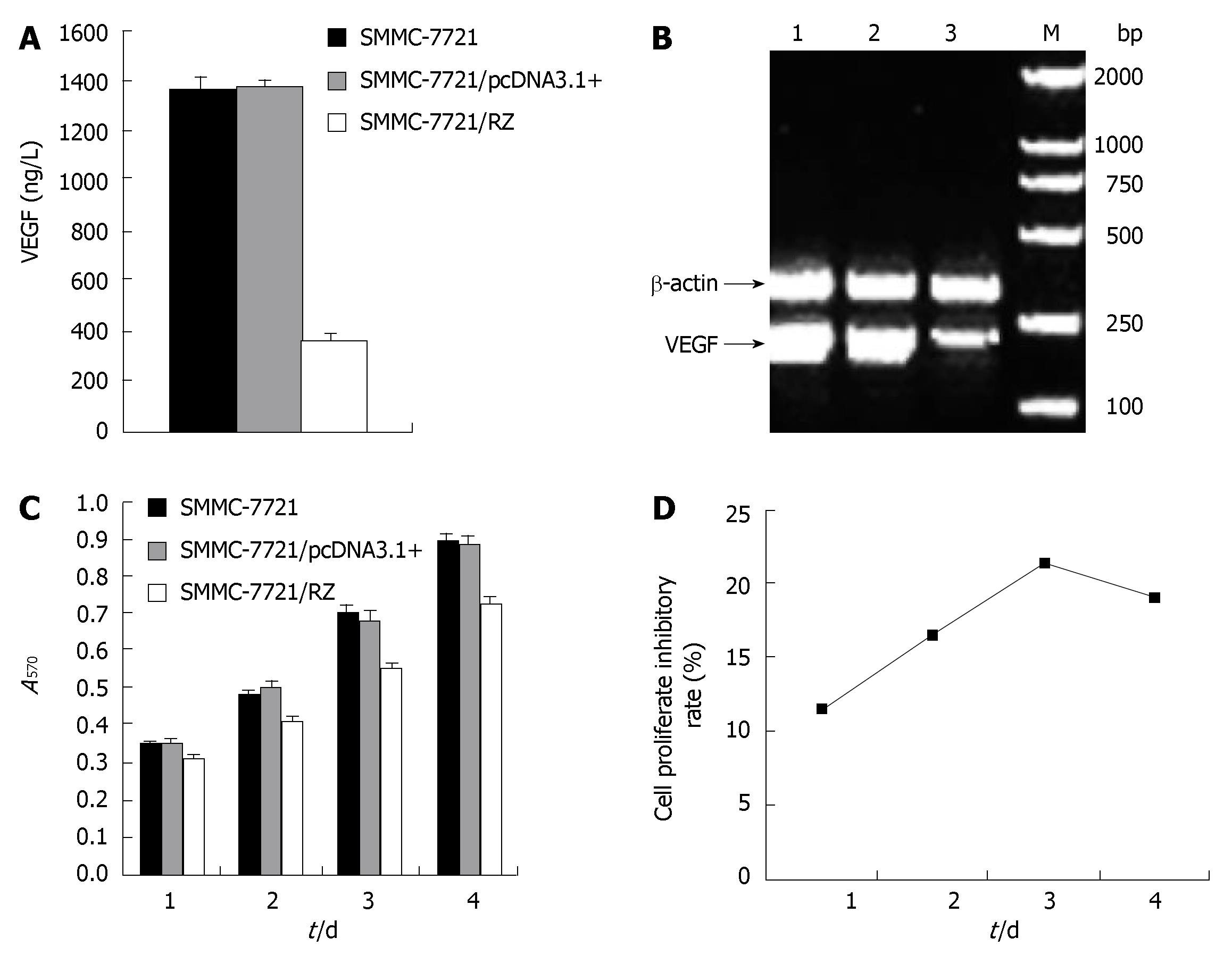
Figure 2 Effects of anti-hVEGF hairpin ribozyme on expression of VEGF and proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells in vitro.
A: ELISA validation of VEGF expression; B: RT-PCR validation of VEGF mRNA transcription in SMMC-7721 group(1), SMMC-7721/pcDNA3.1+ group(2) and SMMC-7721/RZ group(3), (M: DL2000 marker); C: Influence of ribozyme on SMMC-7721 cell proliferation; D: Influence of ribozyme on inhibitory rate for proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells.
