Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2007; 13(39): 5253-5260
Published online Oct 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i39.5253
Published online Oct 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i39.5253
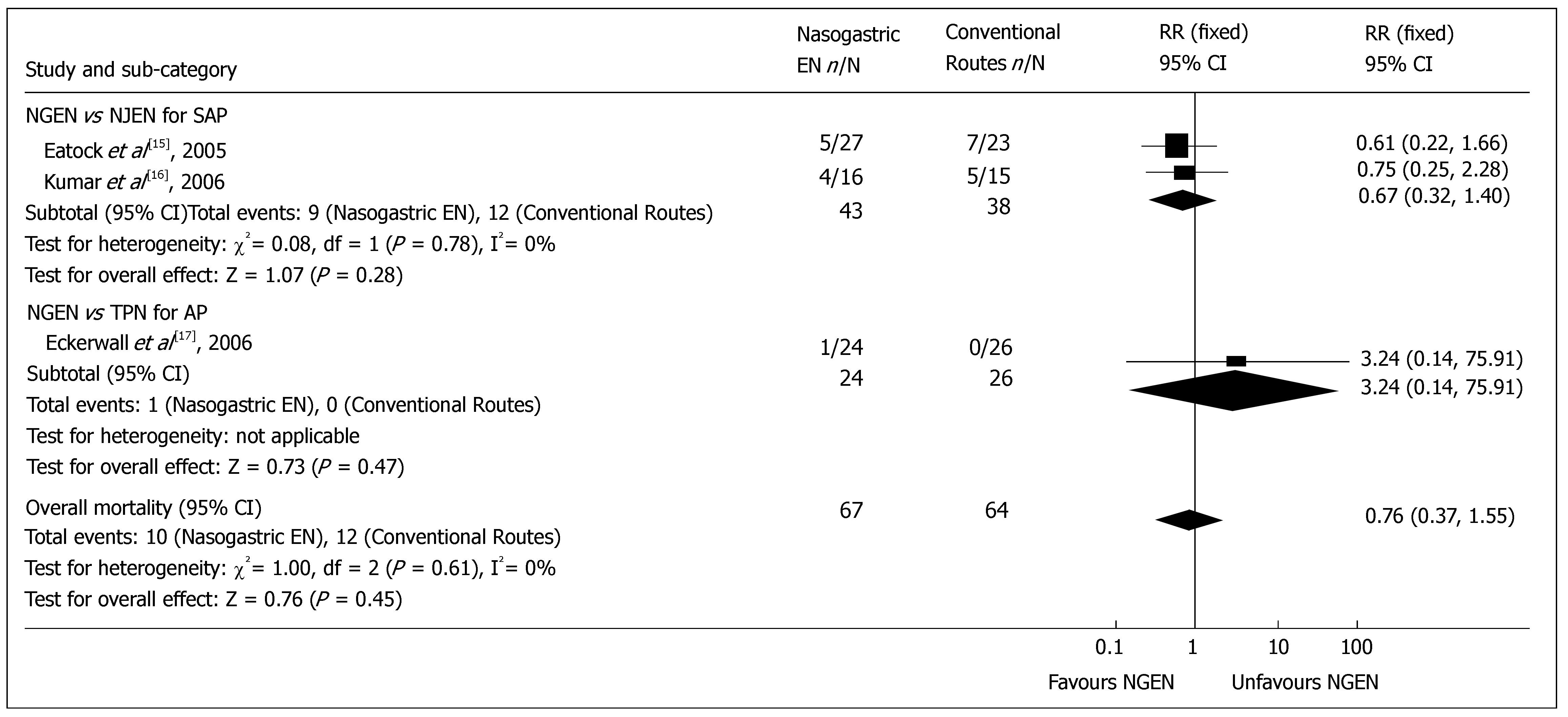
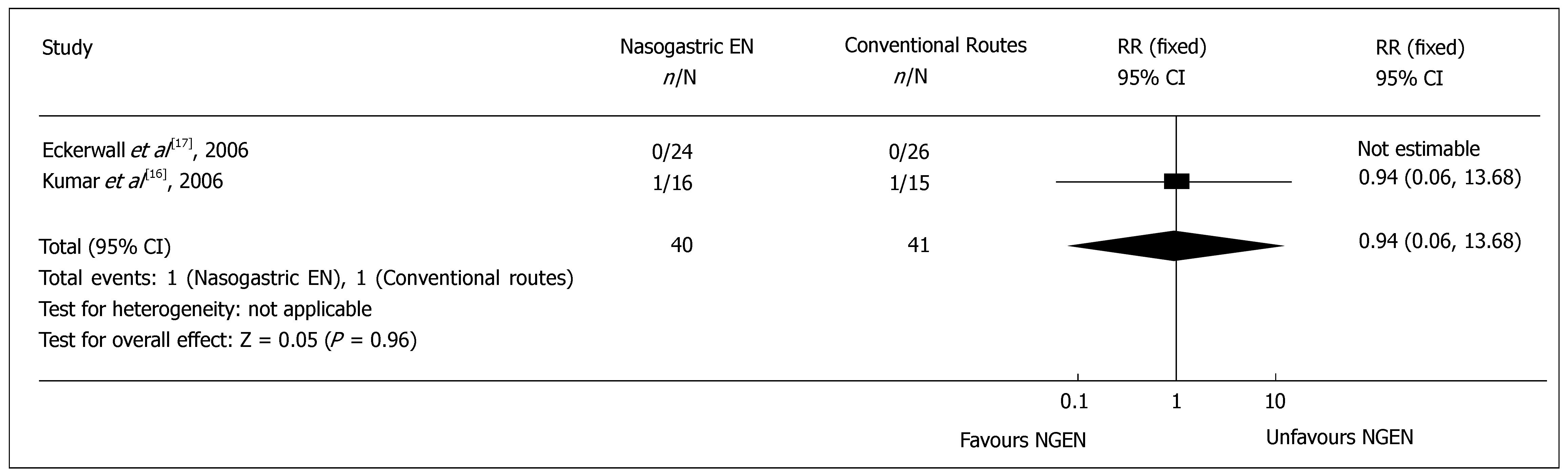
Figure 1 Comparison of overall mortality between nasogastric enteral nutrition and conventional nutritional routes.
