Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2005; 11(9): 1345-1350
Published online Mar 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i9.1345
Published online Mar 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i9.1345
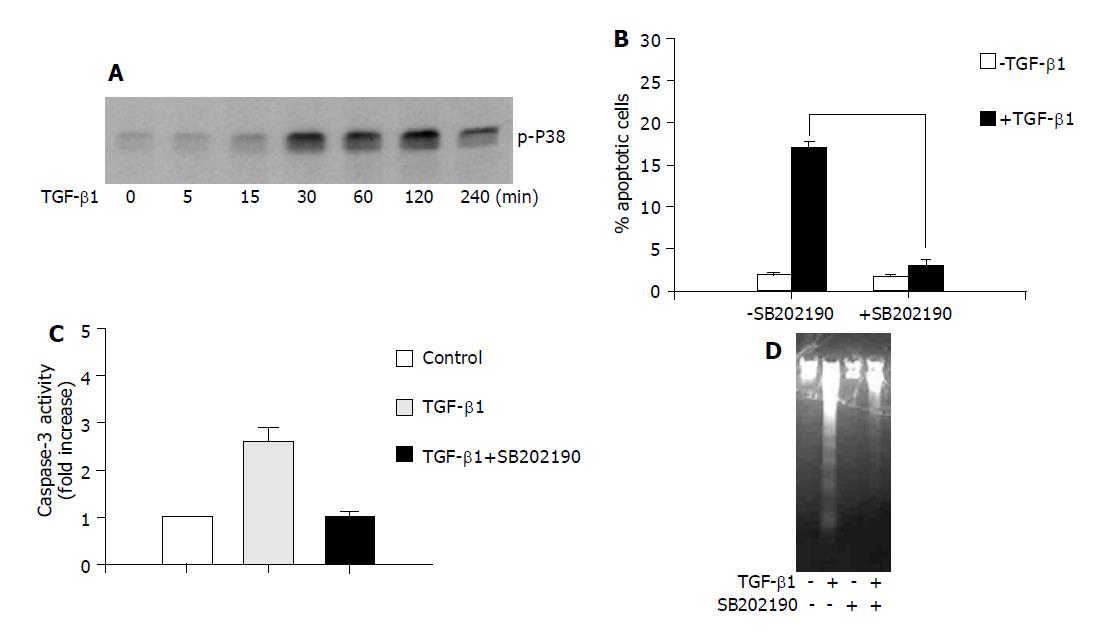
Figure 1 The role of p38 in TGF-β1-induced apoptosis in AML-12 hepatocytes.
A: AML-12 cells were treated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) for the indicated time, and the phosphorylation of p38 was examined with anti phospho-p38 antibody; B, C and D: Cells were treated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) for 24 h in the presence or absence of SB202190 (10 μmol/L). Apoptotic rate was determined by measuring DNA content with flow cytometry analysis (B); the caspase-3 activity (C); and DNA fragmentation assay (D).
