Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2007; 13(40): 5299-5305
Published online Oct 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i40.5299
Published online Oct 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i40.5299
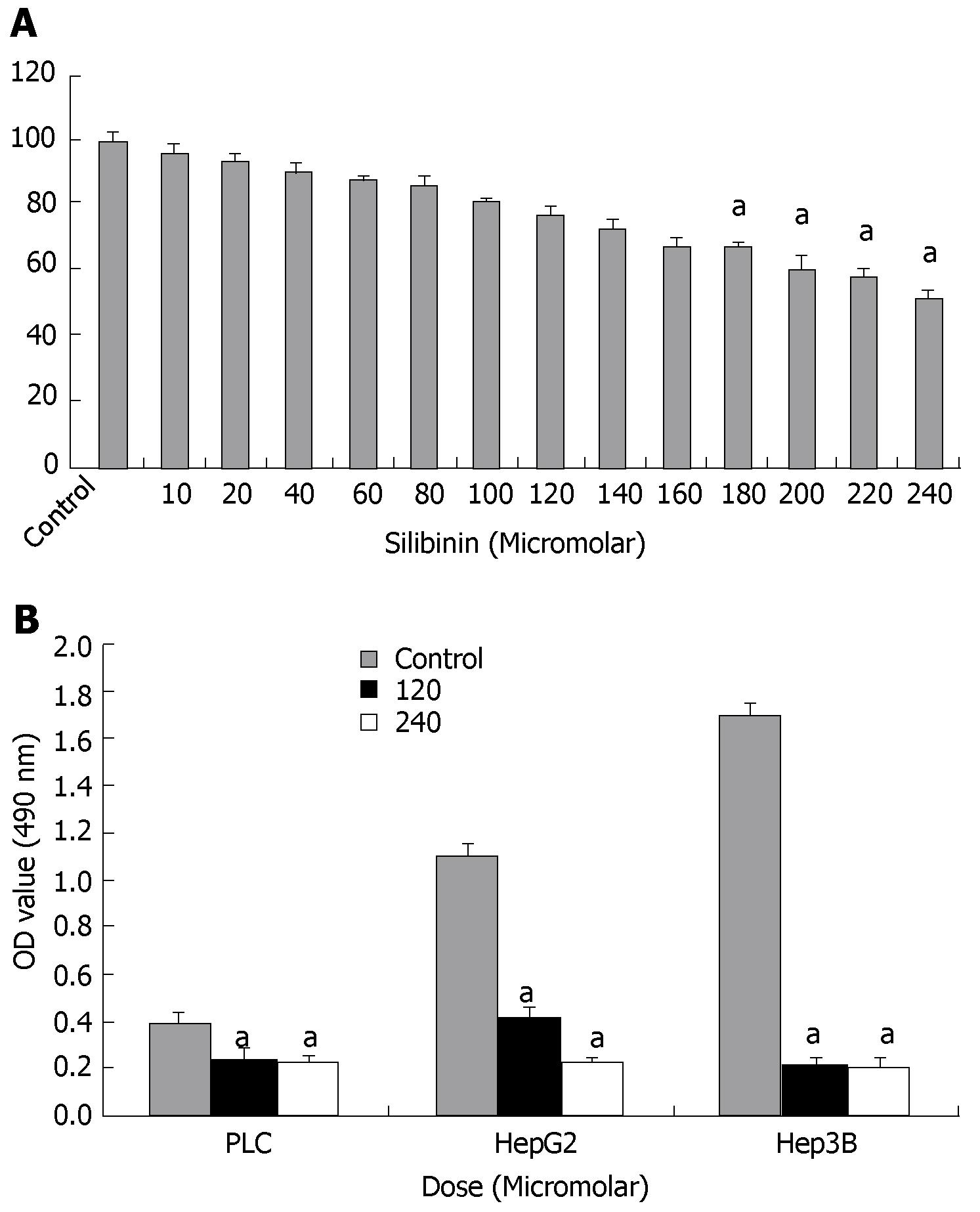
Figure 1 Silibinin's effects on growth of human hepatoma cells.
