Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2005; 11(43): 6884-6887
Published online Nov 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i43.6884
Published online Nov 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i43.6884
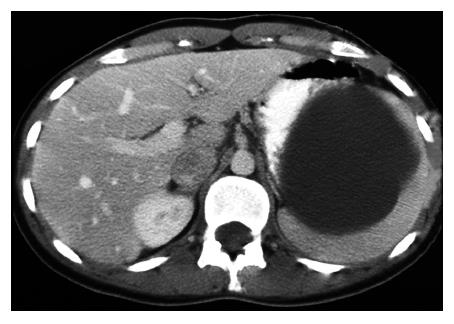
Figure 1 Plain abdominal CT scan showing the splenic localization of a large cyst displacing the remaining splenic parenchyma, the so-called “beak-sign”.
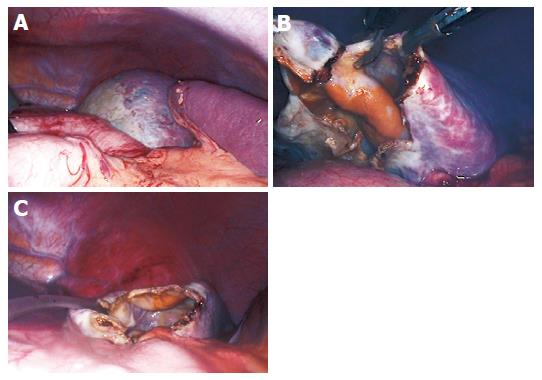
Figure 2 Laparoscopic view of the cyst.
Most parts of the cyst are covered with a thin layer of splenic tissue; only a small portion in the upper pole of the spleen displays a “white roof” (A). The cyst was punctured and evacuated and a 3 cm×3 cm portion of the cyst was excised using the monopolar scissor (B). A drainage tube was inserted in the remaining cavity (C).
- Citation: A M, EP M, T L, D M, C F, G K. Non-parasitic splenic cysts: A report of three cases. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(43): 6884-6887
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i43/6884.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i43.6884