Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2007; 13(17): 2446-2454
Published online May 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i17.2446
Published online May 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i17.2446
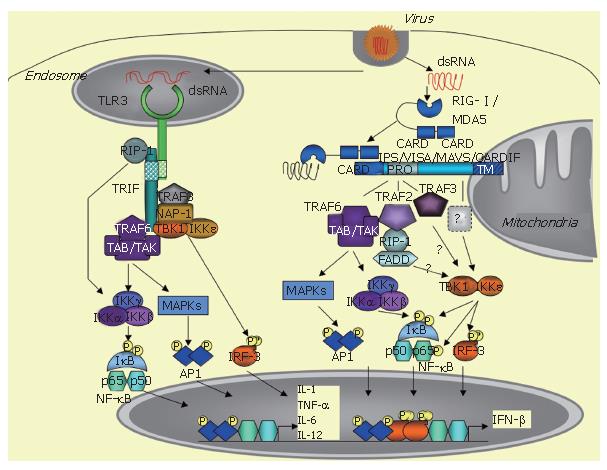
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the dsRNA-activated TLR3 and RNA helicase IFN inducing pathways.
dsRNA: double-stranded RNA; TLR3: Toll-like receptor 3; RIP-1 Receptor interacting protein -1; TRIF: TIR (Toll/IL-1-like receptor) domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-β; TRAF2, TRAF3 and TRAF6: TNFR-associated factor; NAP-1: NAK ( NF-κB activating kinase) Associated Protein-1; TBK1: TANK (TRAF family member-associated NFκB activator) Binding Kinase 1 (also known as NAK); IKKε: IkB kinase epsilon; TAB: TAK binding protein; TAK: TGFβ-associated kinase; IKKγ: also known as NEMO (NF-κB Essential Modulator), associates with the IKKα and IKKβ kinases; IKKα IκB Kinase α; IKKβ IκB Kinase β; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; IkB: Inhibitor NF-κB; P65: NF-κB subunit; P50: NF-κB subunit; AP1: ATF2/c-jun transcription factor; IRF3: Interferon regulatory factor 3; RIG-I: Retinoic inducible gene-1; MDA5: Melanoma differentiation associated gene 5; CARD: Caspase association recognition domain; IPS-1: Interferon-β promoter stimulator 1; MAVS: Mitochondrial antiviral signaling; VISA: Virus-induced signaling adaptor; CARDIF: CARD adapter inducing IFNβ; PRO: Proline rich domain; FADD: FAS associated protein via death domain. IL-1, IL-6 and IL-12: Interleukines, TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor α;
- Citation: Meurs EF, Breiman A. The interferon inducing pathways and the hepatitis C virus. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(17): 2446-2454
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i17/2446.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i17.2446