Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2006; 12(35): 5593-5598
Published online Sep 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i35.5593
Published online Sep 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i35.5593
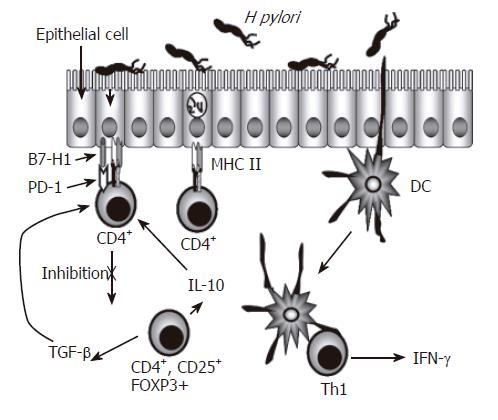
Figure 1 Regulation of CD4+ T Cells During H pylori Infection.
CD4+ T cell numbers increase in the gastric lamina propria of individuals infected with H pylori. These cells are predominantly Th1 cells characterized by their production of IFN-γ. Because the epithelium separates H pylori from CD4+ T cells, and also expresses key proteins associated with antigen presenting cells, the gastric epithelium, in addition to dendritic cells, could be involved in the presentation of antigens to these CD4+ T cells. The expression of inhibitory B7 related molecules along with CD4+ T cells with a regulatory T cell phenotype could be playing a role in limiting the function of effector CD4+ T cells.
-
Citation: Suarez G, Reyes VE, Beswick EJ. Immune response to
H pylori . World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(35): 5593-5598 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i35/5593.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i35.5593