Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2007; 13(33): 4458-4466
Published online Sep 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i33.4458
Published online Sep 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i33.4458
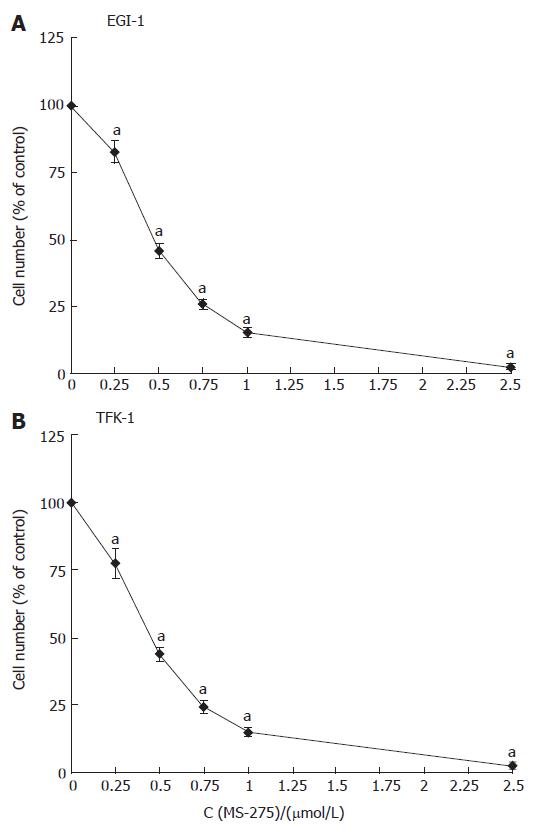
Figure 1 Anti-proliferative effects of MS-275 on human EGI-1 and TFK-1 cholangiocarcinoma cells.
mean ± SEM, n > 5, aP < 0.05 vs controls.
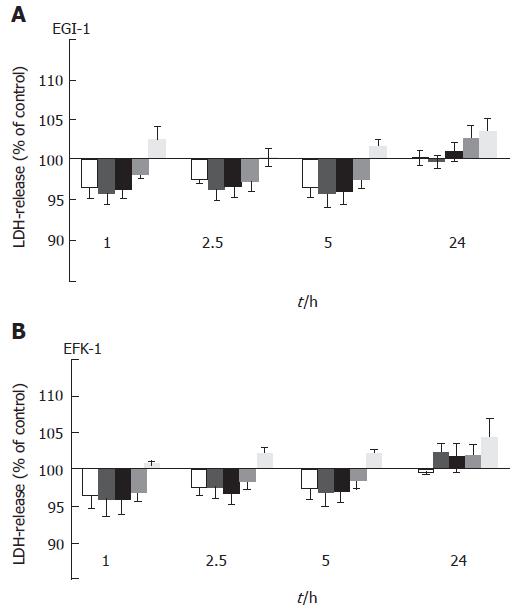
Figure 2 MS-275-induced LDH release into the supernatant of EGI-1 and TFK-1 cells.
mean ± SEM, n > 3 independent experiments; No significant increase in LDH release was observed.
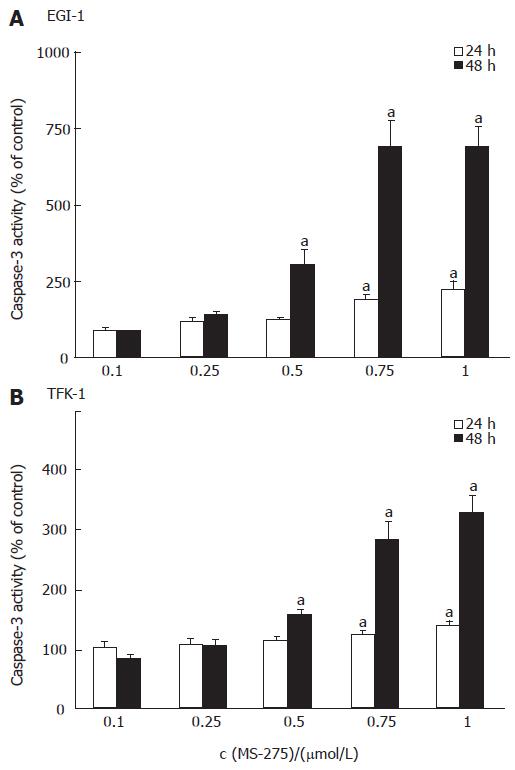
Figure 3 MS-275-induced apoptosis-specific caspase-3 activity increase in EGI-1 and TFK-1 cells.
mean ± SEM, n > 3 independent experiments, aP < 0.05 vs controls.
