Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2007; 13(41): 5421-5431
Published online Nov 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i41.5421
Published online Nov 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i41.5421
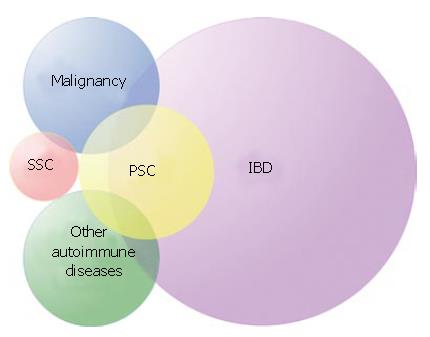
Figure 1 Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a patchwork of different phenotypes in addition to the bile duct involvement.
Most important are inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), malignancy and other autoimmune diseases. PSC is distinct from secondary sclerosing cholangitis (SSC).
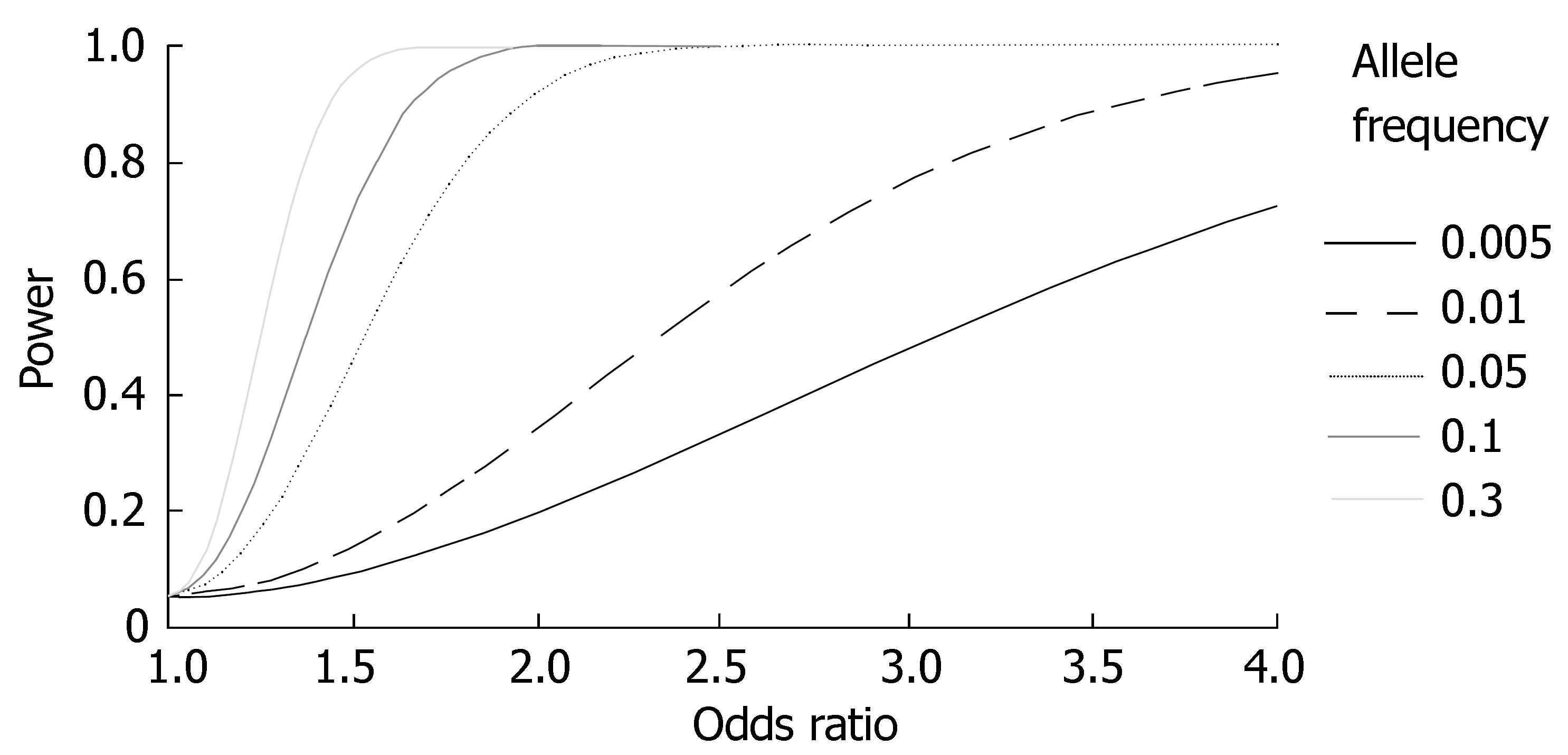
Figure 2 Statistical power (α = 0.
