Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2007; 13(2): 299-305
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.299
Published online Jan 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.299
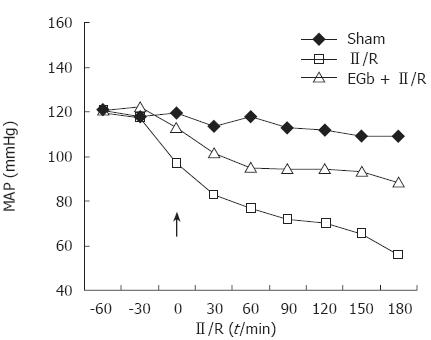
Figure 1 Effects of EGb 761 (arrow indicates the starting point of reperfusion) on mean arterial pressure (MAP) after II/R in anaesthetized rats.
A rapid drop in MAP was recorded immediately after the beginning of reperfusion of the ischemic bowel. Data are the means of 8 rats (SD not shown). EGb 761 markedly increased MAP. There were significant differences in MAP at all time points after reperfusion between II/R and EGb + II/R groups (P < 0.01).
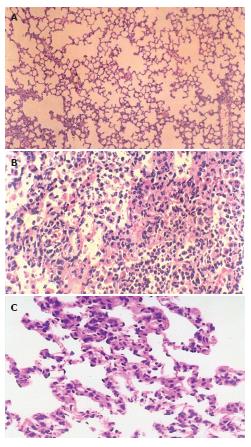
Figure 2 Light microscopic observation of the lung tissues after II/R with pretreatment of EGb 761 in rats.
A: The normal lung tissue structure was found in sham group (× 100); B: Lung edema, hemorrhage and inflammatory cell sequestration were found in II/R group (× 200); C: Decreased morphological changes induced by II/R were found in EGb +II/R group (× 200).
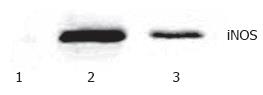
Figure 3 Western blotting analysis of iNOS in rat lung.
1. Sham group; 2. II/R group; 3. EGb + II/R group. The intensity of the bands was greater in II/R group compared with EGb +II/R group. A prominent band of iNOS protein was demonstrated at approximately 70 Kd.
- Citation: Liu KX, Wu WK, He W, Liu CL. Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) attenuates lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats: Roles of oxidative stress and nitric oxide. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(2): 299-305
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i2/299.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.299