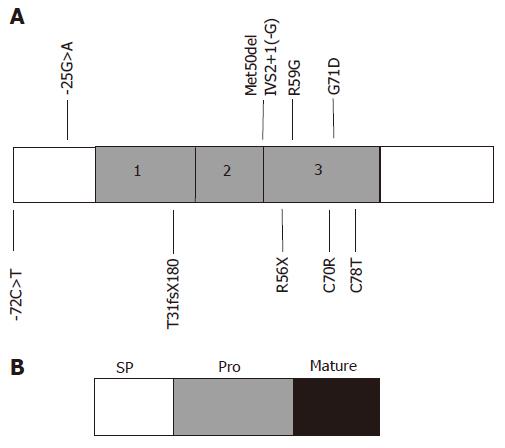
Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2007; 13(35): 4690-4698
Published online Sep 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4690
Published online Sep 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4690
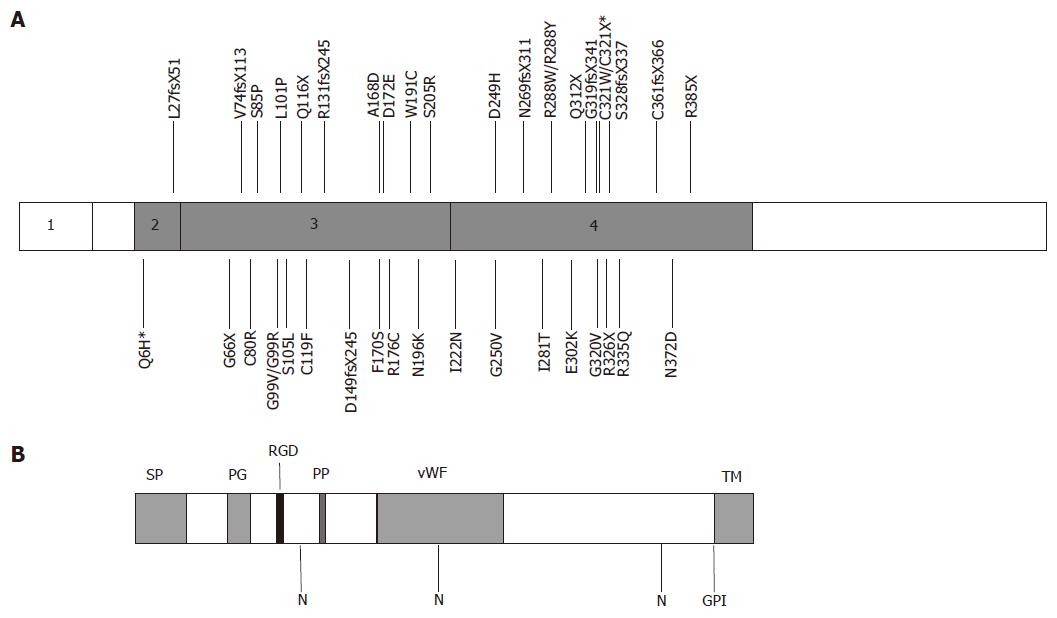
Figure 1 Structure of human hemojuvelin and positions of mutations.
A: The exon structure of human hemojuvelin is shown with positions of known mutations marked[6,13-24,30,39]. *Q6H was found associated with C321X; B: Predicted structure of the full length HJV protein, showing the positions of structural domains and motifs. SP, signal peptide; PG, poly-glycine sequence; RGD, RGD motif; PP, poly-proline sequence; vWF, partial von Willebrand factor type D domain; N, potential N-linked glycosylation sites; GPI, GPI-attachment site; TM, transmembrane domain, cleaved after GPI attachment.