Abbreviations: AP, acute pancreatitis; SAP, severe acute pancreatitis; EN, enteral nutrition; TPN, total parenteral nutrition; NGEN, nasogastric enteral nutrition; NJEN, nasojejunal enteral nutrition; RR, risk ratio; CI, confidence interval.
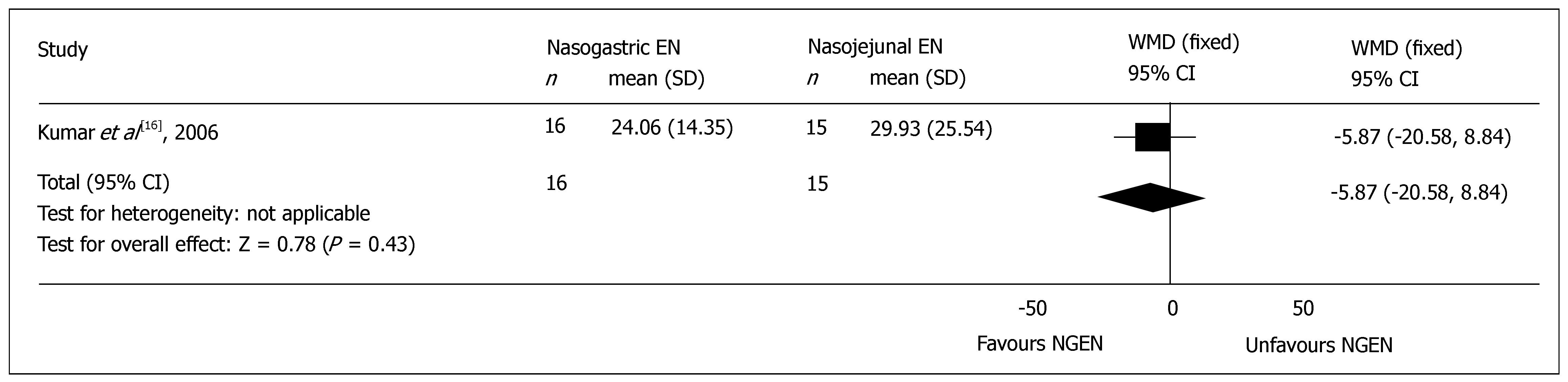
Figure 2 Comparison of total hospital stay (days) between nasogastric and nasojejunal enteral nutrition.
