Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2006; 12(18): 2908-2913
Published online May 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i18.2908
Published online May 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i18.2908
Figure 1 Development of chylomicronemia after Triton WR1339 injection.
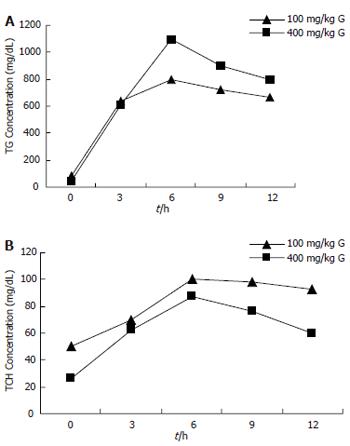
Figure 2 Curves of serum TG and TCH induced by Triton WR 1339 in rats.
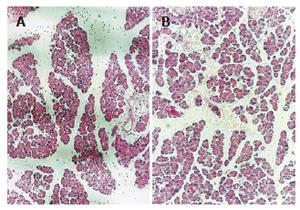
Figure 3 Microscopic pancreatic changes in rats with AP induced by cerulean (A) and hyperlipidemic AP induced by cerulein and Triton WR1339 (B) 6 h after injection (HE × 200).
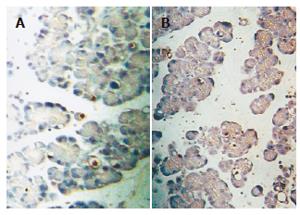
Figure 4 Detection of apoptotic cells by TUNEL in rats with AP induced by cerulein (A) and hyperlipidemic AP induced by cerulean and Triton WR1339 (B) counterstained with hematoxylin (H × 200).
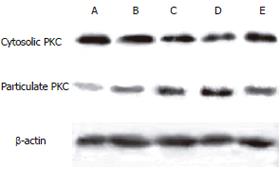
Figure 5 Effects of hyperlipidemia, AP, AP accompanying hyperlipidemia and albumin therapy on PKC membrane translocation detected by Western blot in rats of control group (A), Triton group (B), caerulein group (C), Triton+caerulein group (D), Triton+caerulein+albumin group (E).
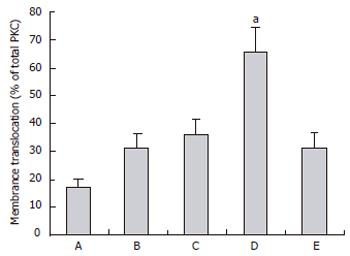
Figure 6 Effects of Triton hyperlipidemia, caerulein pancreatitis, AP with hyperlipidemia and albumin therapy on PKC membrane translocation in rats.
Quantitative analysis of PKC membrane translocation level was detected by Western blot. aP < 0.05 Triton+caerulein group vs caerulein and Triton+caerulein+albumin group (n = 6).
- Citation: Wang YJ, Sun JB, Li F, Zhang SW. Hyperlipidemia intensifies cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis associated with activation of protein kinase C in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(18): 2908-2913
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i18/2908.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i18.2908