A: MTT assay showed silibinin's dose dependent anti-proliferative effects on HuH7 cells. A significant decrease in proliferation compared to control was noted from silibinin ≥ 180 μmol/L. The IC25 is determined to be 120 μmol/L and the IC50 is determined to be 240 μmol/L; B: Silibinin's effects on other human HCC cell growth. PLC/PRF/5, HepG2, and Hep3B HCC cells were treated with silibinin at IC25 and IC50 doses for HuH7 cells. Silibinin significantly reduced growth of all three HCC cells in different rates. aP < 0.05 vs control.
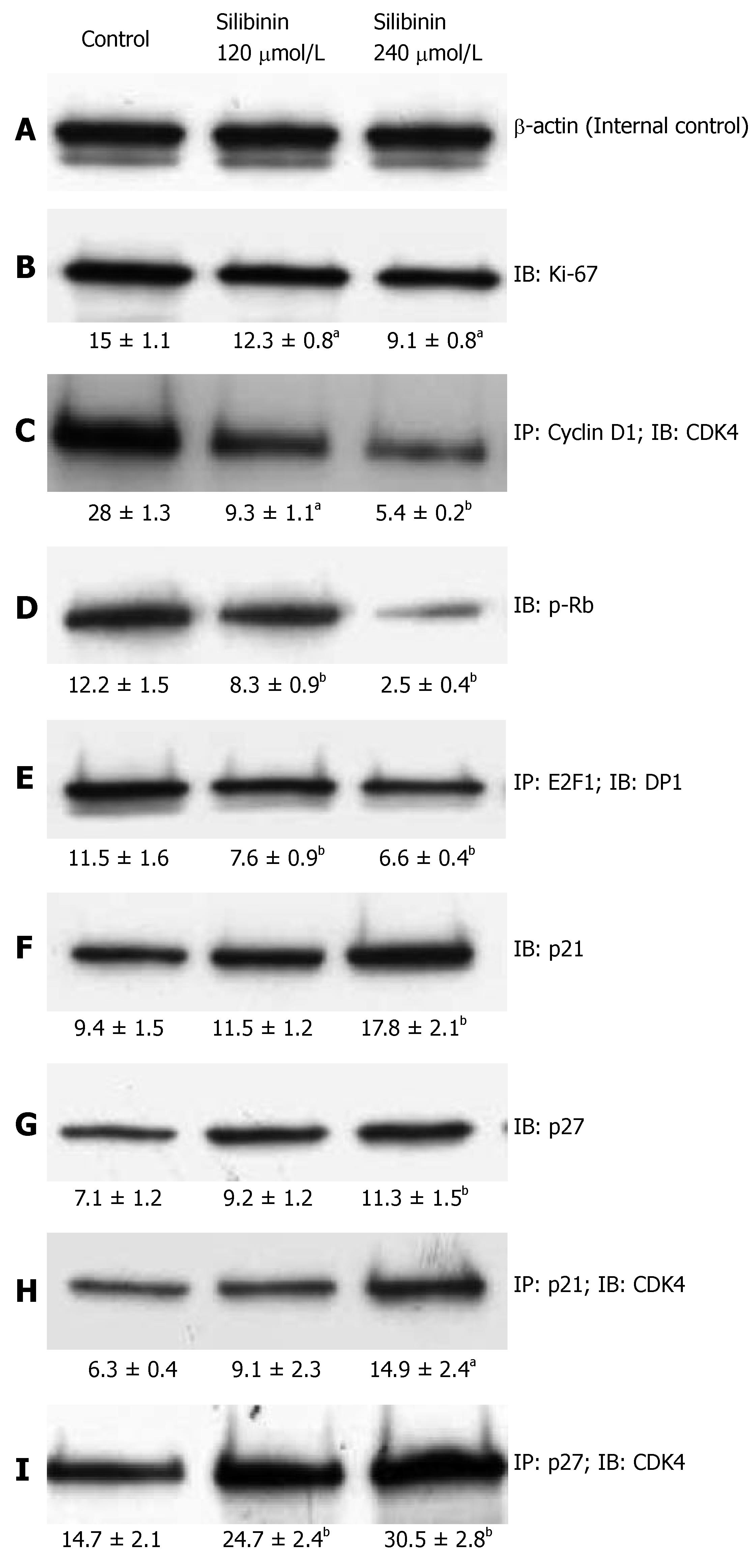
Figure 2 Silibinin's effects on proliferation of HCC cells.
