Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2006; 12(2): 234-239
Published online Jan 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.234
Published online Jan 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.234
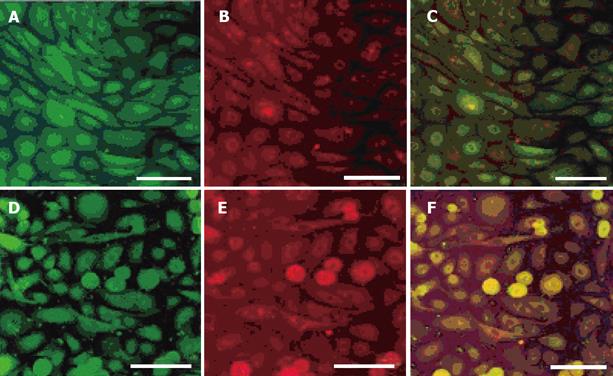
Figure 1 Expression of pepsin, MUC5AC and proton-pump in cultured gastric epithelial cells observed by double immunolabelling.
A confocal microscopic image demonstrates the FITC-positive anti-pepsin-positive cells (A) and Texas Red-positive anti-MUC5AC-positive cells (B) in the same area. The anti-pepsin-positive cells, which co-express MUC5AC, are indicated yellow (C). A confocal microscopic image also demonstrates the FITC-positive anti-pepsin-positive cells (D) and Texas Red-positive anti-proton pump-positive cells (E) in the same area. The anti-pepsin-positive cells which co-express proton pump are indicated yellow (F).Scale bars indicate 100 μm.
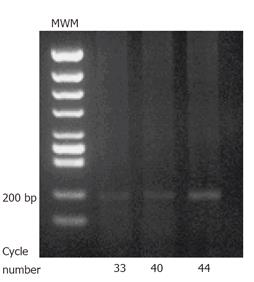
Figure 2 RT-PCR analysis of EPO-R in cultured gastric epithelial cells.
207 bp products are detected. MWM; molecular weight marker.
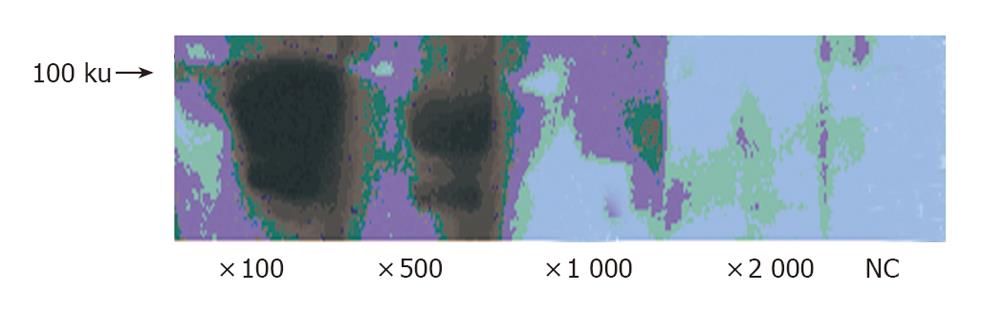
Figure 3 Western blotting analysis of EPO-R in cultured gastric epithelial cells.
EPO-R is detected as a predicted size. The intensity of signals is dependent on anti-EPO-R antibody dilution.
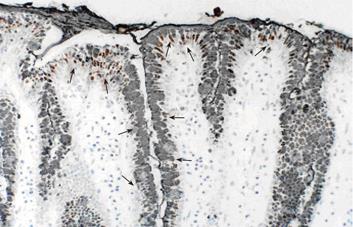
Figure 4 Immunolocalization of EPO-R and MUC5AC on porcine gastric mucosa.
Immunolocalization of EPO-R as well as gastric mucin MUC5AC is detected in epithelial cells. (× 60).
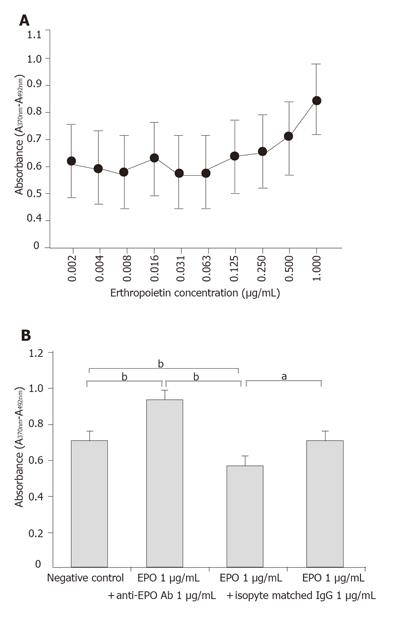
Figure 5 Evaluation of erythropoietin effects on cultured gastric epithelial cells.
(A) BrdU assay shows a dose-dependent effect of EPO on growth stimulation of porcine gastric mucosal epithelial cells. (B) Growth stimulation effects of EPO on gastric mucosal epithelial cells. Treatment with EPO (closed bar) significantly increased cell growth. This effect is inhibited by anti-EPO neutralizing antibody (hatched bar), not by isotype matched IgG (dotted bar). Results are expressed as the means ± SD of six different experiments. aP < 0.05,bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Itoh K, Sawasaki Y, Takeuchi K, Kato S, Imai N, Kato Y, Shibata N, Kobayashi M, Moriguchi Y, Higuchi M, Ishihata F, Sudoh Y, Miura S. Erythropoietin -induced proliferation of gastric mucosal cells. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(2): 234-239
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i2/234.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i2.234