WMD, weighted mean difference; SD, standard deviation.
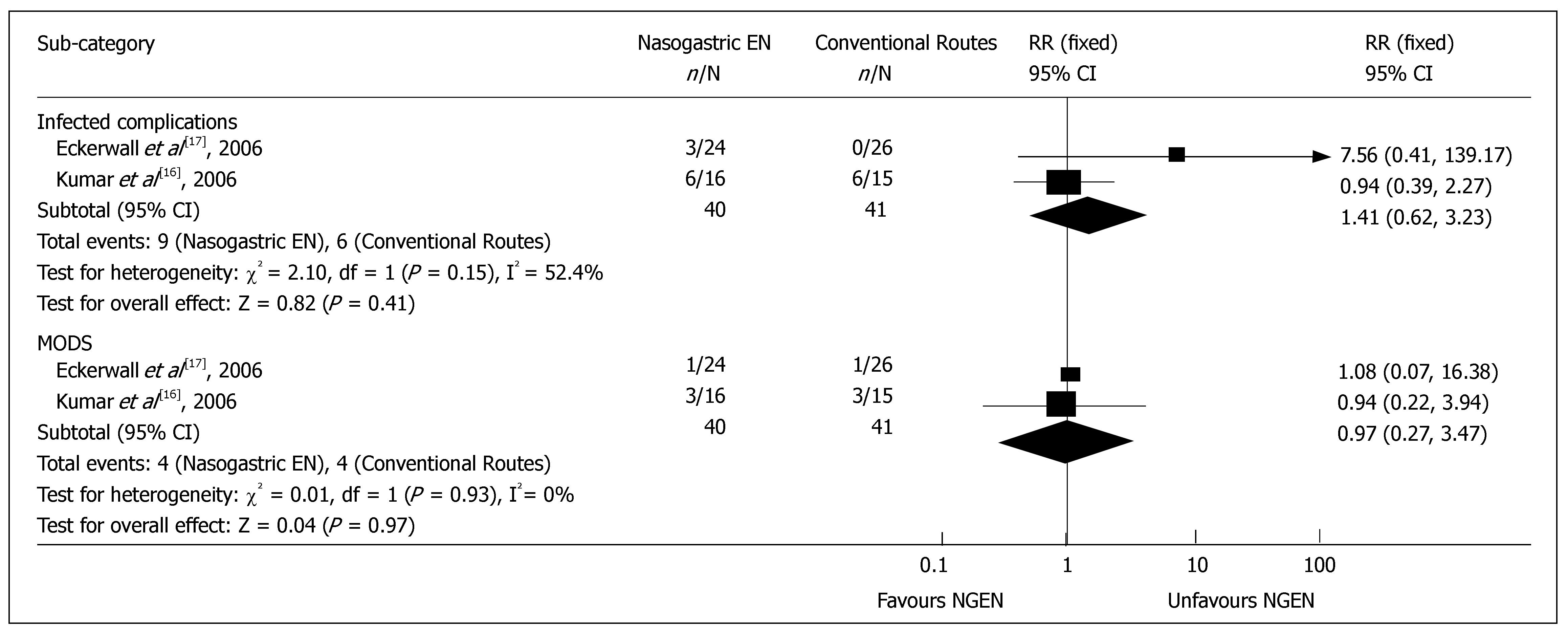
Figure 3 Comparison of complications of acute pancreatitis between nasogastric enteral nutrition and conventional nutritional routes.
MODS, multiple organ deficiency syndrome.