After HuH7 cells were treated with silibinin at IC25 and IC50 doses, immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblots (IB) were performed in triplicate for each specimen. A mean densitometer reading was expressed in the respective box and used for statistical analysis. A: β-actin for internal control; B: Ki-67; C: CD1/CDK4 complex; D: p-Rb; E: E2F1-DP1 complex; F: p21Waf1/Cip1; G: p27Kip1; H: p21Waf1/Cip/CDK4 complex; I: p27Kip1/CDK4 complex. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs control.
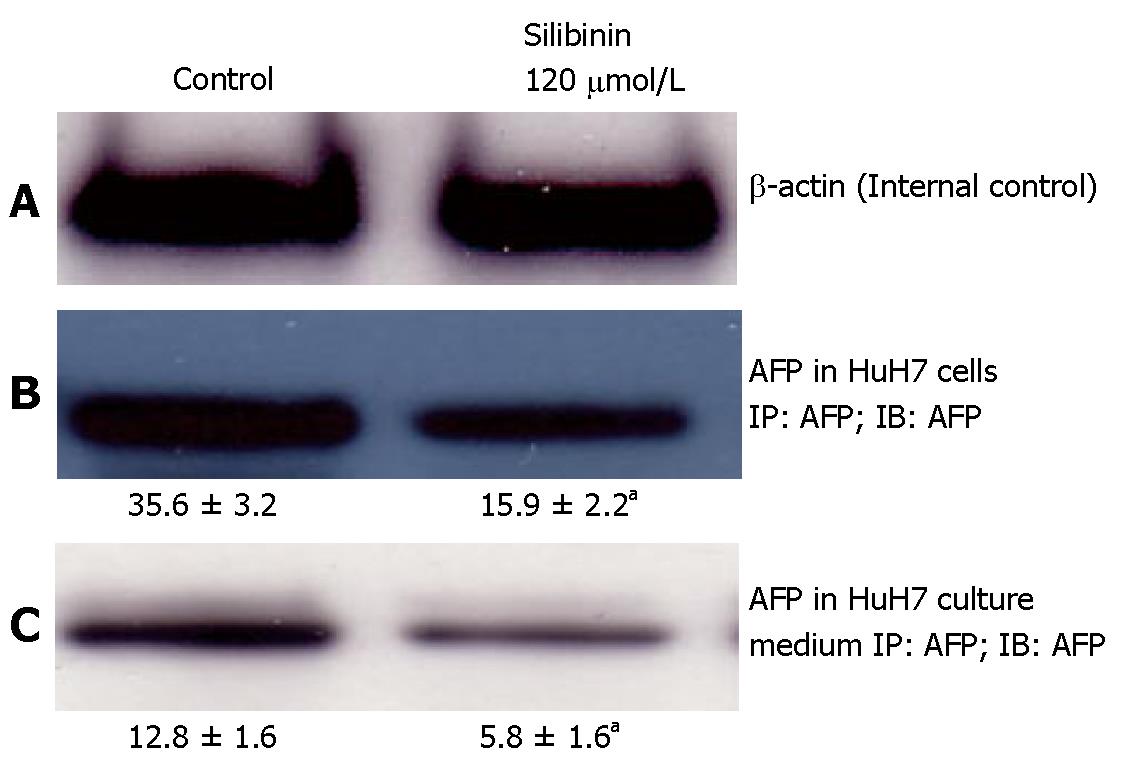
Figure 3 Silibinin's effects on AFP production and secretion from HuH7 cells.
A: β-actin for internal control; B: Silibinin at IC25 dose decreased AFP production in HuH7 cells; C: Silibinin at IC25 dose decreased AFP secretion from HuH7 cells. aP < 0.05 vs control.