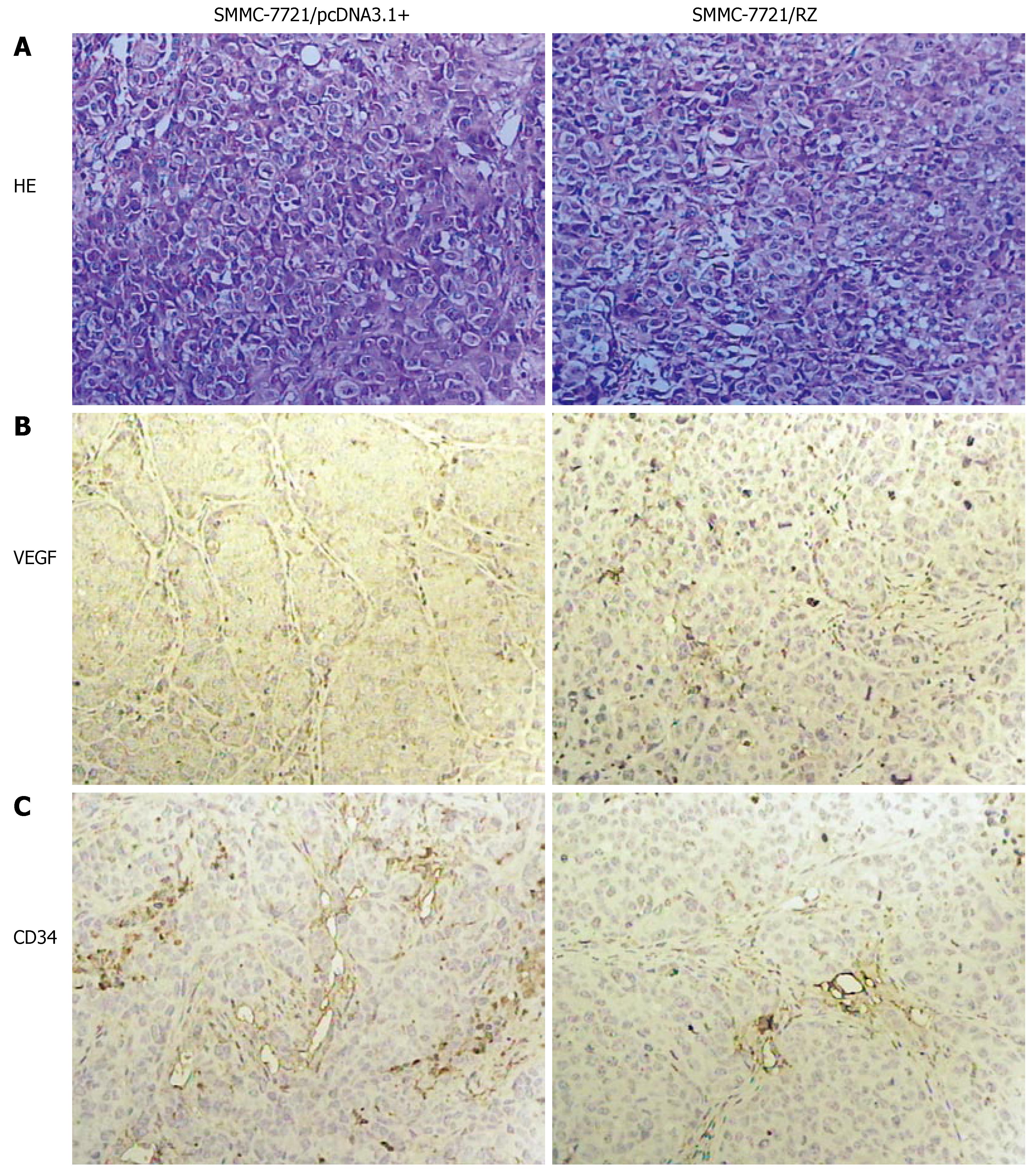
Figure 3 HE staining of tumor tissue (A), immunohistochemical staining of VEGF antibody (B) and CD34 antibody (C) for assay of their positive particles.
- Citation: Li LH, Guo ZJ, Yan LL, Yang JC, Xie YF, Sheng WH, Huang ZH, Wang XH. Antitumor and antiangiogenic activities of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor hairpin ribozyme in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell cultures and xenografts. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(47): 6425-6432
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i47/6425.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i47.6425