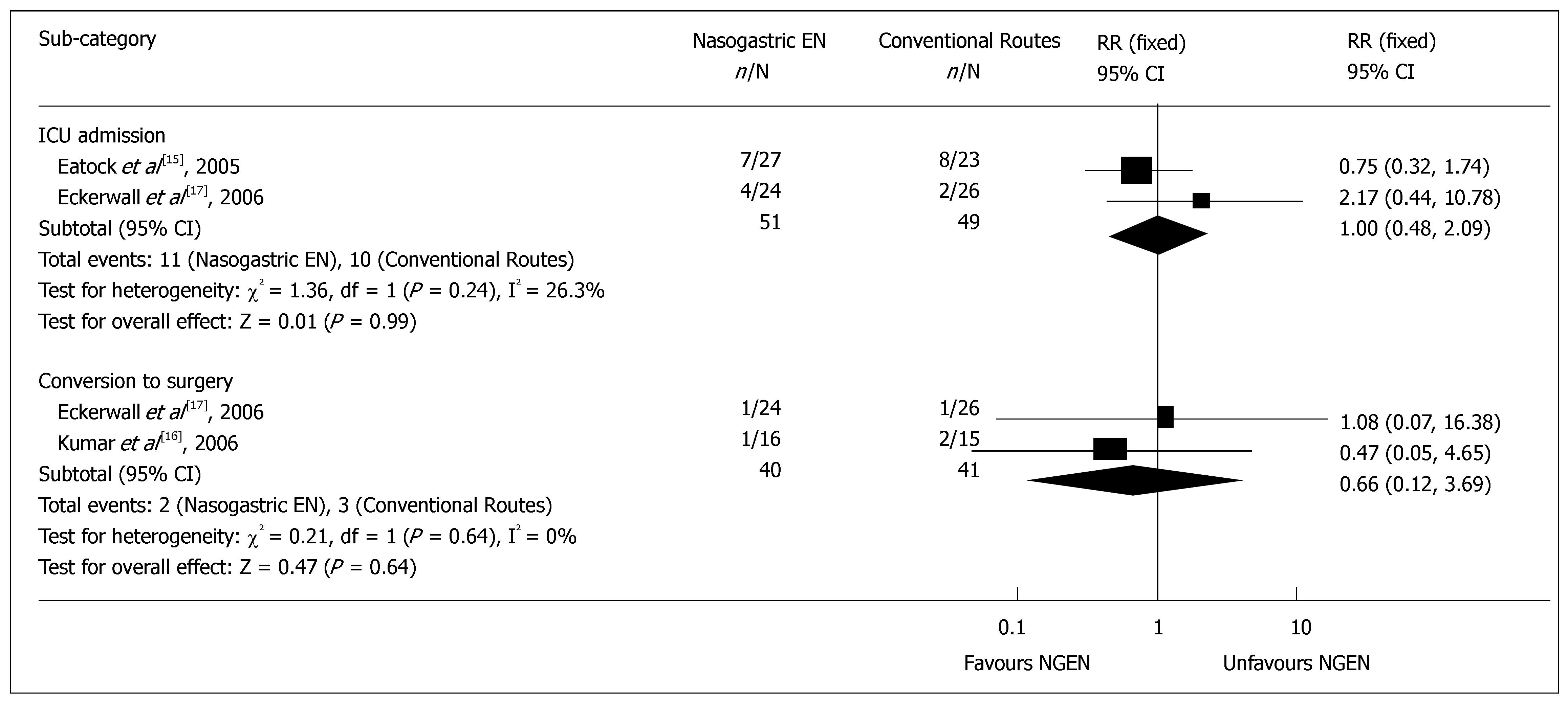
Figure 4 Comparison of management of complications between nasogastric enteral nutrition and conventional nutritional routes.
ICU, intensive care unit.
Figure 5 Comparison of refeeding pain recurrence between nasogastric enteral nutrition and conventional nutritional routes.
