Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2005; 11(48): 7555-7559
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7555
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7555
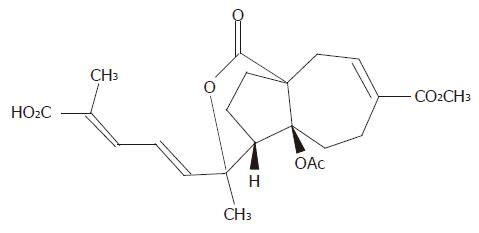
Figure 1 Chemical structure of pseudolaric acid B (C23H28O8, MW = 432.
5).
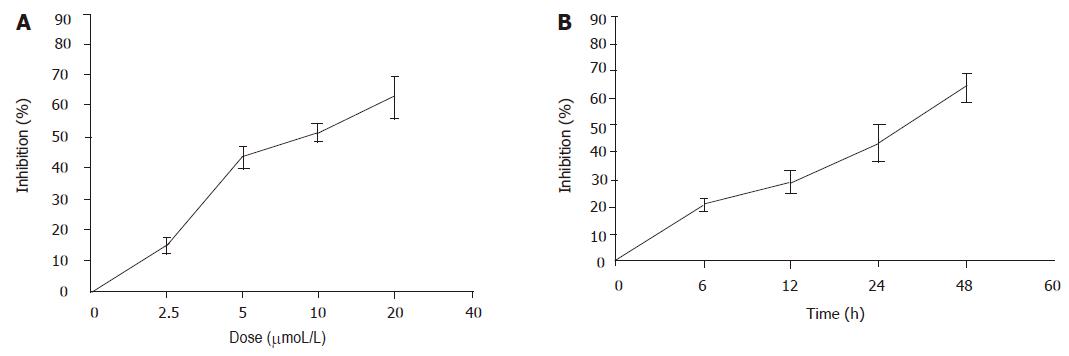
Figure 2 Dose- and time-dependent inhibitory effect of pseudolaric acid B on growth of AGS cells.
A: AGS cells were treated with various doses of pseudolaric acid B for 24 h; B: AGS cells were treated with 5 μmol/L pseudolaric acid B for various time periods. Each point indicates mean±SD of three independent experiments.
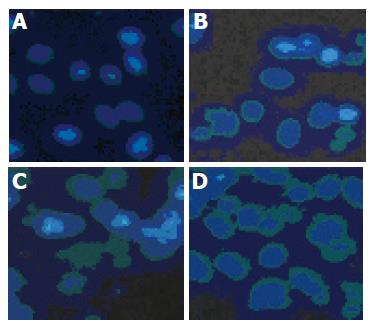
Figure 3 Time-dependent effect of 5 μmol/L pseudolaric acid B on morphological changes in AGS cells.
A: 0; B: 12; C: 24; D: 48 h.
Figure 4 Time-dependent effect of 5 μmol/L pseudolaric acid B on internucleosomal DNA fragmentation in AGS cells.
M: Marker; lane 1: 0 h; lane 2: 12 h; lane 3: 24 h; lane 4: 48 h.
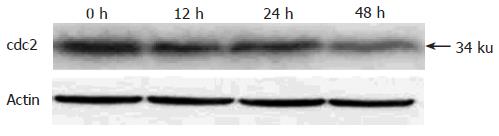
Figure 5 cdc2 levels in AGS cells down-regulated by pseudolaric acid B treatment.
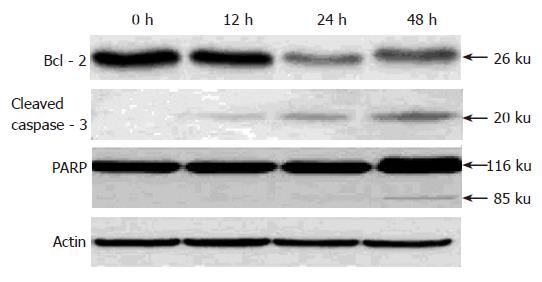
Figure 6 Time-dependent down-regulation of Bcl-2, activation of caspase-3, and PARP cleavage in cultured AGS cells induced by pseudolaric acid B.
- Citation: Li KS, Gu XF, Li P, Zhang Y, Zhao YS, Yao ZJ, Qu NQ, Wang BY. Effect of pseudolaric acid B on gastric cancer cells: Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(48): 7555-7559
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i48/7555.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7555