Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2006; 12(15): 2345-2350
Published online Apr 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i15.2345
Published online Apr 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i15.2345
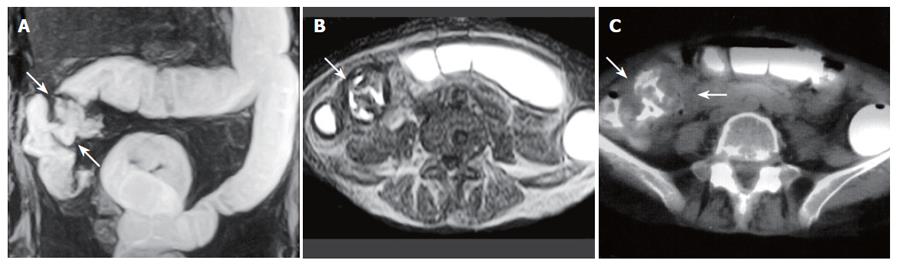
Figure 1 A 59-year-old woman with cecum and ascending colon carcinoma.
A: MR colonography MIP (maximum intensity projection) image showing asymmetrical, irregular wall thickening at the cecum and ascending colon segments (arrows); B: SE T1W axial image; C: axial CT image showing asymmetrical, irregular wall thickening of the ascending colon (arrows).
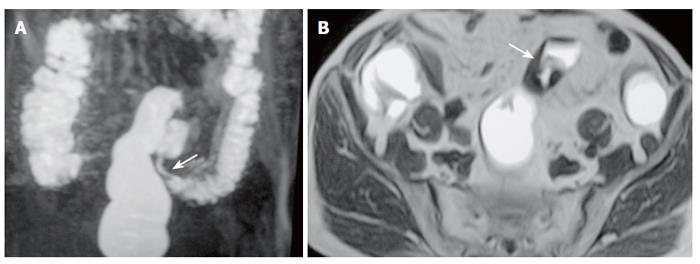
Figure 2 A 77-year-old man with sigmoid carcinoma.
A: MR colonography MIP (maximum intensity projection) image showing asymmetrical, annular wall thickening at the sigmoid colon segment (arrow); B: SE T1W axial image showing asymmetrical, irregular wall thickening of the sigmoid colon (arrow).
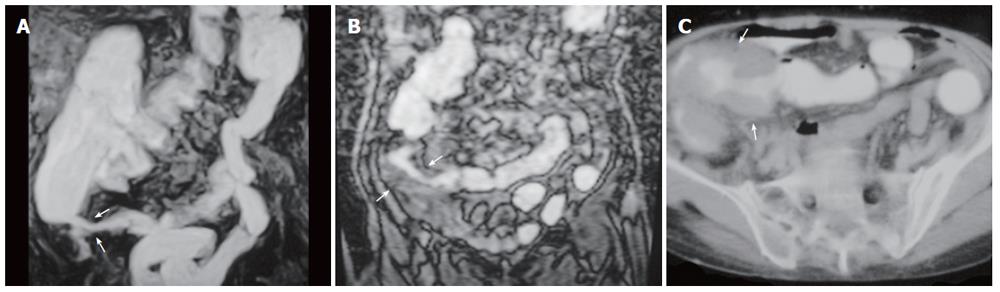
Figure 3 A 63-year-old man with ulcerative colitis.
A: MR colonography MIP (maximum intensity projection) image; B: axial CT image showing haustral flattening at transverse and descending colon segments (arrows); C: SE T1W axial image showing a 0.5-cm polyp at the rectosigmoid junction (arrow).
Figure 4 A 70-year-old man with inflammatory disease in the ileocaecal region.
A: MR colonography MIP (maximum intensity projection) image; B: coronal plane MR colonography raw data image; C: axial CT image showing asymmetrical, irregular wall thickening of the ileocaecal region (arrows) and serpiginous strands extending into soft tissue due to inflammatory disease.
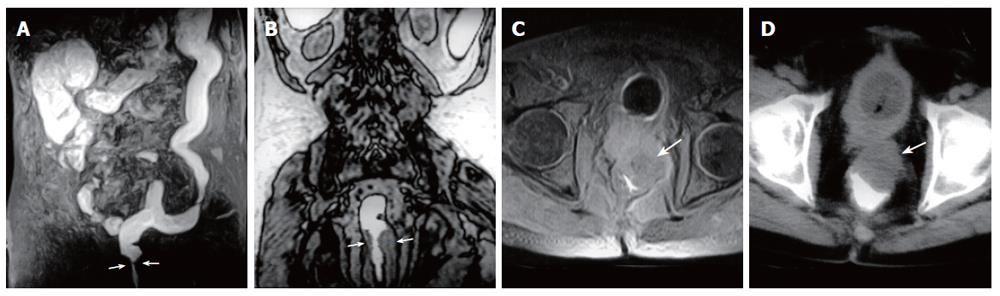
Figure 5 A 63-year-old man with rectum carcinoma invasion to prostate.
A: MR colonography MIP (maximum intensity projection) image showing luminal narrowing at rectum (arrows); B: MR colonography raw data coronal image showing luminal narrowing due to annular thickening of the rectum wall (arrows); C: SE axial T1W image; D: axial CT image showing asymmetric wall thickening at rectum (arrows), and invasion to the fatty tissue arround the mass.
- Citation: Haykir R, Karakose S, Karabacakoglu A, Sahin M, Kayacetin E. Three-dimensional MR and axial CT colonography versus conventional colonoscopy for detection of colon pathologies. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(15): 2345-2350
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i15/2345.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i15.2345