05) for different odds ratios and allele frequencies in a study of 365 patients and 365 controls, i.e., the number of alleles in each group is 2 n = 730.
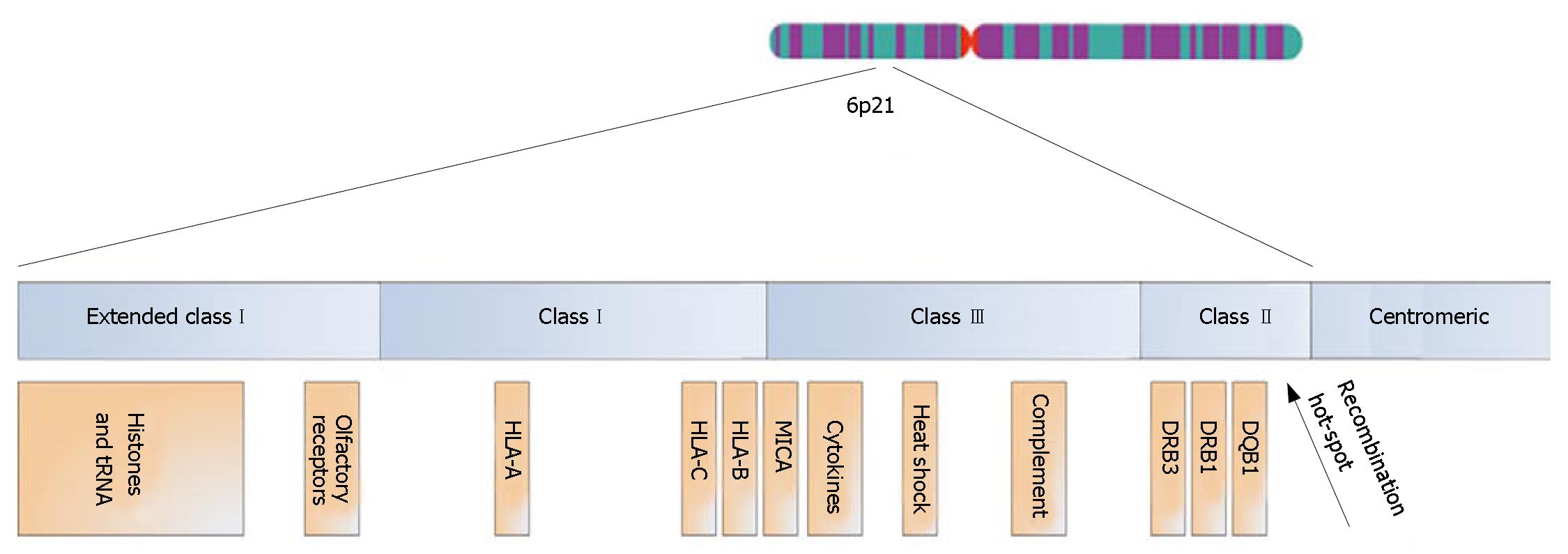
Figure 3 Schematic outline of the HLA complex on chromosome 6.
Distances are arbitrary. By convention, the extended HLA complex stretches from the centromeric border of the HLA class II loci (HLA-DP) to the telomeric limit of the histone gene cluster more than 4 million bp from HLA-A[43,120]. Centromeric to the HLA-DQ loci, a region with intense recombination can be found ("recombination hot-spot")[132].
- Citation: Karlsen TH, Schrumpf E, Boberg KM. Genetic epidemiology of primary sclerosing cholangitis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(41): 5421-5431
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i41/5421.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i41.5421