Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2006; 12(5): 716-722
Published online Feb 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i5.716
Published online Feb 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i5.716
Figure 1 No increase of COX and iNOS expression levels by IL-1β.
(A) The cultured cat ESMCs were treated with IL-1β for 18 h at each dose scale. The COX-1 and COX-2 expression levels were not altered by IL-1β at concentrations up to 50 ng/mL. (B) The IL-1β (25 ng/mL) treatment also failed to elevate the level after 24 h. (C) iNOS expression was unaffected by IL-1β.
Figure 2 Concentration- and time-dependent activation of MAP kinases after IL-1β treatment.
(A) To obtain dose-dependent course of p44/42 MAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase, the cat ESMCs were treated with IL-1β for 3 and 18 h, respectively. The levels of p44/42 MAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase phosphorylation were increased above a dose of 10 ng/mL, which was maintained up to 50 ng/mL. (B) After treatment the cells with IL-1β (25 ng/mL), the level of p44/42 MAP kinase phosphorylation reached a maximum within 3 h with a subsequent decrease to the basal level (upper panel). The phosphorylated forms of p38 MAP kinase were increased within 12 h, which were sustained to 24 h.
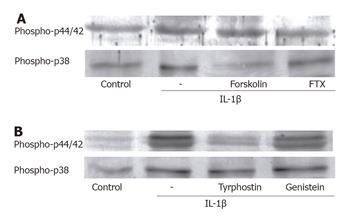
Figure 3 Relation of Gi protein and tyrosine kinase with activation of p44/42 MAP kinase, and negative regulation of p38 MAP kinase by adenylate cyclase.
(A) Pretreatment with the pertussis toxin (100 ng/mL, 24 h) decreased the density of phosphorylated p44/42 MAP kinase only. On the other hand, forskolin (10 μmol/L) attenuated p38 MAP kinase phosphorylation by IL-1β. (B) The receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, tyrphostin 51 (30 μmol/L), markedly reduced the IL-1β-induced phosphorylation of p44/42 MAP kinase. The activation of p38 MAP kinase was unrelated to the tyrosine kinases.
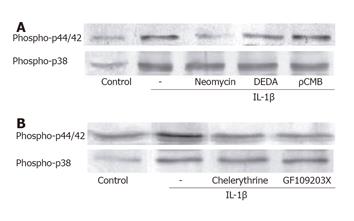
Figure 4 IL-1β-induced activation of p44/42 MAP kinase is mediated by PLC and PKC.
(A) Neomycin (10 μmol/L, 1 h) decreased the phosphorylated forms of p44/42 MAP kinase. DEDA (10 μmol/L, 1 h) and ρCMB (10 μmol/L, 1 h) had no effect on the IL-1β-induced activation of p44/42 MAP kinase. (B) PKC inhibitors chelerythrine (10 μmol/L, 1 h) and GF109203X (10 μmol/L, 1 h) decreased the active form of p44/42 MAP kinase. All the phospholipase inhibitors and PKC inhibitors failed to regulate the activation of p38 MAP kinase by IL-1β.
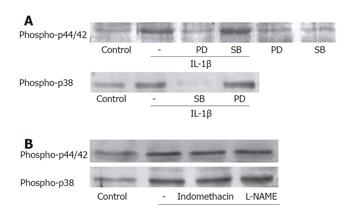
Figure 5 MAP kinase activation by IL-1β was not affected by other kind of MAP kinase, COX and iNOS.
(A) MEK inhibitor PD98059 (10 μmol/L, 1 h) reduced the level of p44/42 MAP kinase phosphorylation by IL-1β. SB202190 (30 μmol/L, 1 h), p38 MAP kinase inhibitor, had no effect on the p44/42 MAPK phosphorylation, which blocked p38 MAP kinase activation. (B) Indomethacin (10 μmol/L) and L-NAME (10 μmol/L) had no effect on the activations of p44/42 MAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase by IL-1β.
- Citation: Lee TS, Song HJ, Jeong JH, Min YS, Shin CY, Sohn UD. IL-1β activates p44/42 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases via different pathways in cat esophageal smooth muscle cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(5): 716-722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i5/716.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i5.716