Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2006; 12(30): 4914-4917
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4914
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4914
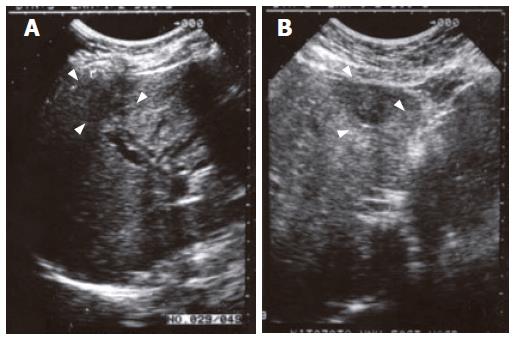
Figure 1 Ultrasonography findings of the liver.
A: Dilatation of the intrahepatic ducts and a hypoechoic mass in the right lower anterior segment; B: A heterogeneous mass in the inner left segment.
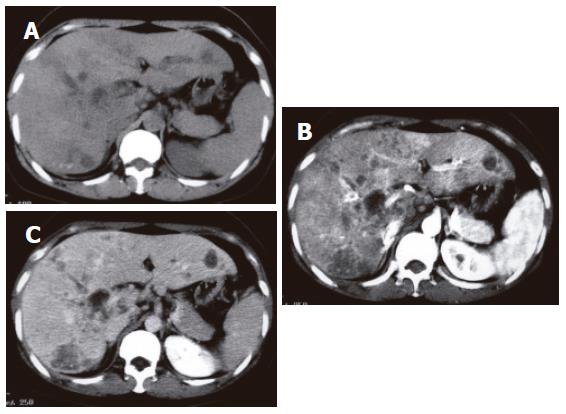
Figure 2 Abdominal computed tomography (CT).
A: Plain CT images show intrahepatic ductal dilatation, micro-calcifications, and multiple hypodense lesions in the liver; B: Contrast CT image (early phase) shows clearly delineated hypodense lesions; C: Late phase CT image shows slightly enhanced hypodense lesions.
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS).
A: Soft tissue masses at the liver hilum of the hepatic duct; B: Circumferential thickening of the common hepatic duct.
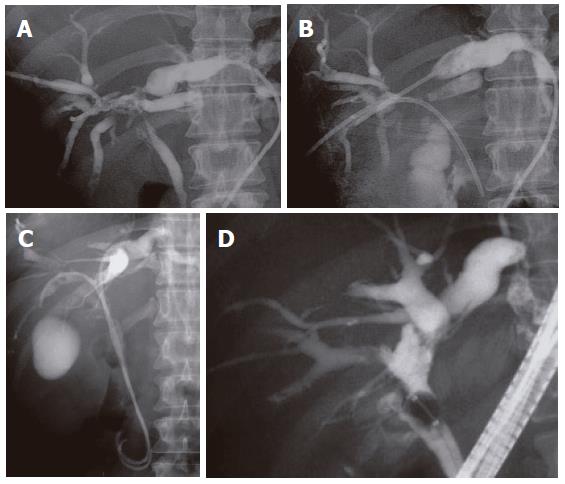
Figure 4 Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography examination.
A: The common hepatic bile duct was narrowed over a 2 cm section, and strictures and irregularities of the hepatic bile duct at the liver hilum were revealed; B: The hepatic ducts at the liver hilum were clumped with strictures of the feeding branches from each section of the liver.
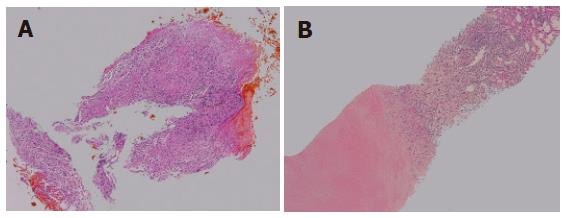
Figure 5 Histological findings of the biopsy specimen stained with HE.
A: Photomicrograph of an endoscopic biopsy specimen from the common hepatic duct showing granulomas with epithelioid cells; B: Photomicrograph of a biopsy specimen from a hypoechoic mass in the liver showing focal caseous necrosis surrounded by granuloma.
Figure 6 ERC following anti-tuberculosis therapy showing marked irregularity of the hepatic ducts and strictures of common hepatic duct.
A: PTBD tubes were inserted via the B8 and B3 branches; B: The PTBD tube from the B5 branch was inserted into the common bile duct; C: EBD tubes were inserted into both hepatic lobes; D: The strictures of the hepatic duct s were recanalized.
- Citation: Iwai T, Kida M, Kida Y, Shikama N, Shibuya A, Saigenji K. Biliary tuberculosis causing cicatricial stenosis after oral anti-tuberculosis therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(30): 4914-4917
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i30/4914.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4914