Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2005; 11(5): 634-640
Published online Feb 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i5.634
Published online Feb 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i5.634
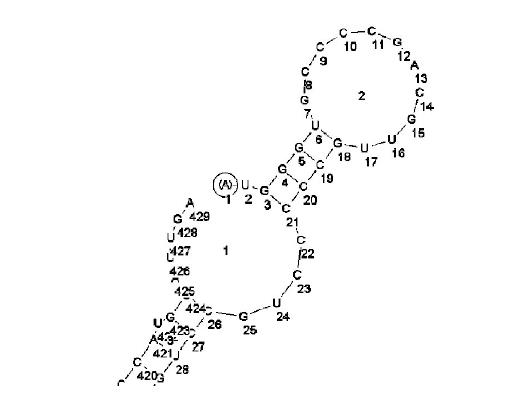
Figure 1 Secondary structure of antisense accessible sites (4-23 bp) of survivin designed only with RNADraw software.
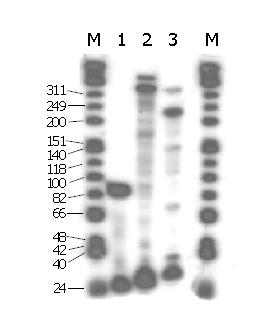
Figure 2 Primer extension analysis for the selection of antisense accessible sites of survivin by random oligonucleotide library/RNase H cleavage method.
M: PhiX174 Hinf I DNA marker. Lane 1: Primer extension positive control; lanes 2-3: Primer extension products of P1 and P2 .
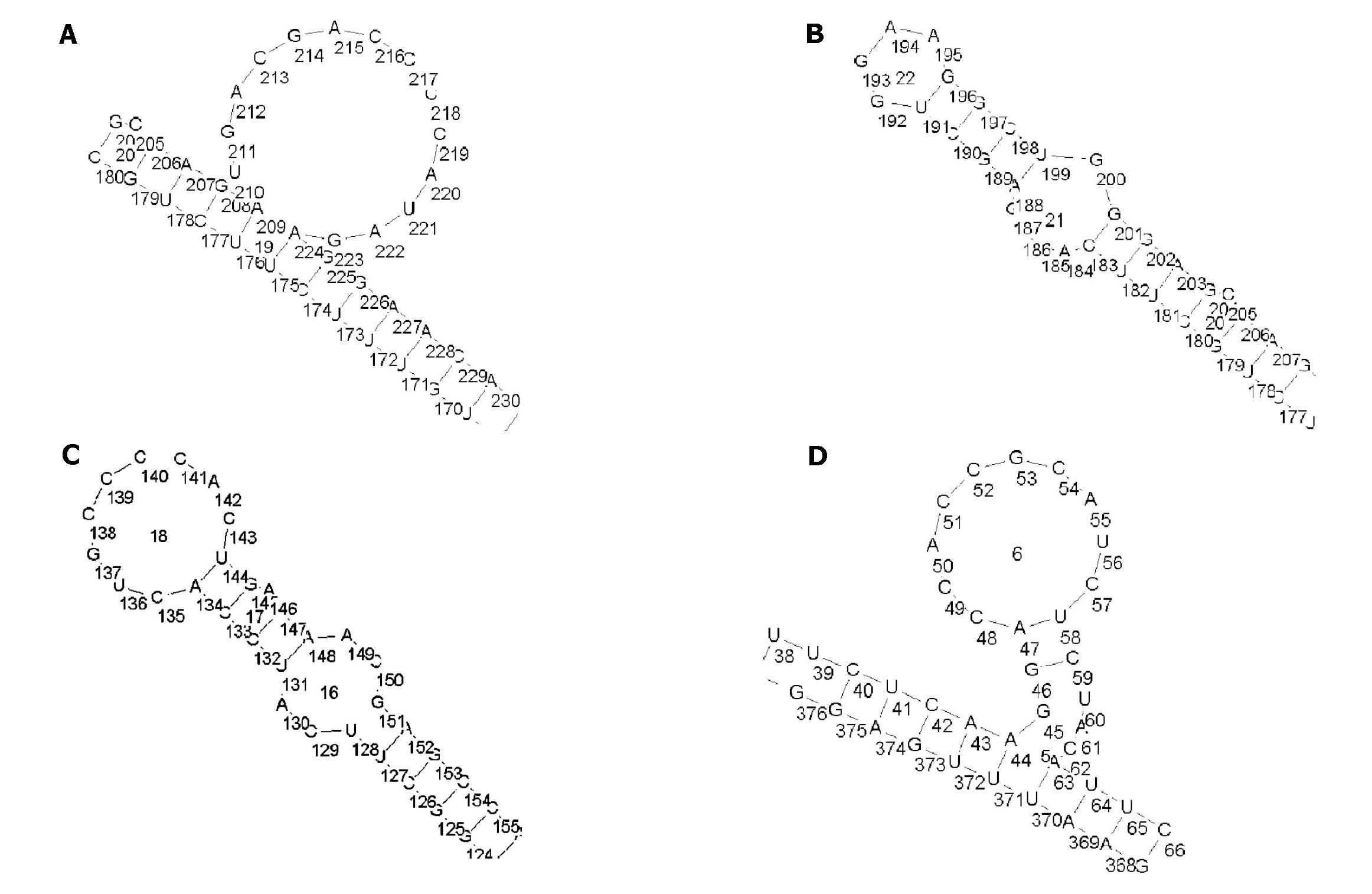
Figure 3 Four secondary structures of antisense accessible sites predicted by RNADraw software.
