Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2006; 12(36): 5909-5912
Published online Sep 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5909
Published online Sep 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5909
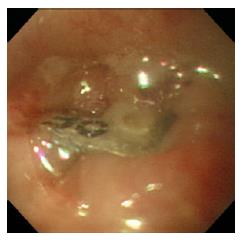
Figure 1 Endoscopic image showing a press-through-pack impacted in the upper esophageal wall.
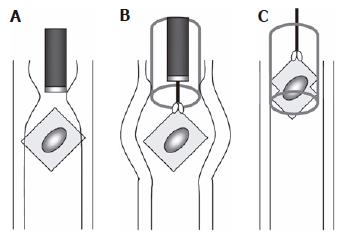
Figure 2 Method for removal of a press-through-pack impacted in the upper esophagus.
A: The press-through-pack was located using a diagnostic endoscope; B: an overtube was inserted and resulted in relaxation of the upper esophagus, which enabled the impacted press-through-pack to be moved; C: forceful pulling of the press-through-pack using forceps caused the edges of the PTP to bend, enabling it to enter the overtube.
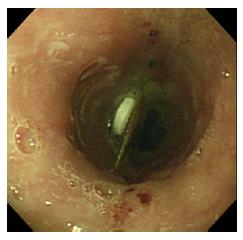
Figure 3 Endoscopic image showing distal relocation of a press-through-pack that was previously impacted and immovable.
Erosions proximal to the press-through-pack indicate the site at which the press-through-pack was impacted until insertion of the overtube.
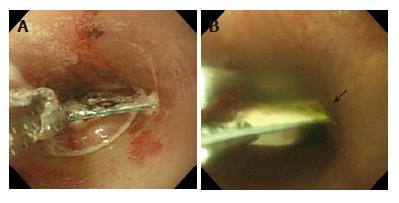
Figure 4 A: Endoscopic image showing forceful retraction of the press-through-pack by a forceps; B shows how the edges of the press-through-pack were bent (arrow) during entry into the overtube.
- Citation: Seo YS, Park JJ, Kim JH, Kim JY, Yeon JE, Kim JS, Byun KS, Bak YT. Removal of press-through-packs impacted in the upper esophagus using an overtube. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(36): 5909-5912
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i36/5909.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5909