Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2006; 12(7): 1049-1055
Published online Feb 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i7.1049
Published online Feb 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i7.1049
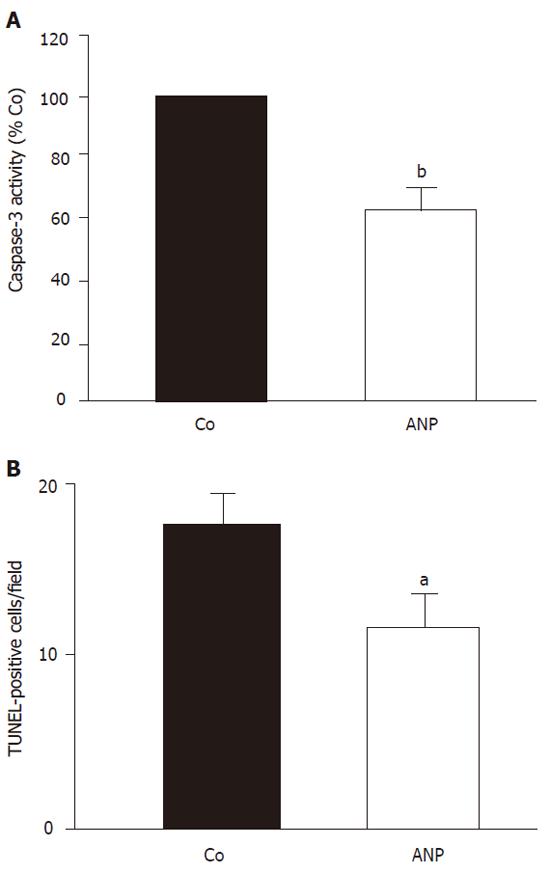
Figure 1 Effect of ANP pretreatment on apoptotic cell death after 24 h ischemia.
Animals received an intravenous infusion of NaCl (Co) or ANP (5 µg/kg) for 20 min and livers were kept in cold UW-solution for 24 h. A: Caspase-3 activity: Snap-frozen tissue was homogenized and caspase-3 like activity was determined as described. Data were expressed as percentage of caspase-3 activity in untreated livers (100%). Columns show mean ± SE, n = 4 animals in each group. bP < 0.01 vs Nacl treatment. B: TUNEL assay: Snap-frozen tissue was cut into 6 µm slices. TUNEL staining was performed as described and apoptotic liver cells per field of view (1.96 mm2) were counted. Results were expressed as means ± SE, n = 4 in each group. aP < 0.05 vs Nacl treatment.
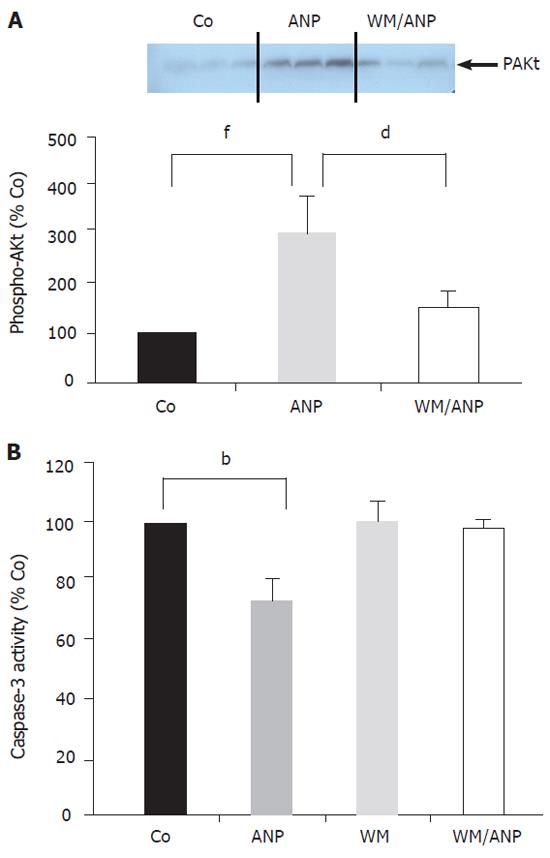
Figure 2 Effect of ANP-preconditioning on PI-3-kinase/Akt pathway.
A: After intravenous infusion of NaCl (Co), ANP (5 µg/kg), wortmannin (WM, 16 µg/kg), or a combination of both (WM/ANP) for 20 min livers were excised and snap frozen. pAkt was examined via Western blotting. Data obtained from densitometry were presented as percent of Co (100%) and expressed as mean ± SE, n = 4 in each group. dP < 0.01 vs ANP treatment; fP < 0.001 vs Co treatment. B: Animals were treated as described under A. After 24 h ischemia livers were homogenized and caspase-3 activity was determined as described before. Data were expressed as percent of caspase-3 activity in untreated livers (Co, 100%) and mean ± SE, n = 4 in each group. bP < 0.01 vs WM treatment.
