Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2007; 13(14): 2113-2117
Published online Apr 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i14.2113
Published online Apr 14, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i14.2113
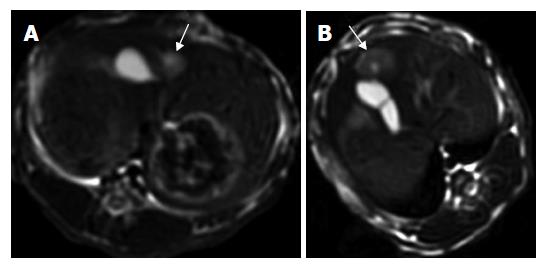
Figure 1 Images in a VX2 rabbit with a solid HCC in group B.
A: Pretherapeutic unenhanced T2-weighted axial MR imaging with FSE sequence (3000/89.2). The hyperintense lesion with a size of 9 mm×10 mm is well discernible from the surrounding liver tissue. B: Post-therapeutic unenhanced T2-weighted axial MR imaging with FSE sequence (3000/89.2) showing the hyperintense lesion (15 mm × 11 mm) with central hypointense area corresponding to the intratumoral necrosis.
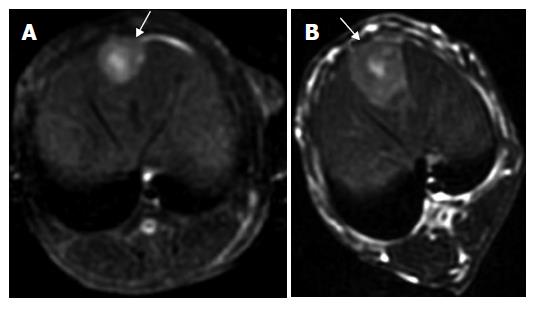
Figure 2 Images in a VX2 rabbit with a solid HCC in group D.
A: Pretherapeutic unenhanced T2-weighted axial MR imaging with FSE sequence (3000/89.2). The hyperintense lesion with a size of 12 mm × 13 mm is well discernible from the surrounding liver tissue; B: Post-therapeutic unenhanced T2-weighted axial MR imaging with FSE sequence (3000/89.2) showing an inhomogeneous area corresponding to the intrahepatic metastasis. The tumor with a size of 23 mm × 27 mm had a rapid growth compared with that before therapy.
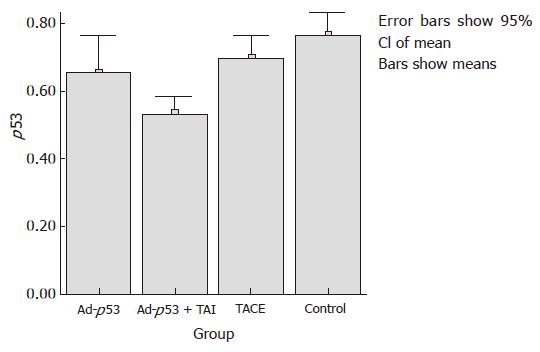
Figure 3 Positive cell rate of mutant-type p53 protein in different groups.
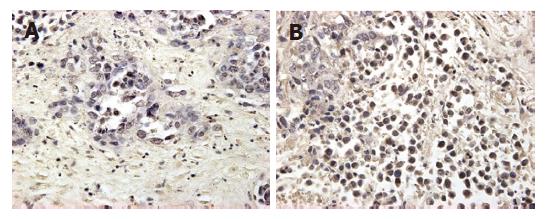
Figure 4 Histological examination of VX2 tumor in different groups.
A: immunohistochemical stain showing the low expression of mutant-type p53 gene high in VX2 cells in group B, magnification × 400, B: The same stain showing the expression in group D, (× 400).
- Citation: Gu T, Li CX, Feng Y, Wang Q, Li CH, Li CF. Trans-arterial gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in a rabbit model. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(14): 2113-2117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i14/2113.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i14.2113