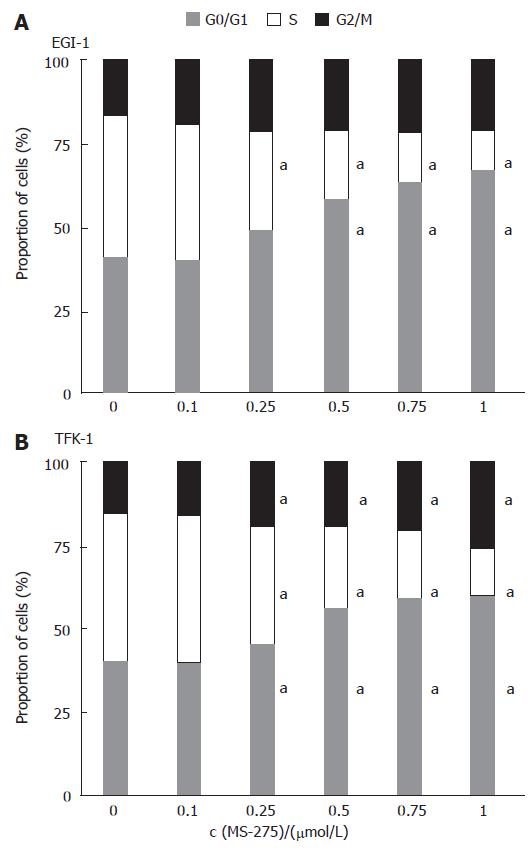
Figure 4 Induction of cell cycle arrest by MS-275 on EGI-1 and TFK-1 cells.
means of > 3 independent experiments, aP < 0.05 vs controls.
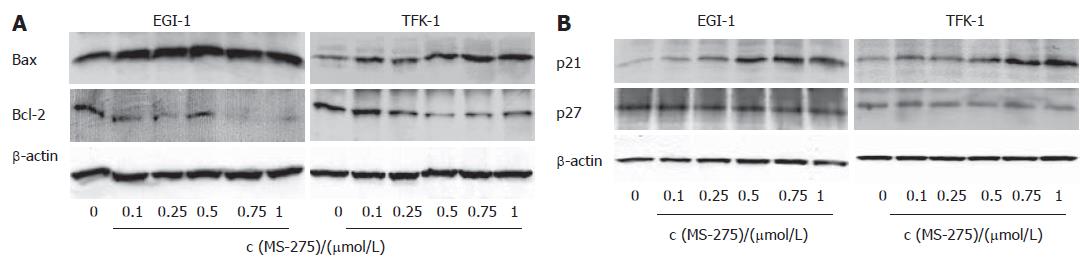
Figure 5 MS-275-induced modulation of apoptosis- and cell cycle-relevant proteins (n = 3 independent experiments).
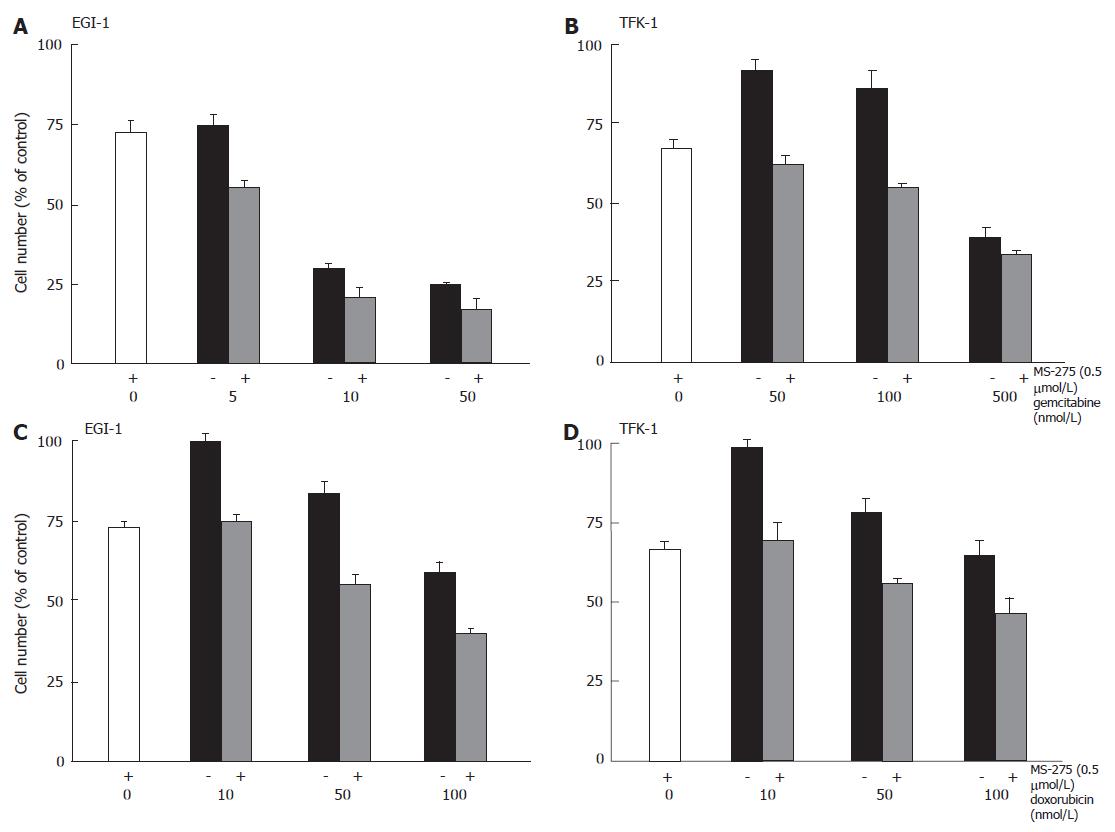
Figure 6 Anti-proliferative effects of MS-275 plus cytostatics on EGI-1 and TFK-1 cells.
