Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2005; 11(40): 6395-6401
Published online Oct 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6395
Published online Oct 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6395
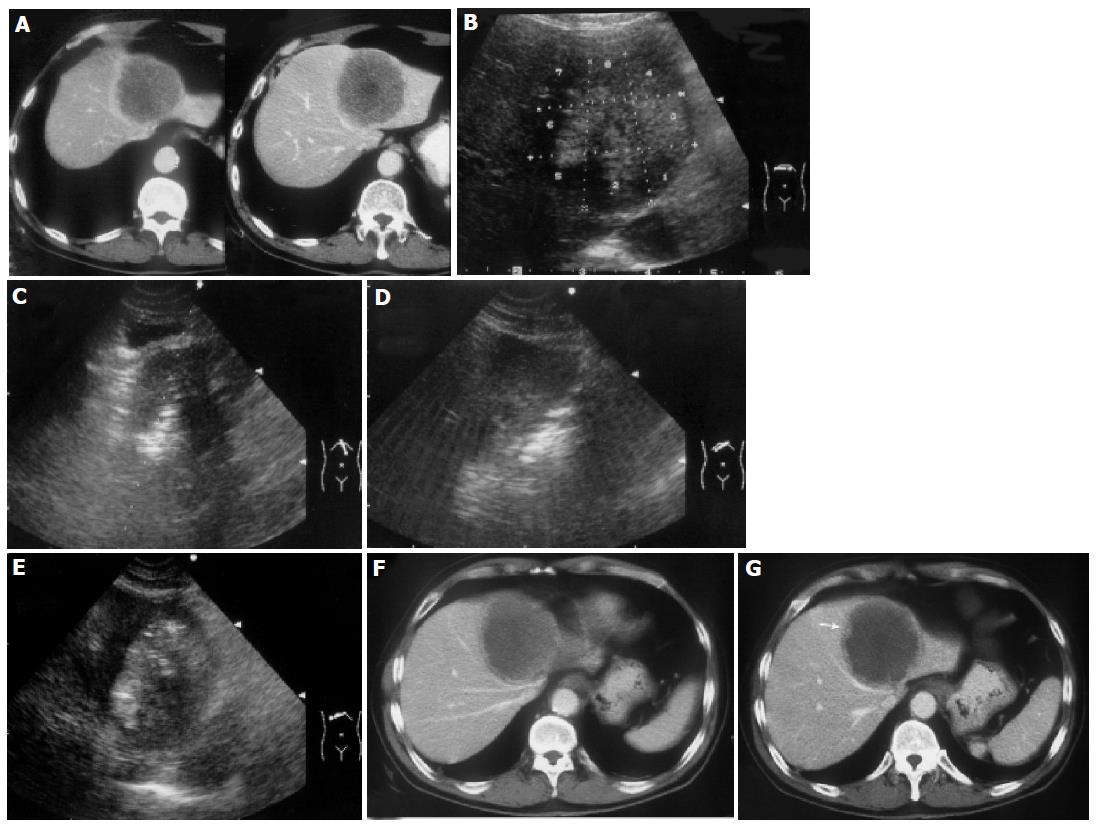
Figure 1 A 55-year-old man developed liver metastasis from colon cancer.
A: Enhanced transverse CT scans obtained before treatment showed a spherical tumor invading into the diaphragm; B: The ablation protocol was designed and eight target sites were determined in this section. The tumor area near the heart and stomach were ablated first. C: The fourth ablation was conducted; D: The fifth ablation was conducted; E: The ablation was finished and the tumor area was presented as hyperechoic; F: Enhanced transverse CT scans obtained 1 d after the treatment showed that most of the tumor was coagulated and necrosis; G: Enhanced transverse CT scans obtained 1 d after the treatment showed slight enhancement (↑) on the lower margin of the tumor. The patient received the second treatment and achieved complete ablation.
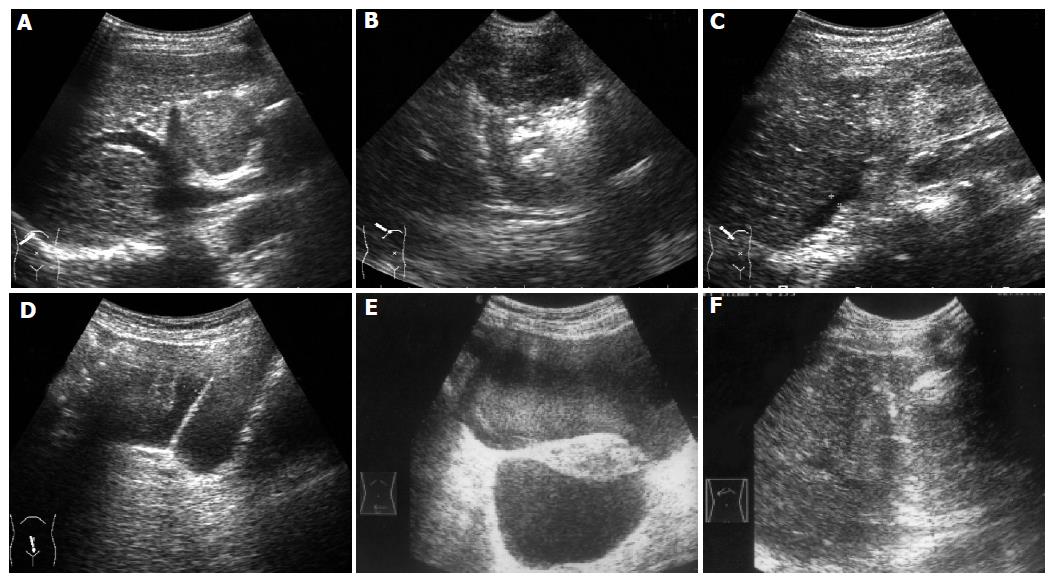
Figure 2 A 72-year-old woman developed intrahepatic recurrence 2 years after hepatic resection for HCC.
A: US scan before treatment showed a large tumor protruding from the liver surface; B: US guided ablation was conducted; C: US scan immediately obtained after treatment showed little fluid under the liver. D: Five minutes later, US scan showed accumulative fluid in pelvic cavity; E: Nine hours later, US scan showed a great deal of hemorrhage in pelvic cavity. F: Ten hours later, US guided ablation of bleeding site was performed.
- Citation: Chen MH, Yang W, Yan K, Gao W, Dai Y, Wang YB, Zhang XP, Yin SS. Treatment efficacy of radiofrequency ablation of 338 patients with hepatic malignant tumor and the relevant complications. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(40): 6395-6401
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i40/6395.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6395