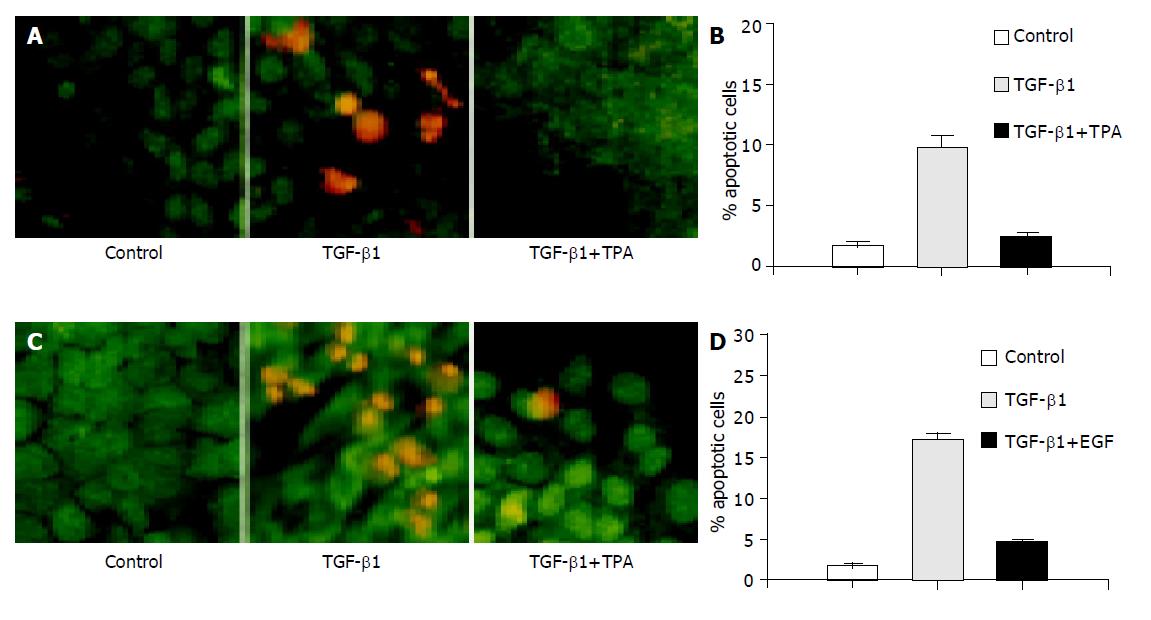
Figure 2 TPA and EGF block TGF-β1-induced apoptosis.
AML-12 cells were incubated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of TPA (50 ng/mL) as indicated for 18 h or in the presence or absence of EGF (50 ng/mL) as indicated for 24 h. A and C: The cells were stained with AO/EB (400×magnifications); B and D: Apoptotic rate was determined by flow cytometry analysis.
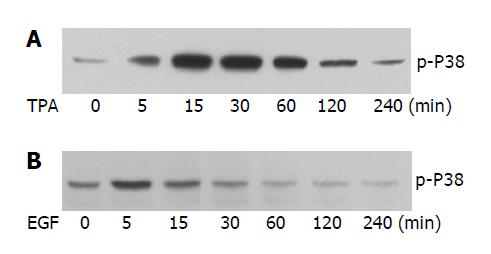
Figure 3 The effect of TPA and EGF on the phosphorylation of P38.
Cells were treated with TPA (50 ng/mL) (A) or EGF (50 ng/mL) (B) for the indicated time. The phosphorylation of p38 was examined with anti phospho-p38 antibody.
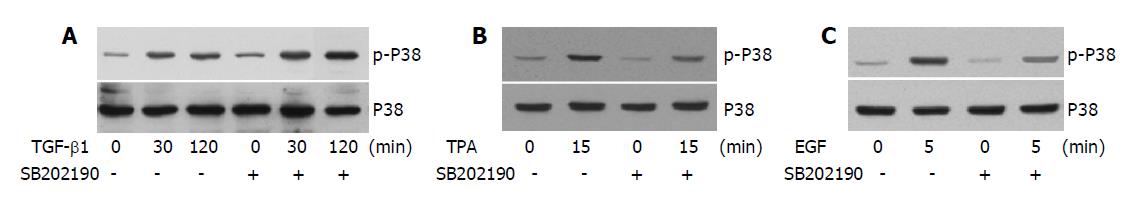
Figure 4 SB202190 distinguishes the differential phosphorylation of P38 induced by TGF-β1, TPA and EGF.
A: AML-12 cells were treated with TGF-β1 (5 ng/mL) for 30 min or 2 h in the presence or absence of SB202190 (10 μmol/L). The phosphorylation of p38 was examined by immunoblotting and the protein level of p38 was examined by reprobing the membrane with anti-p38 antibody after stripping; B and C: Cells were treated with TPA (50 ng/mL) for 15 min (B) or with EGF (50 ng/mL) for 5 min (C) in the presence or absence of SB202190 (10 μmol/L) as indicated. The phosphorylation and the protein level of p38 were examined as in A.
- Citation: Guo LX, Xie H. Differential phosphorylation of p38 induced by apoptotic and anti-apoptotic stimuli in murine hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(9): 1345-1350
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i9/1345.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i9.1345