Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2007; 13(15): 2145-2149
Published online Apr 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i15.2145
Published online Apr 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i15.2145
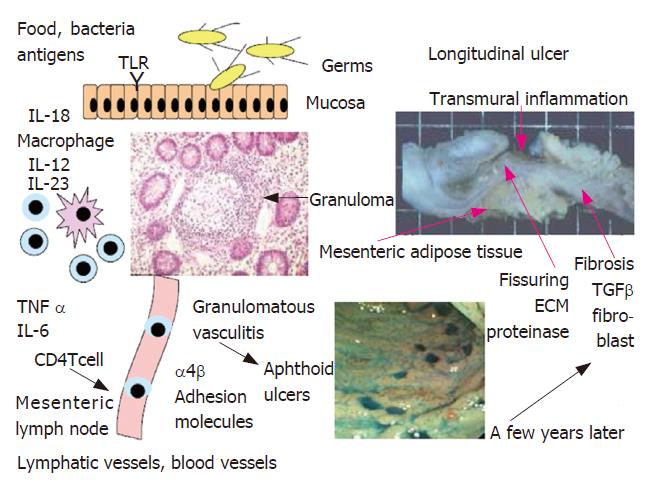
Figure 1 Schema of the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease.
TLR: toll-like receptors; IL: interleukin; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; ECM: extracellular matrix; TGF: transforming growth factor.
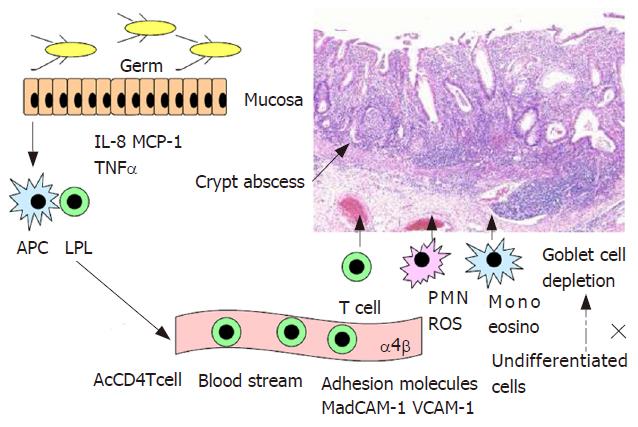
Figure 2 Schema of the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis.
IL: interleukin; MCP: monocyte chemoattractant protein; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; APC: antigen-presenting cells; LPL: lamina propria lymphocytes; AcCD4Tcell: activated CD4Tcell; PMN: polymorphonuclear cell; ROS: reactive oxygen species; mono: monocyte; MadCAM: mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule; VCAM: vascular cell adhesion molecule.
- Citation: Asakura H, Suzuki K, Honma T. Recent advances in basic and clinical aspects of inflammatory bowel disease: Which steps in the mucosal inflammation should we block for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease? World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(15): 2145-2149
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i15/2145.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i15.2145