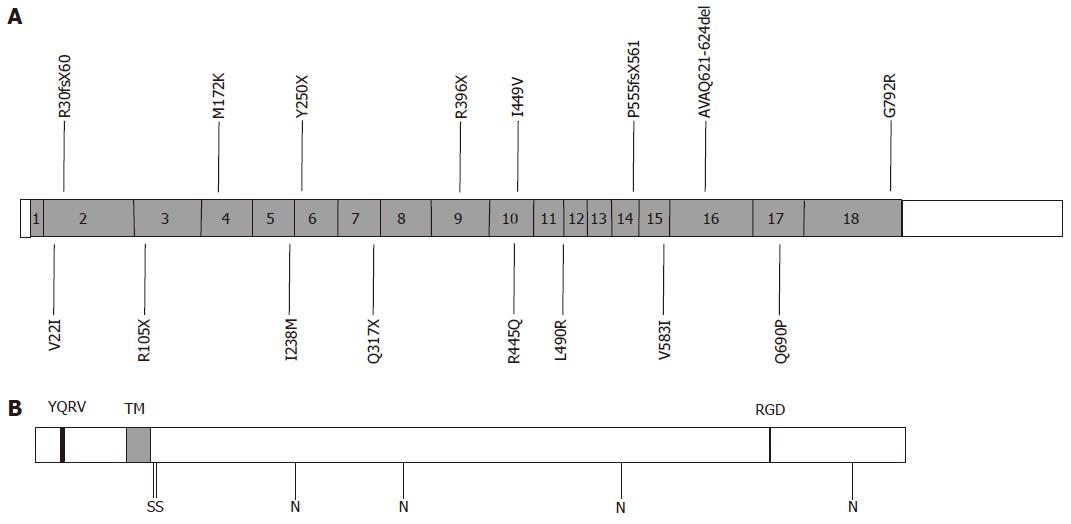
Figure 3 Structure of human transferrin receptor 2 (TfR2) and positions of mutations.
A: The exon structure of human TfR2 is shown with positions of known mutations marked[7,30,40-52]. The frameshift mutations R30fsX60 and P555fsX561 are also known as E60X and V561X respectively. G792R may be associated with R396X; B: Predicted structure of TfR2 protein. YQRV, endocytosis signal; TM, transmembrane domain; RGD, RGD motif; S, predicted interchain disulphide bonds; N, potential N-linked glycosylation sites.
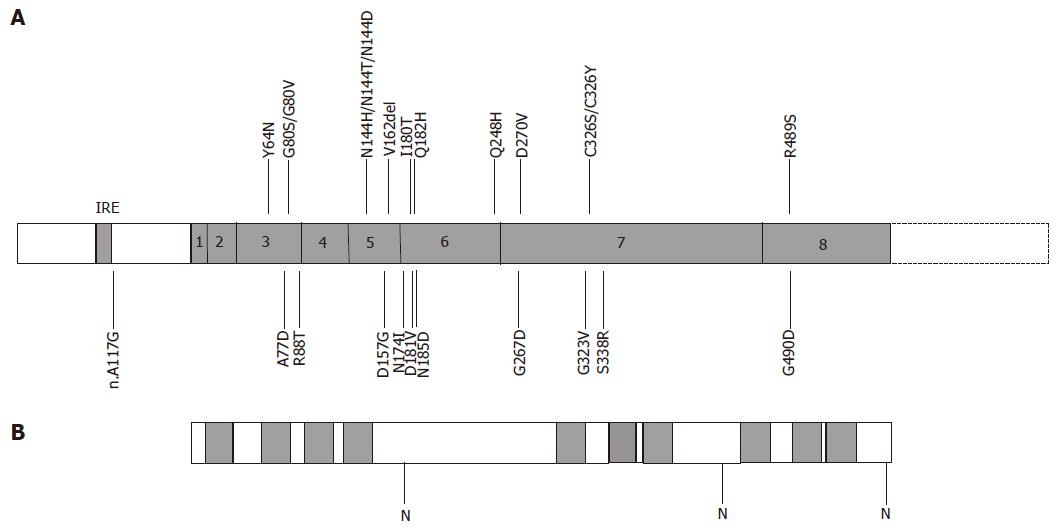
Figure 4 Structure of human ferroportin and positions of mutations.
A: The exon structure of human ferroportin is shown with positions of known mutations marked[8,9,60-85]. IRE, iron response element; B: Predicted structure of ferroportin protein. Predicted transmembrane domains are shaded; N, potential N-linked glycosylation sites.
- Citation: Wallace DF, Subramaniam VN. Non-HFE haemochromatosis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(35): 4690-4698
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i35/4690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4690