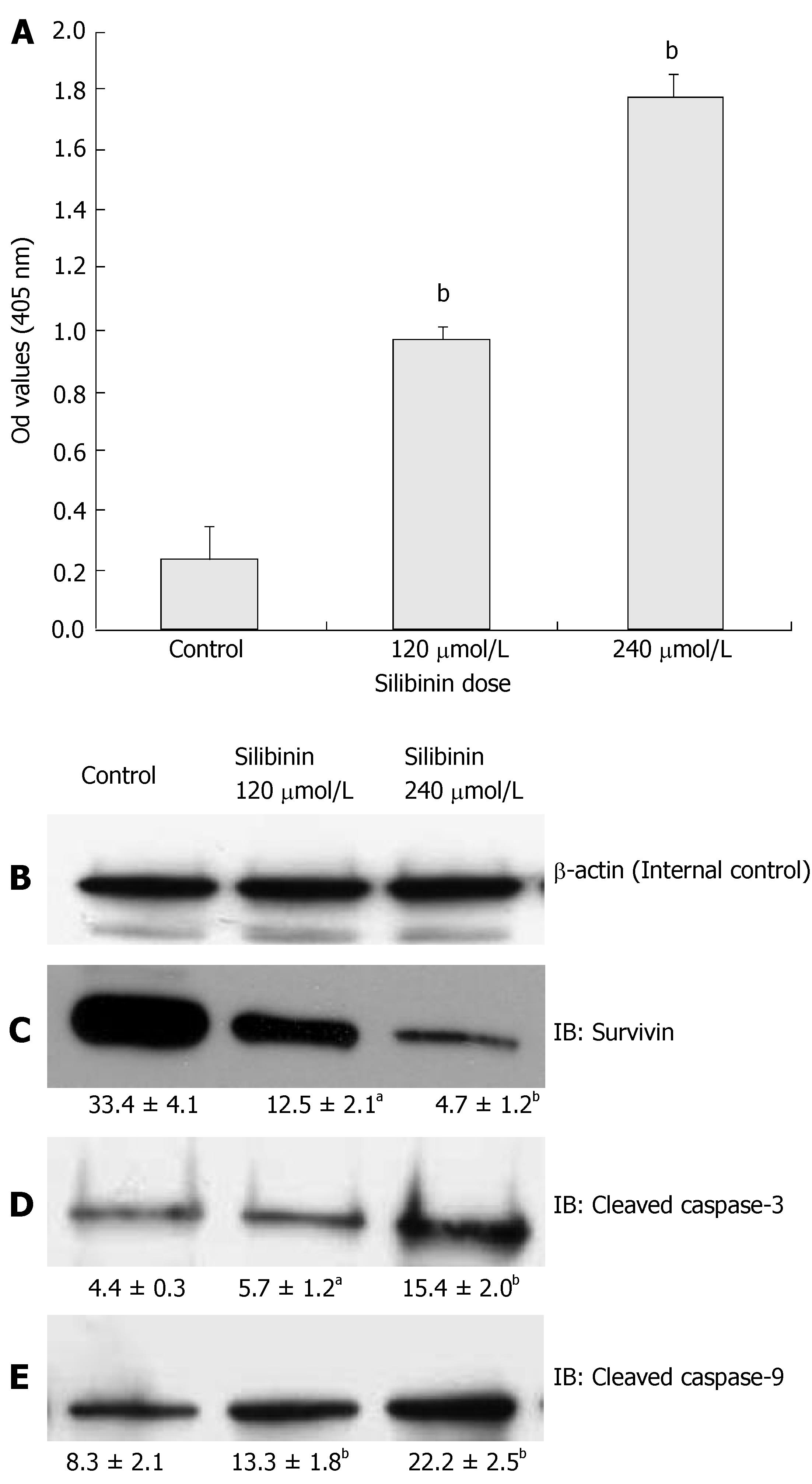
Figure 4 Silibinin's effects on apoptosis in HuH7 cells.
A: Silibinin at IC25 and IC50 doses significantly promoted apoptosis of HuH7 cells; B: β-actin for internal control. Silibinin at IC25 and IC50 doses decreased survivin expression (C), but increased activated caspase-3 (D), and activated caspase-9 (E). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs control.
