Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2006; 12(32): 5160-5167
Published online Aug 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i32.5160
Published online Aug 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i32.5160
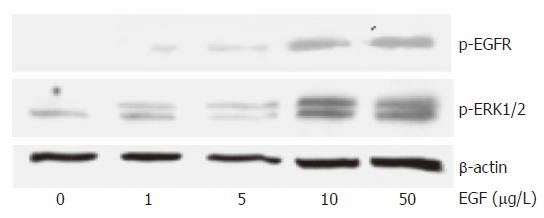
Figure 1 EGF-induced EGFR- and ERK1/2-activation in HCC cells.
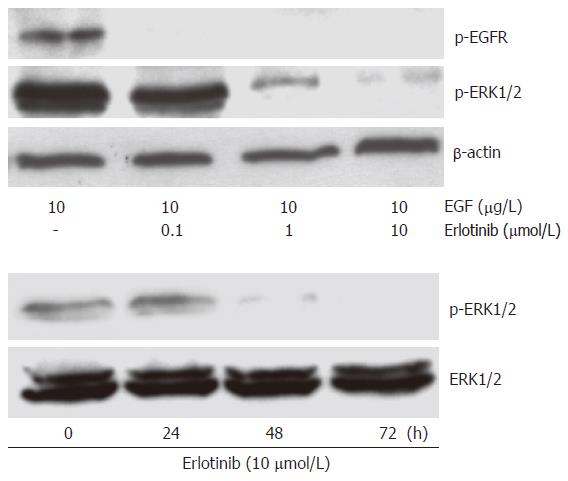
Figure 2 Erlotinib inhibited EGFR (A) and ERK1/2 (B) activation in HCC cells.
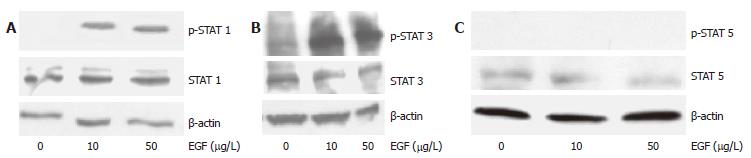
Figure 3 STAT-expression and EGF-induced activation in HCC cells.
EGF induced STAT activation could be shown for STATs 1 and 3 (A and B) but not in the case of STAT5 (C).
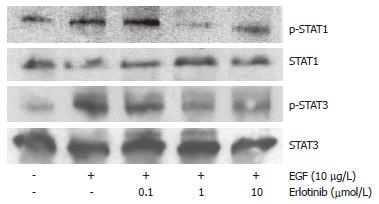
Figure 4 Erlotinib inhibited STAT-activation in HCC cells.
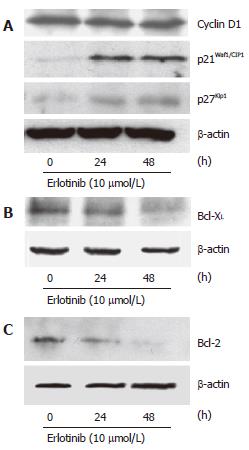
Figure 5 Erlotinib modulated the expression of cell cycle regulators (A) and antiapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family (B and C).
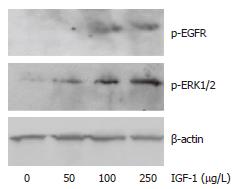
Figure 6 IGF-1-induced activation of ERK1/2 and transactivation of the EGFR.
Figure 7 Erlotinib inhibited EGF and/or IGF-1-induced ERK1/2-activation and EGFR/IGF-1R cross talk.
Figure 8 Erlotinib did not influence IGF-1R expression or activation.
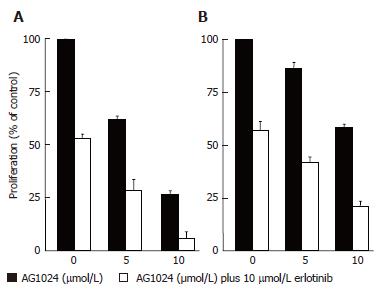
Figure 9 Antiproliferative effects of erlotinib plus AG1024.
A: HepG2; B: Huh-7.
- Citation: Huether A, Höpfner M, Sutter AP, Baradari V, Schuppan D, Scherübl H. Signaling pathways involved in the inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor by erlotinib in hepatocellular cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(32): 5160-5167
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i32/5160.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i32.5160