Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2006; 12(33): 5326-5330
Published online Sep 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i33.5326
Published online Sep 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i33.5326
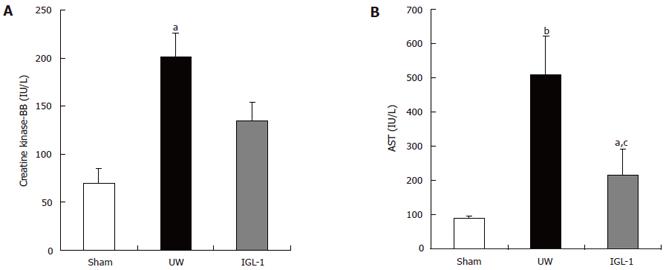
Figure 1 Creatine kinase-BB isoenzyme (A) and aspartate aminotransferase (B) activities in the preservation solution purged from the liver grafts before reperfusion.
Data are expressed as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs sham; bP < 0.01 vs sham; cP < 0.05 vs UW.
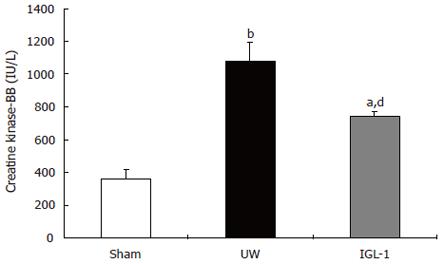
Figure 2 Serum creatine kinase-BB isoenzyme activity 2 h after reperfusion.
Data are expressed as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs sham; bP < 0.01 vs sham; dP < 0.01 vs UW.
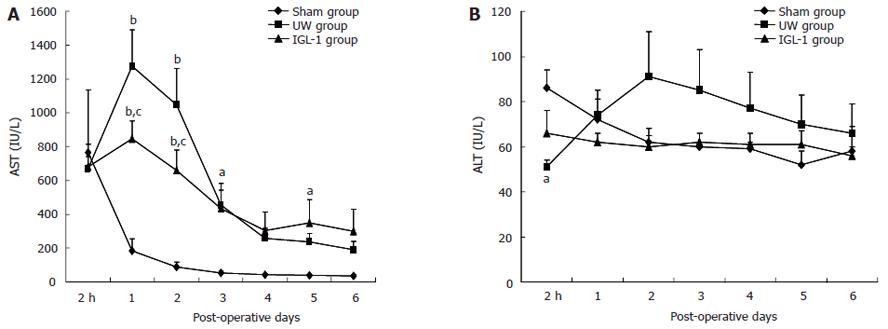
Figure 3 Serum aspartate aminotransferase (A) and alanine aminotransferase (B) activities after liver transplantation.
Data are expressed as mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs sham; bP < 0.01 vs sham; cP < 0.05 vs UW.
Figure 4 Light micro-graphs of liver after vascular dissection (A), liver of sham group (B) and liver grafts preserved in UW (C) and IGL-1 (D) solutions (HE x 400).
- Citation: Abdennebi HB, Elrassi Z, Scoazec JY, Steghens JP, Ramella-Virieux S, Boillot O. Evaluation of IGL-1 preservation solution using an orthotopic liver transplantation model. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(33): 5326-5330
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i33/5326.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i33.5326