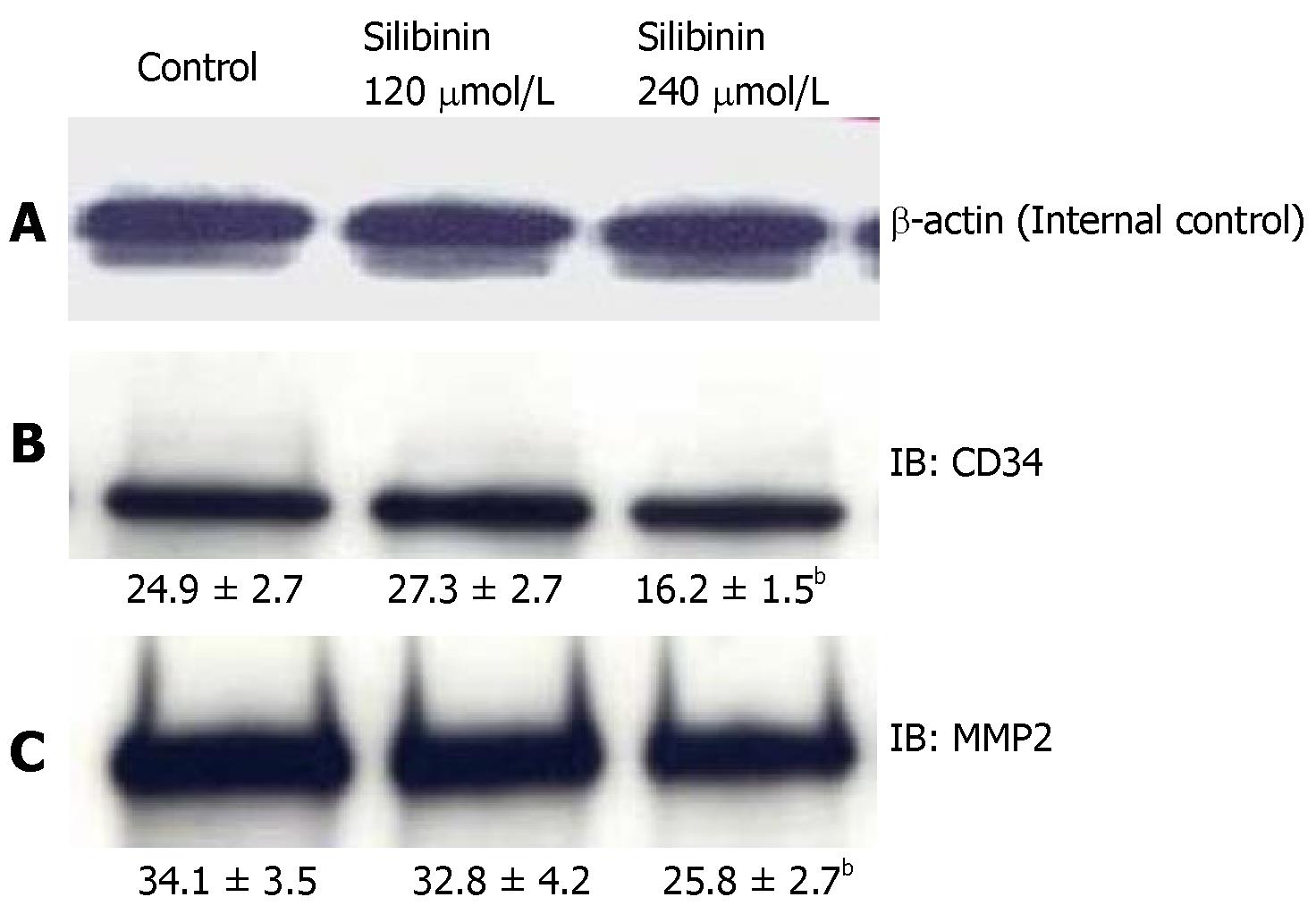
Figure 5 Silibinin's effects on angiogenesis in HuH7 cells.
A: β-actin for internal control. Silibinin decreased CD34 (B), and MMP-2 (C). bP < 0.01 vs control.
