Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2006; 12(25): 4020-4025
Published online Jul 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i25.4020
Published online Jul 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i25.4020
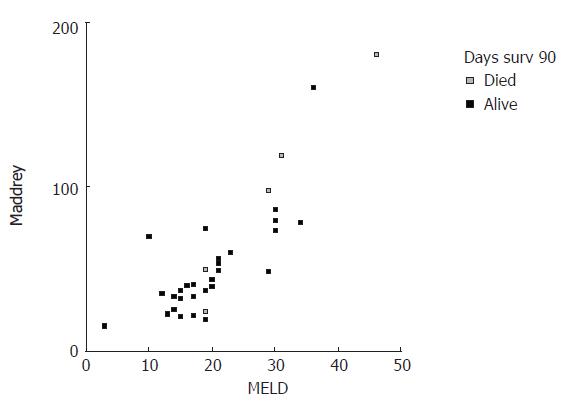
Figure 1 Scatter plot graphed for patient death events within 90 d in correlation with corresponding MELD and DF values.
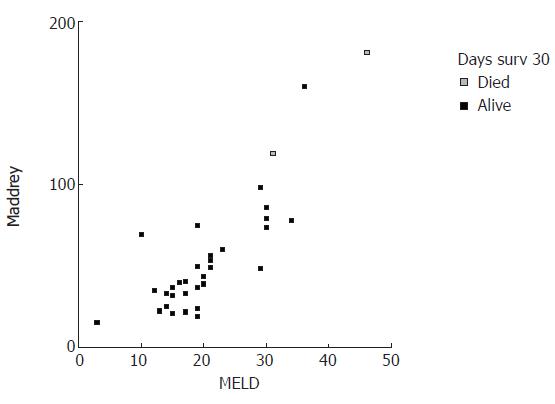
Figure 2 Scatter plot graphed for patient death events within 30 d in correlation with corresponding MELD and DF values.
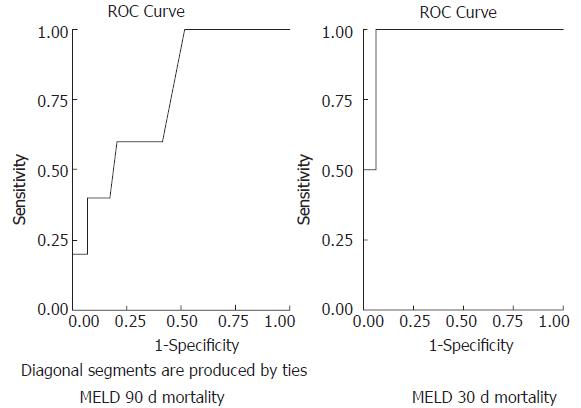
Figure 3 Predicting utility of MELD score in assessing 30- and 90-d mortality rates in alcoholic hepatitis.
Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated and the area under the curve and confidence intervals are indicated.
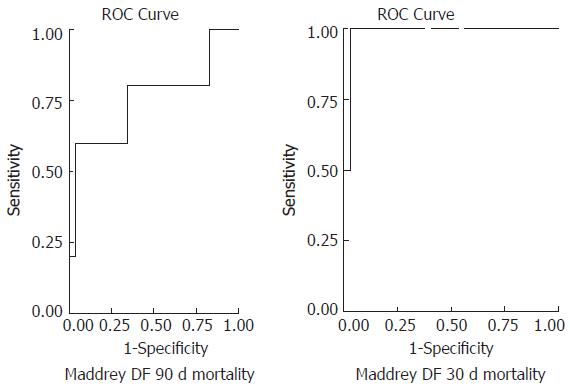
Figure 4 Predicting utility of DF score in assessing 30- and 90-d mortality rates in alcoholic hepatitis.
Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated and the area under the curve and confidence intervals are indicated.
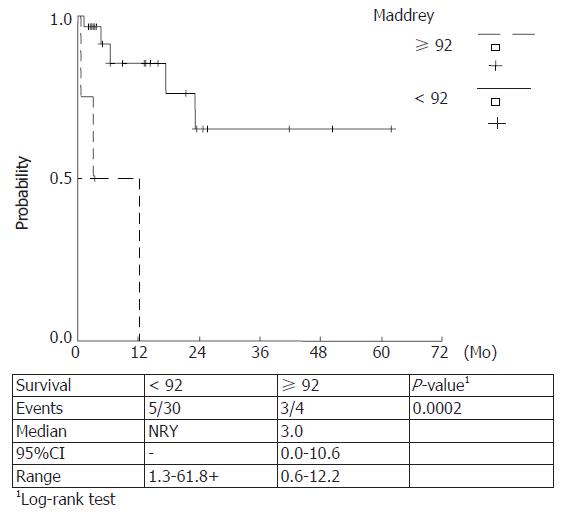
Figure 5 Kaplan Meier survival curves estimated for DF values < 92 and ≥ 92.
