Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2007; 13(29): 4006-4010
Published online Aug 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.4006
Published online Aug 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.4006
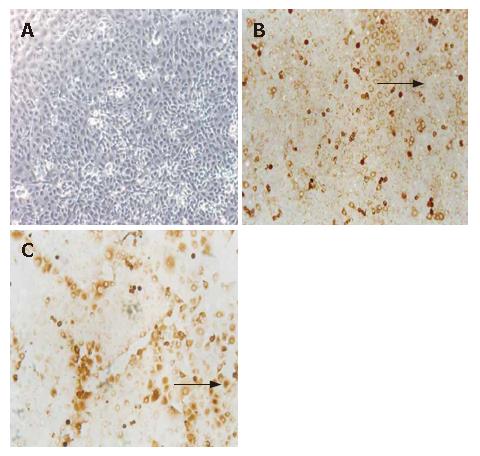
Figure 1 A: The 3rd passage of HUVEC, lined like cobblestone (× 100); B: Negative expression of control antibody on HUVEC detected by immunocytochemistry staining (arrow, negative, SP, × 100); C: Positive expression of KDR on HUVEC detected by immunocytochemistry staining (arrow, positive, SP, × 100).
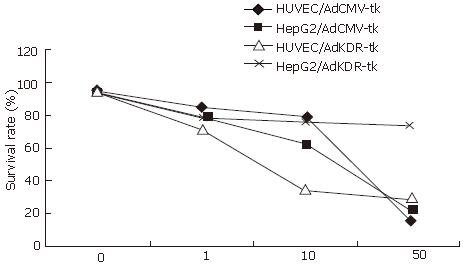
Figure 2 Survival rate of cells transfected by AdKDR-tk or AdCMV-tk after GCV administration.
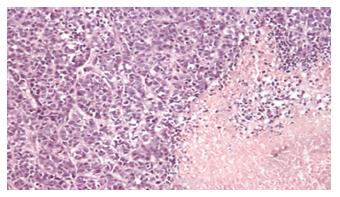
Figure 3 Histological examination of subcutaneous HepG2 tumor observed by light microscopy after the treatment.
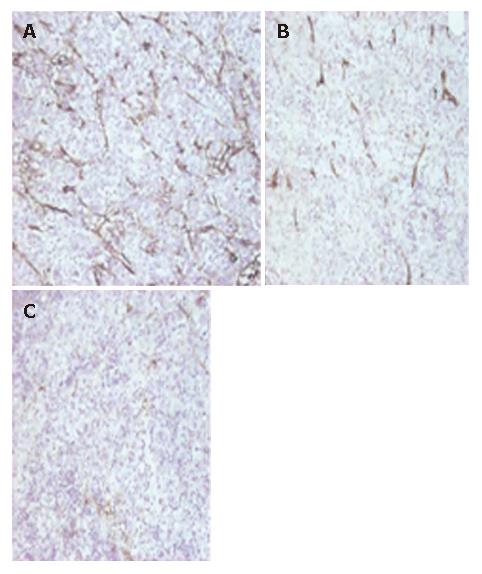
Figure 4 Microvessel density of tumors detected by anti-CD31 immunochemistry staining (S-P, × 100).
A: MVD (CD31 staining, × 200) of hepatoma treated with Ad group (II); (30.6 ± 7.8); B: MVD (CD31 staining, × 200) of hepatoma treated with AdCMV-TK group (III); (27.6 ± 7.1); C: MVD (CD31 staining, × 200) of hepatoma treated with AdKDR-TK group (IV); (10.7 ± 4.1).
- Citation: Li BJ, Zhang C, Yi YX, Hao Y, Liu XP, Ou QJ. Vascular damage and anti-angiogenic effects of tumor vessel-targeted adenovirus-mediated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(29): 4006-4010
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i29/4006.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.4006