Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2006; 12(40): 6531-6535
Published online Oct 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i40.6531
Published online Oct 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i40.6531
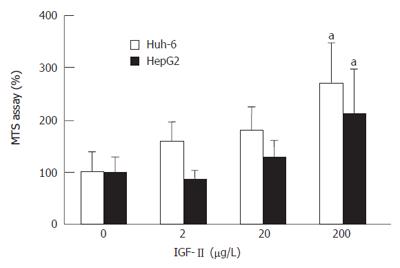
Figure 1 IGF-II stimulated proliferation of hepatoblastoma cells.
IGF-II was added to the medium without serum, followed by MTS assay, a modified method of MTT assay (aP < 0.05).
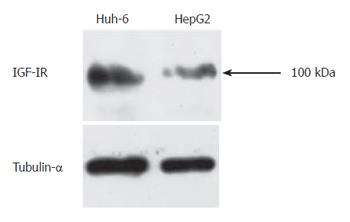
Figure 2 Western blot analysis clearly shows specific bands to IGF-IR.
Protein was isolated 72 h after stimulation with IGF-II (200 μg/L). The same membrane was reprobed with anti-Tubulin-α antibody to confirm an equal amount of protein loadings.
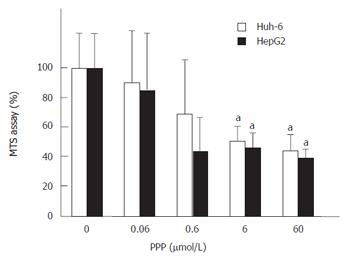
Figure 3 PPP was added to the medium 30 min prior to the stimulation with IGF-II (200 μg/L) and suppressed proliferation of Huh-6 and HepG2 (aP < 0.
05).
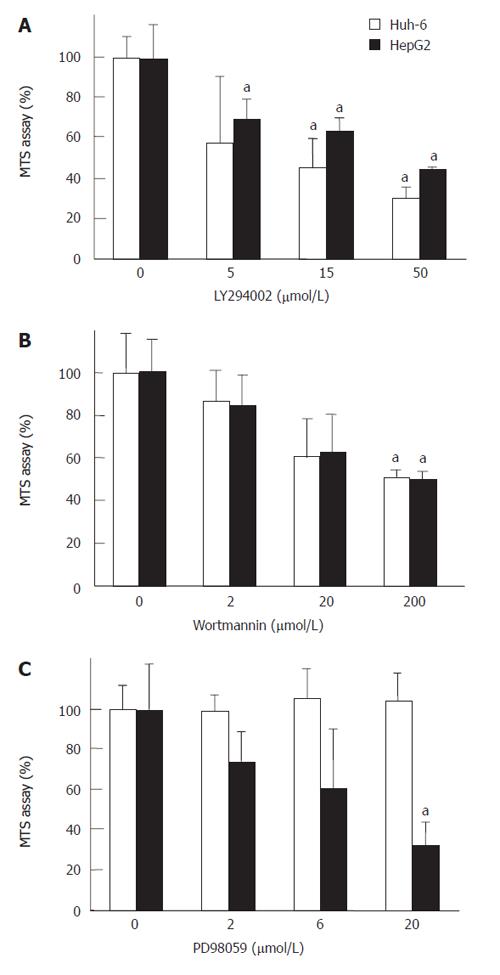
Figure 4 LY294002 or Wortmannin, selective inhibitors of PI3 kinase, or PD98059, a selective inhibitor of MAP kinase, was added to the medium 30 min prior to the stimulation with IGF-II (200 μg/L).
LY294002 (A) and Wortmannin (B) suppressed the proliferation of Huh-6 and HepG while PD98059 suppressed HepG2 (C)
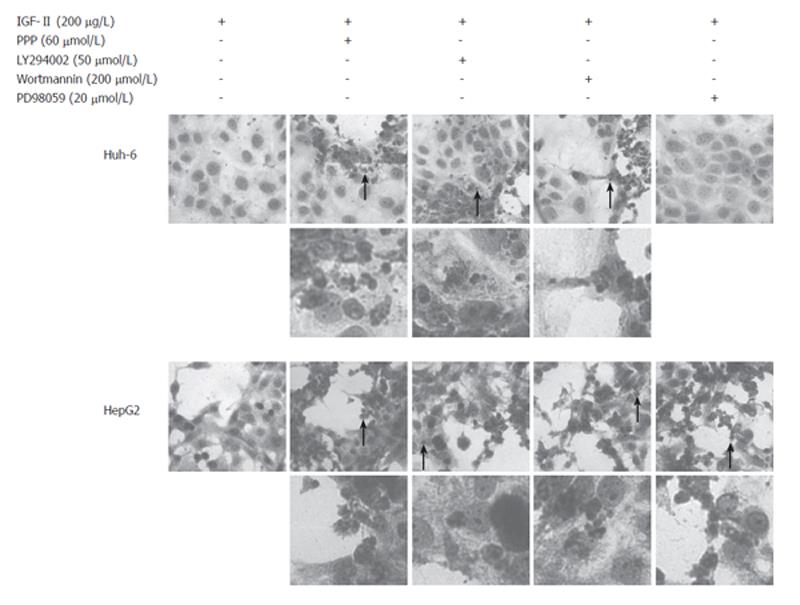
Figure 5 Huh-6 and HepG2 dead due to apoptosis.
HE staining was performed to analyze morphological changes after addition of inhibitors. Many Huh-6 cells were dead treated with PPP (60 μmol/L), LY294002 (50 μmol/L), or Wortmannin (200 μmol/L) while HepG2 with PPP, LY294002, Wortmannin, or PD98059 (20 μmol/L). Most of the dead cells had pyknotic or fragmented nuclei (arrows), suggesting apoptosis. Areas indicated by arrows were magnified (x 400).
- Citation: Tomizawa M, Saisho H. Signaling pathway of insulin-like growth factor-II as a target of molecular therapy for hepatoblastoma. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(40): 6531-6535
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i40/6531.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i40.6531