Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2007; 13(36): 4909-4911
Published online Sep 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i36.4909
Published online Sep 28, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i36.4909
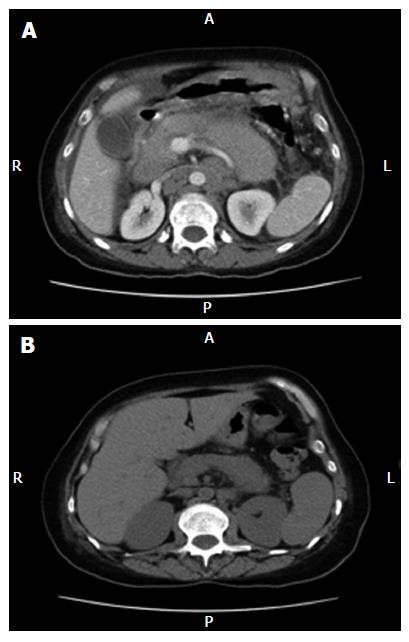
Figure 1 A: Baseline CT scan (pre-therapy).
Abdominal CT scan shows diffusely enlarged pancreas due to infiltrative neoplasm, along with bulky retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy, bulky peripancreatic, mesenteric adenopathy, ascites and peritoneal carcinomatosis; B: Post-therapy CT Scan ( non-enhanced). A follow-up CT scan of the abdomen reveals a marked decrease in size of the pancreas and retroperitoneal lymph nodes.
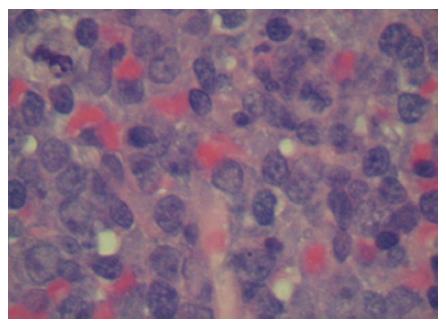
Figure 2 Biopsy of the axillary mass reveals a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
- Citation: Saif MW, Khubchandani S, Walczak M. Secondary pancreatic involvement by a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting as acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(36): 4909-4911
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i36/4909.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i36.4909