Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2006; 12(6): 874-879
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.874
Published online Feb 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.874
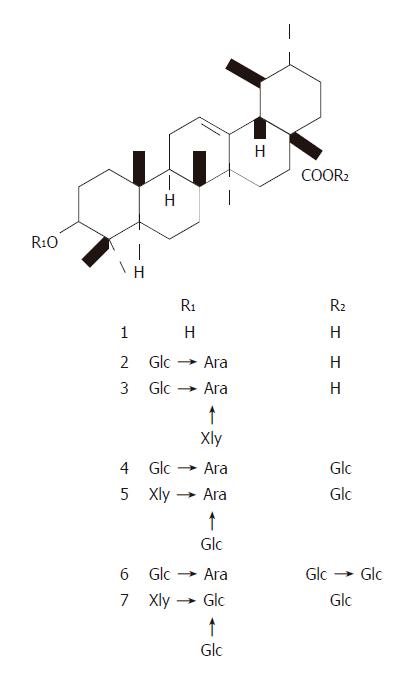
Figure 1 Structures of UA and its derivatives.
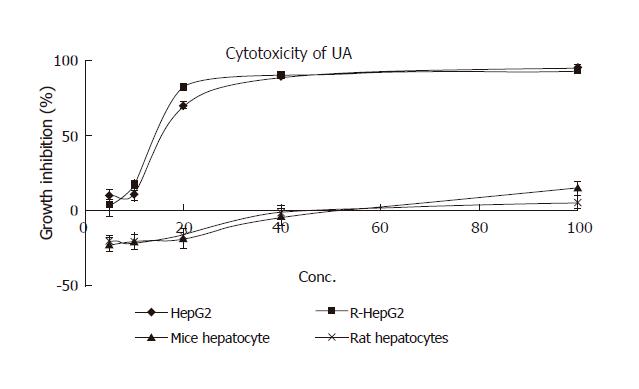
Figure 2 Cytotoxicity of UA to a panel of hepatocytes.
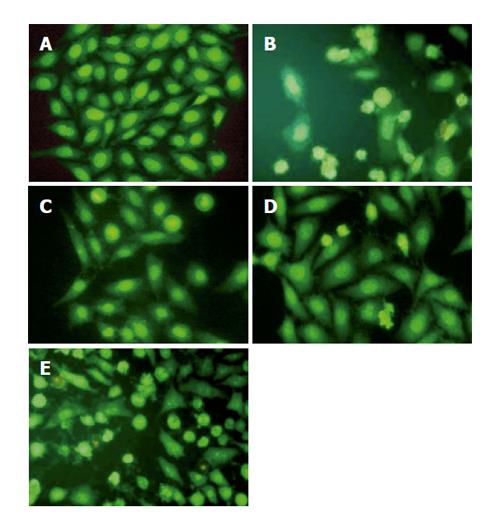
Figure 3 Morphological changes of HepG2 cells in response to harringtonin and UA.
Cells were stained with AO/EB and observed under an inverted Leica fluorescence 40×10 microscope. A: Normal HepG2 cells; B: harringtonin (20 μmol/L) for 24 h; C-E: UA (20 μmol/L) for 6, 12, and 24 h, respectively.
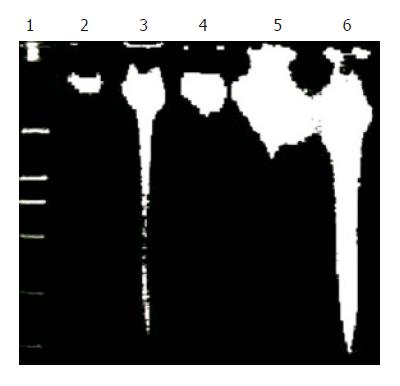
Figure 4 Induction of time-dependent fragmentation of nuclear DNA by harringtonin and UA.
Genomic DNA of the treated cells was collected at different time points during the incubation. Lane 1: DNA marker (DL-2000); lane 3: harringtonin (20 μmol/L) for 24 h; lanes 2, 4–6: UA (20 μmol/L) for 0, 6, 12, and 24 h, respectively.