Higher score values were correlated with a lower survival (P-value 0.0002).
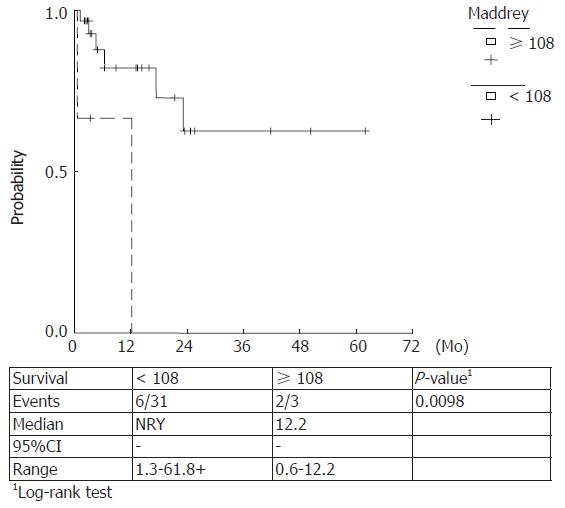
Figure 6 Kaplan Meier survival curves estimated for DF values < 108 and ≥ 108.
Higher score values were correlated with a lower survival (P-value 0.0098).
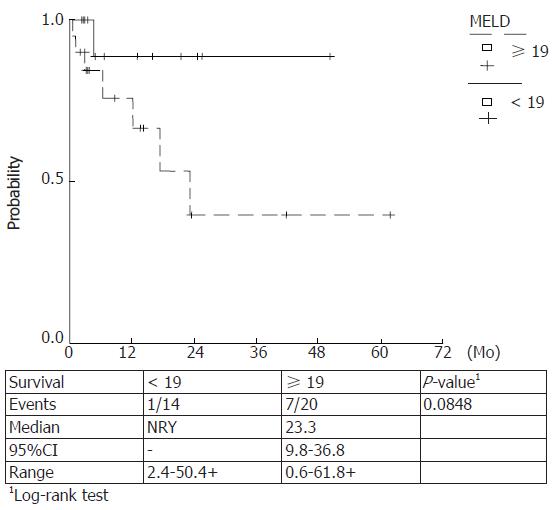
Figure 7 Kaplan Meier survival curves estimated for MELD values < 19 and ≥ 19.
Higher score values were estimated to be correlated with a lower survival (P-value 0.0848).
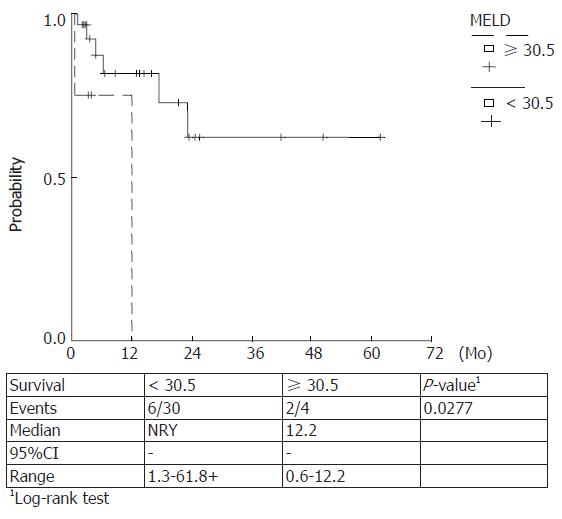
Figure 8 Kaplan Meier survival curves estimated for MELD values < 30.
5 and ≥ 30.5. Higher score values were correlated with a lower survival (P-value 0.0277).
- Citation: Soultati AS, Dourakis SP, Alexopoulou A, Deutsch M, Vasilieva L, Archimandritis AJ. Predicting utility of a model for end stage liver disease in alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(25): 4020-4025
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i25/4020.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i25.4020