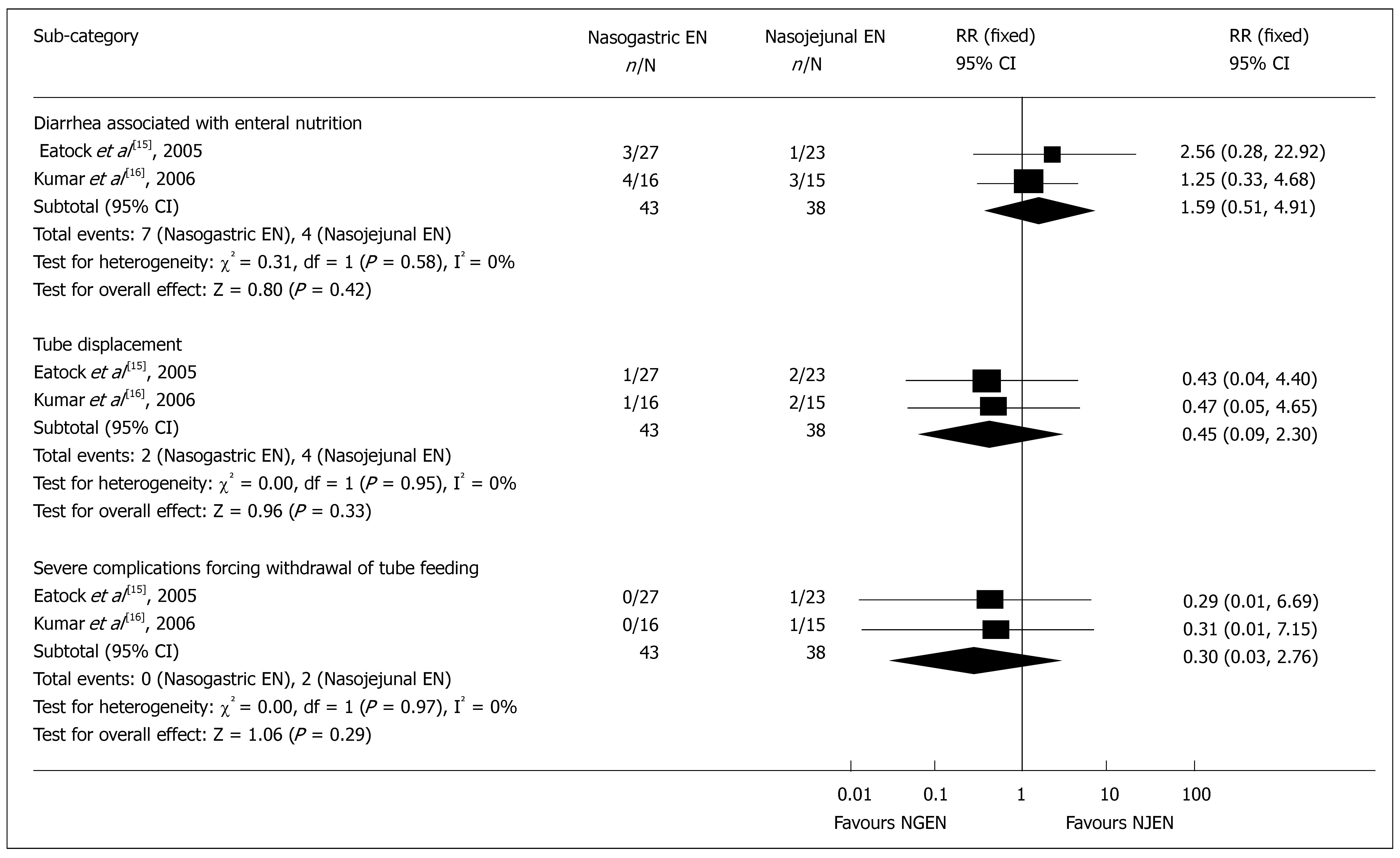
Figure 6 Comparison of nutrition associated adverse events between nasogastric and nasojejunal enteral nutrition (NJEN).
- Citation: Jiang K, Chen XZ, Xia Q, Tang WF, Wang L. Early nasogastric enteral nutrition for severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(39): 5253-5260
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i39/5253.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i39.5253