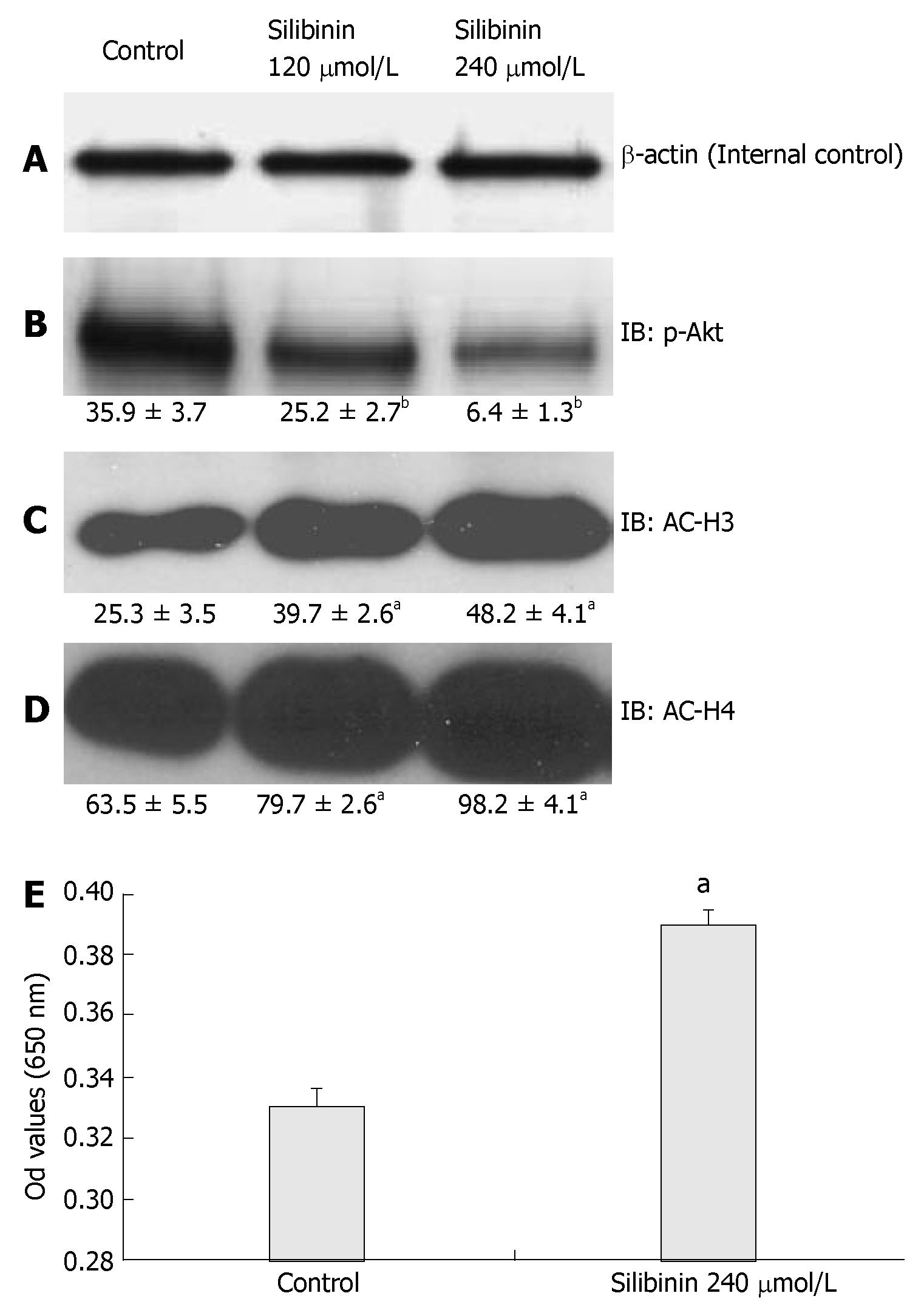
Figure 6 Silibinin's Effects on PTEN, p-Akt, AC-H3 and AC-H4 in HuH7 Cells (A).
β-actin for internal control. Silibinin significantly decreased p-Akt (B); increased AC-H3 (C); AC-H4 (D). Silibinin at 240 µmol/L significantly increased PTEN activity in HuH7 cells (E). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, vs control.
- Citation: Lah JJ, Cui W, Hu KQ. Effects and mechanisms of silibinin on human hepatoma cell lines. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(40): 5299-5305
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i40/5299.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i40.5299