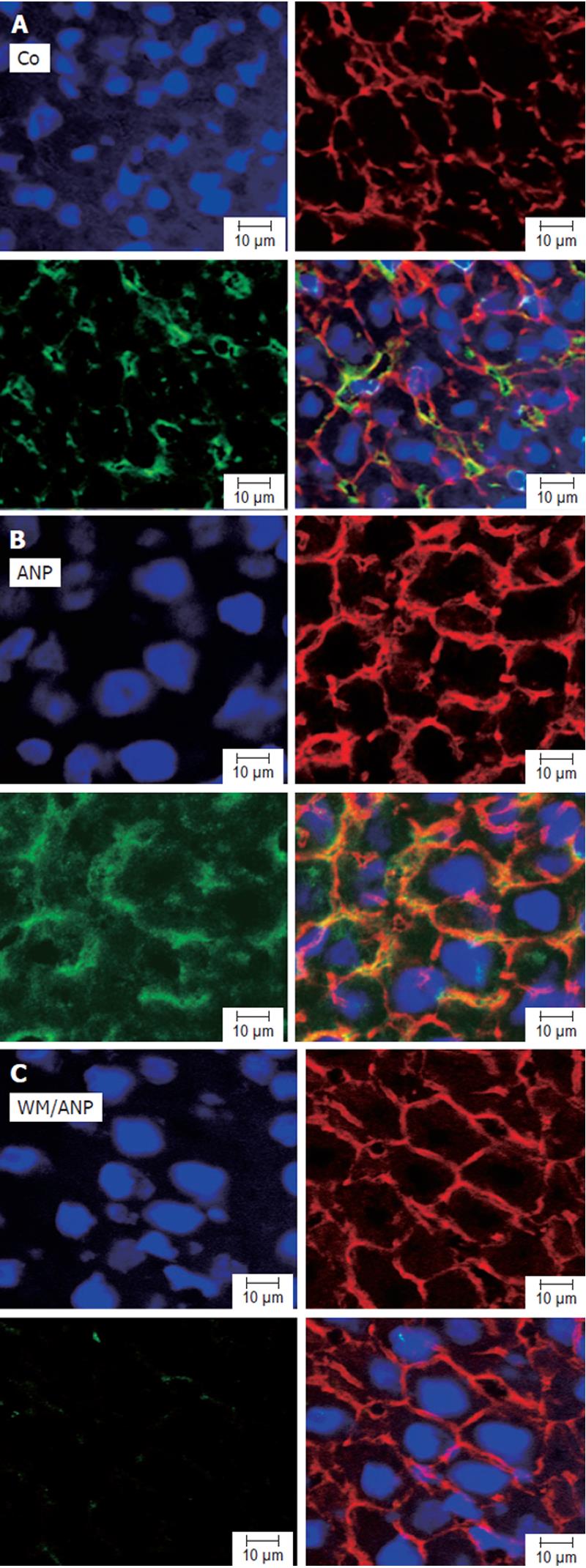
Figure 3 Effect of ANP-preconditioning on distribution and amount of pAkt in liver by confocal microscopy.
Animals were infused with NaCl (Co, A), ANP (B), or a combination of ANP and wortmannin (WM/ANP, C) for 20 min. Livers were snap-frozen, cut into 6 µm slices and stained with rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin (F-actin, cytoskeleton, red), HOECHST dye (nuclei, blue), and anti-pAkt antibody, followed by incubation with Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse antibody (green) as described before. Liver sections were observed under confocal laser microscope (×63 amplification).
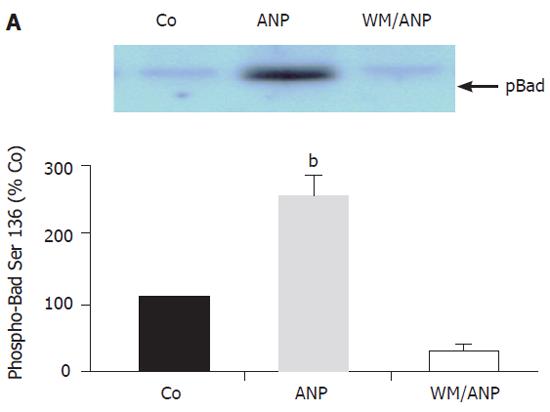
Figure 4 Effect of ANP-preconditioning on phosphorylation of Bad at Ser136. After intravenous infusion of NaCl (Co), ANP (5 μg/kg), or a combination of ANP and wortmannin (WM/ANP) for 20 min livers were excised and snap frozen.
Homogenized livers were immunoprecipitated using anti-Bad antibody. Examination of pBad (Ser136) was done via Western blotting. Data obtained by densitometry were presented as mean ± SE, n = 4 in each group. Co was set as 100%. bP < 0.001 vs control.
Figure 5 Effect of ANP pretreatment on phosphorylation of Bad at Ser112 and PKA-activity.
A: Animals received an intravenous infusion of NaCl (Co) or ANP (5 μg/kg) for 20 min. Homogenized livers were immunoprecipitated using anti-Bad antibody. Examination of phospho-Bad (Ser112) was done via Western blotting. Data obtained in densitometric analysis were presented as mean ± SE, n = 3 in each group. Co was set as 100%. B: PKA activity was determined in liver homogenates used under (A) by in vitro phosphorylation as described. Results were expressed as percent of PKA activity in untreated livers and mean ± SE, n = 4 in each group.
- Citation: Grutzner U, Keller M, Bach M, Kiemer AK, Meissner H, Bilzer M, Zahler S, Gerbes AL, Vollmar AM. PI 3-kinase pathway is responsible for antiapoptotic effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in rat liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(7): 1049-1055
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i7/1049.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i7.1049