A: ODN1 (207-226 bp); B: ODN2 (187-206 bp); C: ODN3 (126-145 bp); D: ODN4 (44-63 bp).
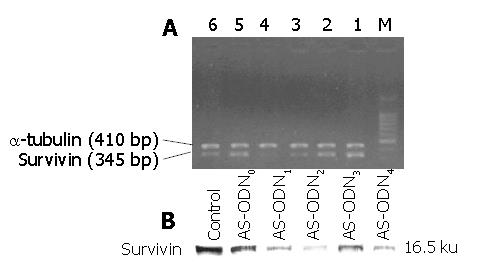
Figure 4 RT-PCR and Western blotting detection of the blocking effects of various antisense oligonucleotides on survivin mRNA and protein expression of MKN-45 cells.
A: RT-PCR detection of the blocking effects of various antisense oligonucleotides on survivin mRNA expression of MKV-45 cells M: PCR marker (100-1000 bp). Lane 1: Non-transfection Control; lane 2: AS-ODN0; lane 3: AS-ODN1 ; lane 4: AS-ODN2; lane 5: AS-ODN3; lane 6: AS-ODN4; B: Western blotting detection of the blocking effects of various antisense oligonucleotides on survivin protein expression of MKN-45 cells.
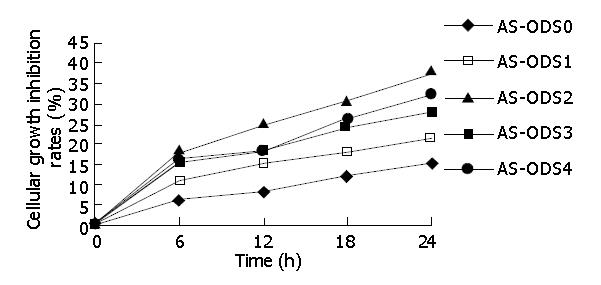
Figure 5 Growth inhibitory effects of various antisense oligonucleotides on MKN-45 cells.
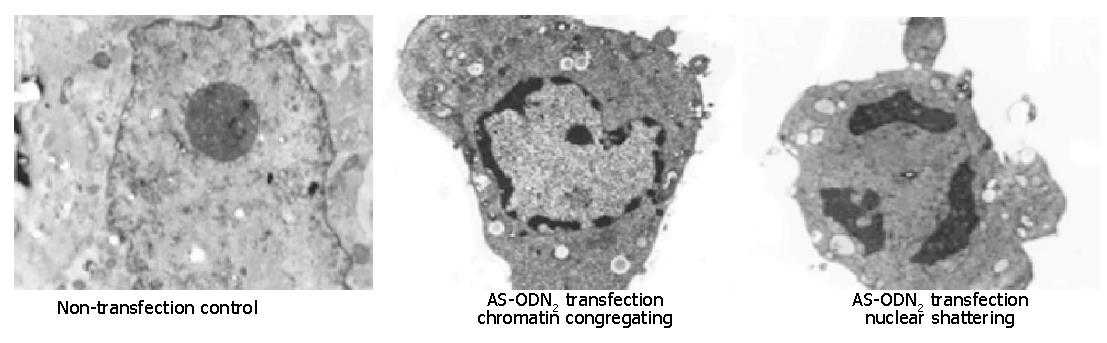
Figure 6 Morphological observation of gastric cancer cells after transfection with antisense oligonucleotides targeting survivin by electronic microscopy.
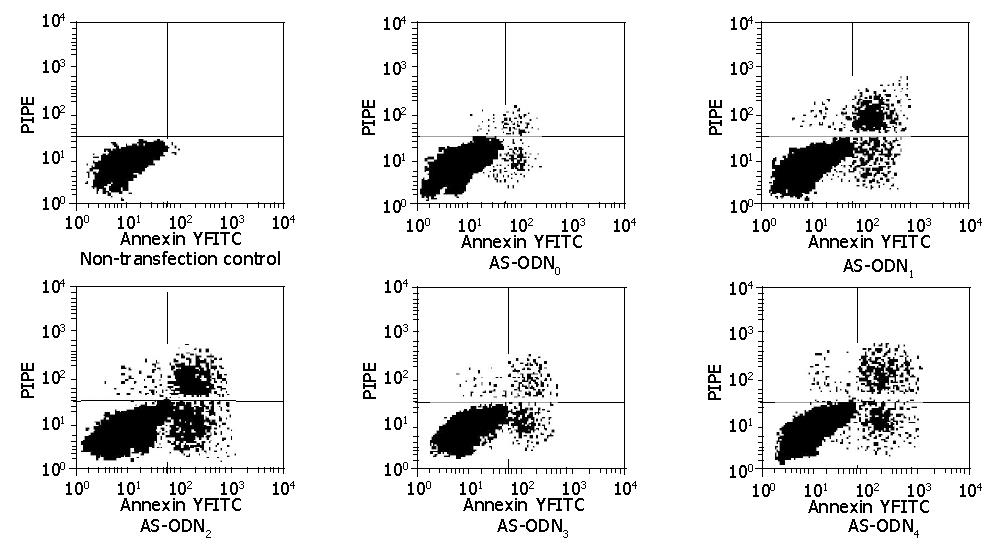
Figure 7 Flow cytometry detection of apoptosis-inducing effects of various antisense oligonucleotides on MKN-45 cells.
- Citation: Tong QS, Zheng LD, Chen FM, Zeng FQ, Wang L, Dong JH, Lu GC. Selection of optimal antisense accessible sites of survivin and its application in treatment of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(5): 634-640
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i5/634.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i5.634