Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2005; 11(37): 5853-5858
Published online Oct 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5853
Published online Oct 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5853
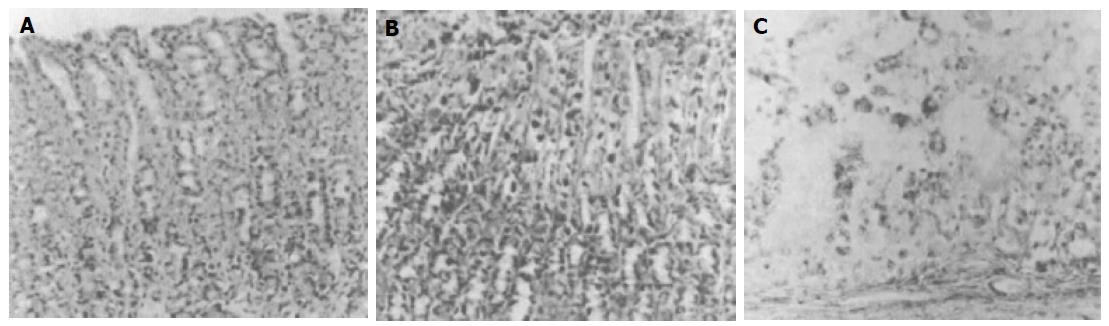
Figure 1 Histological studies of gastric mucosa exposed for 3 h gastric juice in normal, DM, and BQC-fed DM rats.
Note that in normal rat stomachs irrigated with gastric juice (A), gastric mucosal cells look intact. However, gastric juice- irrigated DM rat mucosa (B), a disruption of gastric epithelial layer is observed. When stomachs of BQC-fed DM rats are irrigated with gastric juice (C), a complete disruption of the upper mucosal cells and lamina propria is obtained. The injured cells are characterized by karyorrhexis and dense homogenous acidophilic cytoplasm. In most cases, gastric edema also is observed (×150).
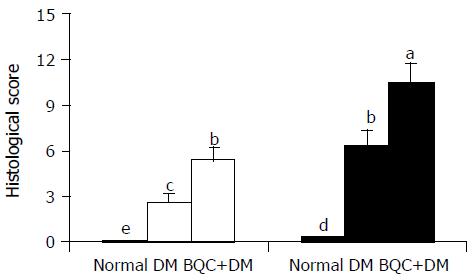
Figure 2 Histological scores of gastric mucosa in normal, DM, and BQC-fed DM rats.
Rats were fed with normal diet or BQC diet for 90 d. Diabetes was induced by intravenous streptozotocin. Rat stomachs were irrigated for 3 h with normal saline (□) or gastric juice (■). Values are mean SE, n = 6-8. Bars labeled with different letters are significantly different at P < 0.05 based on Tukey statistic method.
- Citation: Hung CR. Effect of lysozyme chloride on betel quid chewing aggravated gastric oxidative stress and hemorrhagic ulcer in diabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(37): 5853-5858
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i37/5853.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i37.5853