Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2005; 11(40): 6389-6394
Published online Oct 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6389
Published online Oct 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6389
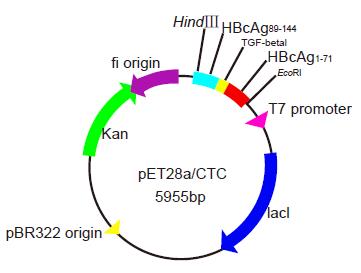
Figure 1 Schematic construction of plasmid pET28a(+)/CTC.
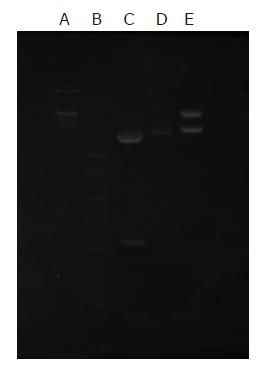
Figure 2 Recombinant vector pET28a/CTC identified by restriction enzyme digestion.
Lane A: 200 bp DNA ladder; lane B: λDNA/ Hind IIIMarkers; lane C: EcoR I+Hind III enzyme digestion(546 bp+3.9 kb); lane D: vector pET28a as negative control; lane E: EcoR I+Hind III enzyme digestion pET28a
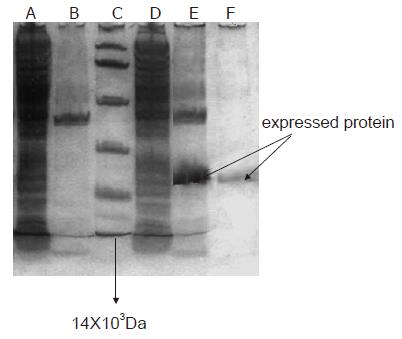
Figure 3 Expressed and purified pET28a/CTC fusion protein by 150 g.
l-1 SDS–PAGE in combination with Coomassie blue staining. Lane A: Bacterial protein expressed in the supermatant fraction of pET-28a(+) vector after induction with IPTG; lane B: Bacterial protein expressed in the precipitation of lysate of fraction of pET-28a(+) vector after induction with IPTG; lane C: Standard protein low-molecular-mass marker (Mr 97.4, 66.2, 43.0, 31.0, 20.1, and 14KD); lane D: Bacterial protein expressed in the supernatant fraction of the vector pET-28a(+)/CTC after induction with IPTG; lane E: Bacterial protein expressed in the precipitation of lysate of fraction of the vector pET-28a(+)/ CTC after induction with IPTG; lane F: Purity of recombinant fusion protein.
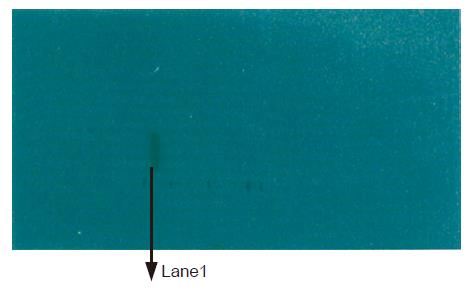
Figure 4 Antigenic analysis of the expression of recombinant vector by Western blot.
Lane 1: BL21/pET28a(+)/CTC.
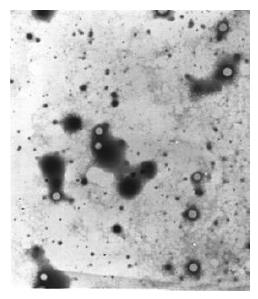
Figure 5 Electron microscopy of the core-like particles formed in fusion protein.
- Citation: Guo YH, Hao ZM, Luo JY, Wang JH. Construction of prokaryotic expression system of TGF-β1 epitope gene and identification of recombinant fusion protein immunity. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(40): 6389-6394
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i40/6389.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6389