Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2006; 12(30): 4902-4905
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4902
Published online Aug 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4902
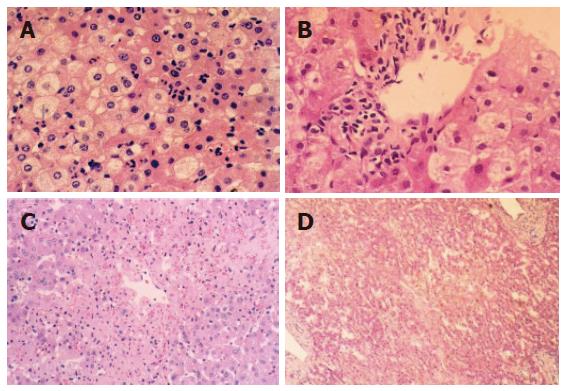
Figure 1 Cytoplasm loosening, cell edema, focal vacuole degeneration after reperfusion (10 × 10) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for < 30 min (A); obvious cell edema, ballooning-like degeneration after reperfusion (40 × 10) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 30 min (B); focal necrosis around central lobule area after reperfusion (10 × 10) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 45 min (C); plaque-like area necrosis after reperfusion (40 × 10) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 60 min (D).
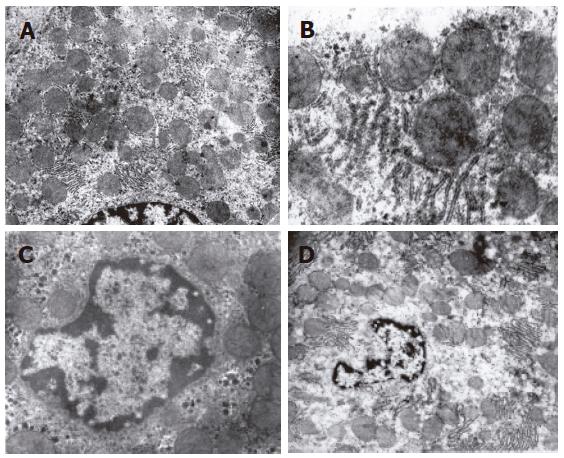
Figure 2 Swollen mitochondria, ruptured crista, rough endoplasmic reticulum degranulation (× 15 000) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 30 min (A); phanero-swollen mitochondria and nuclear chromosome margination, and karyopyknosis after reperfusion (× 10 000) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 45 min (B and C); significant swollen mitochondria, crista extinction, nuclear membrane rupture, karyolysis and karyorrhexis after reperfusion (× 5000) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 60 min (D).
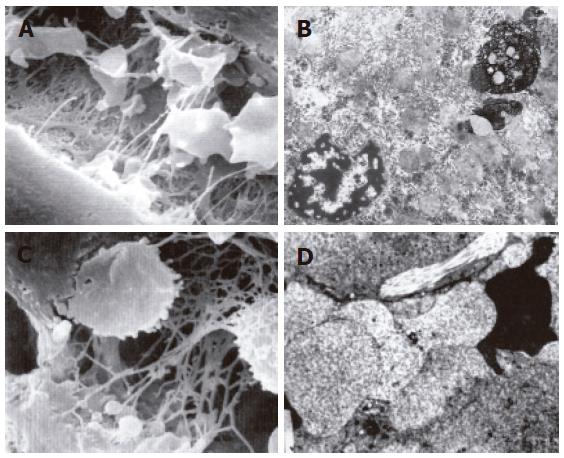
Figure 3 Cytoplasmic blebs and irregular endothelial sieve plate in some sinusoids after reperfusion (scanning electron microscope × 6000) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 45 min (A); apoptosis and necrosis of hepatocytes after reperfusion (× 8000) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 60 min (B); cytoplamic blebs, reticular cellulose and hemocytes after reperfusion (scanning electron microscope × 6000) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 60 min (C); bleb or ballooning like swollen endothelial cells, blocked sinusoids and irreversible microcirculation disturbance after reperfusion (× 5000) in the group undergoing warm ischemia injury for 60 min (D).
- Citation: Ma Y, Wang GD, Wu LW, Hu RD. Dynamical changing patterns of histological structure and ultrastructure of liver graft undergoing warm ischemia injury from non-heart-beating donor in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(30): 4902-4905
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i30/4902.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i30.4902