Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2007; 13(29): 3918-3924
Published online Aug 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3918
Published online Aug 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3918
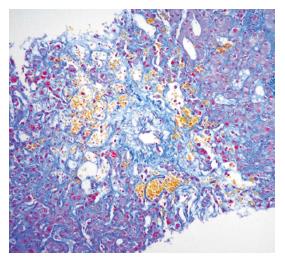
Figure 1 Liver biopsy in a patient with diagnosis of VOD 5 mo post liver transplantation.
There is centrilobular liver cell loss, sinusoidal ectasia, haemorrhage, and a stenotic hepatic outflow venule (in the centre of the picture). The appearance is of venous outflow obstruction. MSB stain.
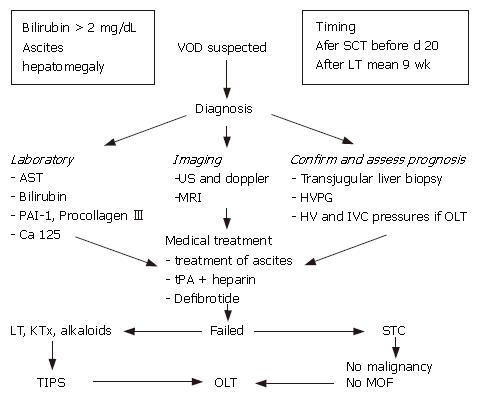
Figure 2 Flow chart in diagnosis and management of veno-occlusive disease.
VOD: veno occlusive disease; SCT, stem cell transplantation; OLT: ortothopic liver transplantation; HVPG: hepatic venous pressure gradient; HV hepatic vein; IVC: inferior vena cava; KT: kidney transplantation; MOF: multi organ failure; TIPS: transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
- Citation: Senzolo M, Germani G, Cholongitas E, Burra P, Burroughs A. Veno occlusive disease: Update on clinical management. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(29): 3918-3924
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i29/3918.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3918