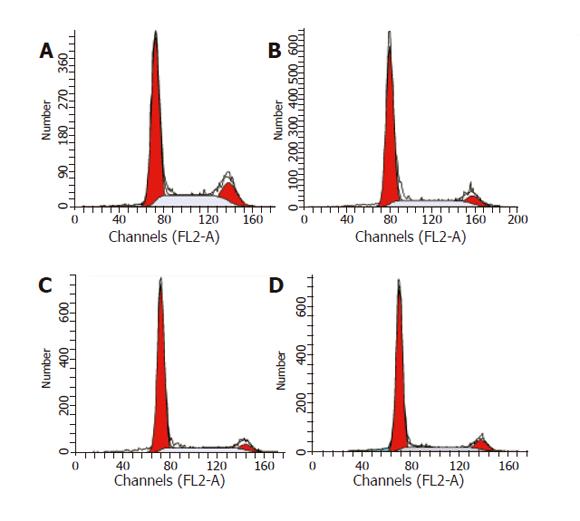
Figure 5 Cell cycle analysis of HepG2 cells treated with UA (20 μmol/L) for 0 (A), 6 (B), 12 (C), and 24 h (D), respectively.
Cells were stained with PI and analyzed by flow cytometry.
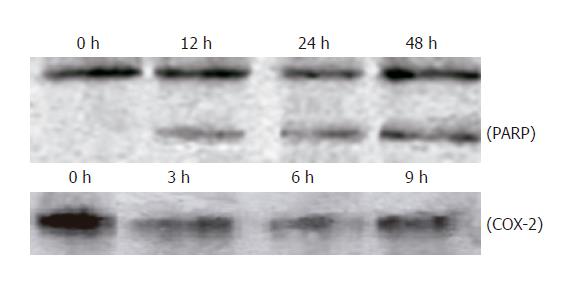
Figure 6 Cleavage of PARP and downregulation of COX-2 protein expression in HepG2 cells treated with UA.
Cellular lysate protein (23 μg/lane) was loaded for 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and subsequently transferred onto nitrocellulose. Immunoblots were probed with antibody specific for PARP and COX-2 protein. Lysates were from HepG2 cells treated with 20 μmol/L UA for indicated times.
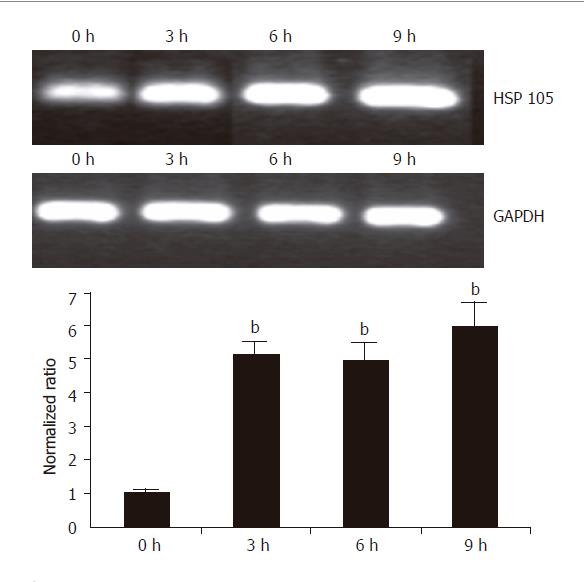
Figure 7 RT-PCR and real time PCR analysis of up-regulated HSP 105 gene in HepG2 cells in response to treatment with UA.
HepG2 cells were treated with 20 μmol/L UA for 0, 3, 6, and 9 h. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to semi-quantitative and quantitative RT-PCR analysis. GAPDH was used as a control. For quantitative analysis, data shown are mean±SD. bP<0.001 vs control, n = 3.
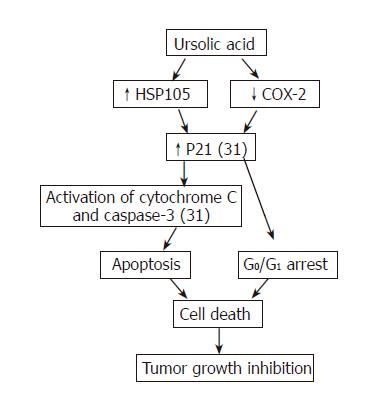
Figure 8 Summary of current understanding of cytotoxicity of UA to hepatoma cells.
Functions with reference number represent known mechanism and bold words without reference number represent the mechanism revealed in our study.
- Citation: Tian Z, Lin G, Zheng RX, Huang F, Yang MS, Xiao PG. Anti-hepatoma activity and mechanism of ursolic acid and its derivatives isolated from Aralia decaisneana. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(6): 874-879
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i6/874.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.874