Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2006; 12(16): 2487-2496
Published online Apr 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i16.2487
Published online Apr 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i16.2487
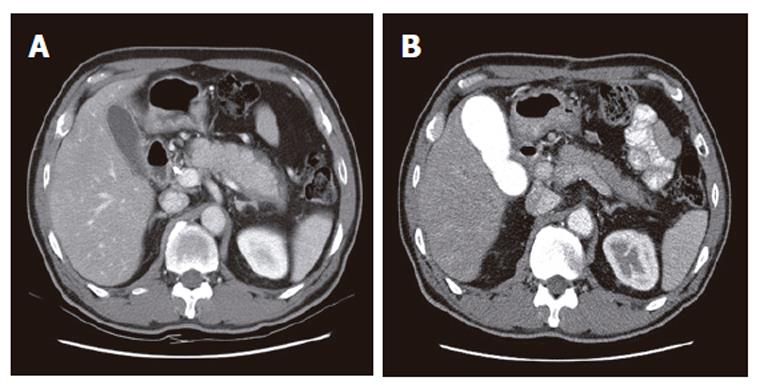
Figure 1 Abdominal CT findings.
A: Diffusely enlarged pancreas without any calcification or stones in a 59 year-old man. A capsule-like low-density rim can also be seen around the pancreas; B: After steroid therapy, the pancreas returned to its normal size and the rim disappeared.
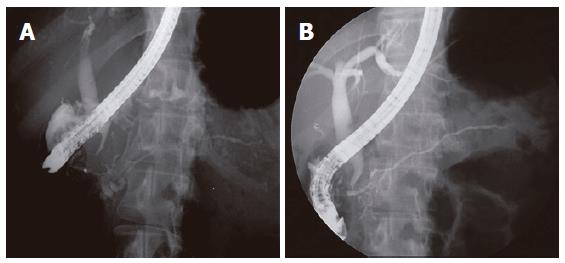
Figure 2 ERCP findings.
A: Diffuse irregular narrowing of more than 2/3 of the entire length of main pancreatic duct noted in the 49 year-old woman; B: After steroid therapy, evidently widening of the main pancreatic duct.
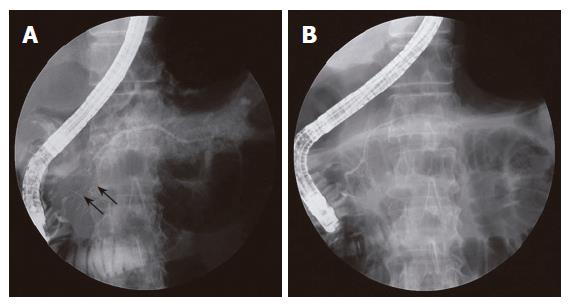
Figure 3 ERCP findings.
A: Segmental narrowing (arrows) of the main pancreatic duct noted at the pancreatic head. The extent of irregular narrowing is less than 1/3 of the entire length of main pancreatic duct; B: Direct pancreatogram revealing a normal-appearing main pancreatic duct following steroid therapy.
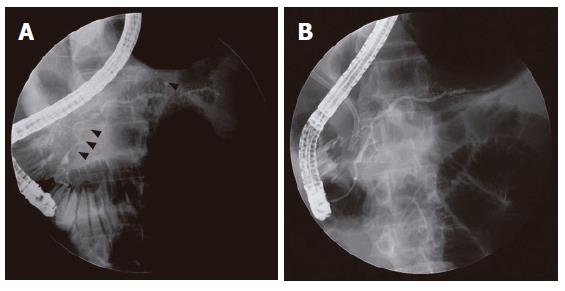
Figure 4 ERCP findings.
A: Segmental irregular narrowing (arrow heads) of the main pancreatic duct that involves the pancreatic head and tail portion is noted in a 53-year-old man; B: After steroid therapy, the narrowing sites on preceding ERCP were resolved. Biliary stenting for narrowing of intrapancreatic common bile duct is noted.
- Citation: Kim KP, Kim MH, Kim JC, Lee SS, Seo DW, Lee SK. Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune chronic pancreatitis revisited. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(16): 2487-2496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i16/2487.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i16.2487