mean ± SEM, n = 3-4 independent experiments.
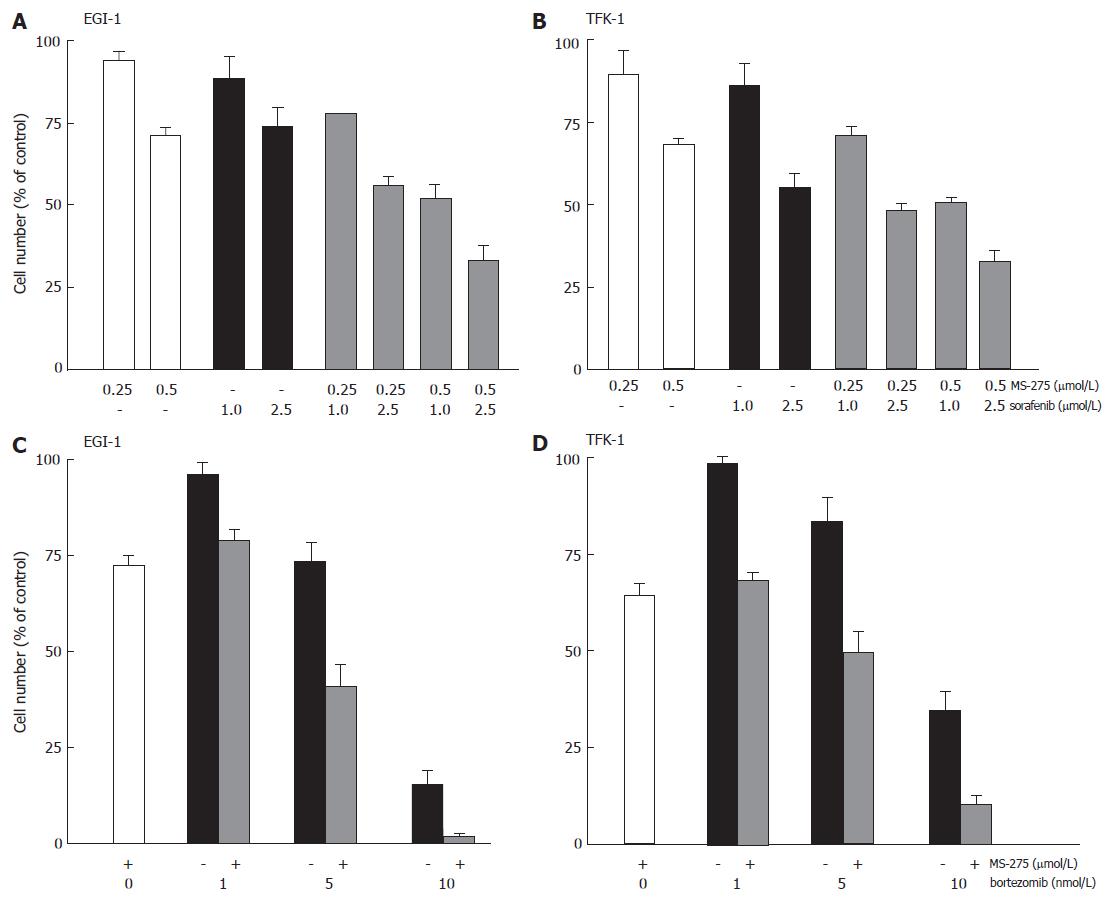
Figure 7 Anti-proliferative effects of MS-275 plus sorafenib or bortezomib on EGI-1 and TFK-1.
mean ± SEM, n = 3-4 independent experiments.
- Citation: Baradari V, Höpfner M, Huether A, Schuppan D, Scherübl H. Histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 alone or combined with bortezomib or sorafenib exhibits strong antiproliferative action in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(33): 4458-4466
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i33/4458.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i33.4458