Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2005; 11(34): 5295-5302
Published online Sep 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i34.5295
Published online Sep 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i34.5295
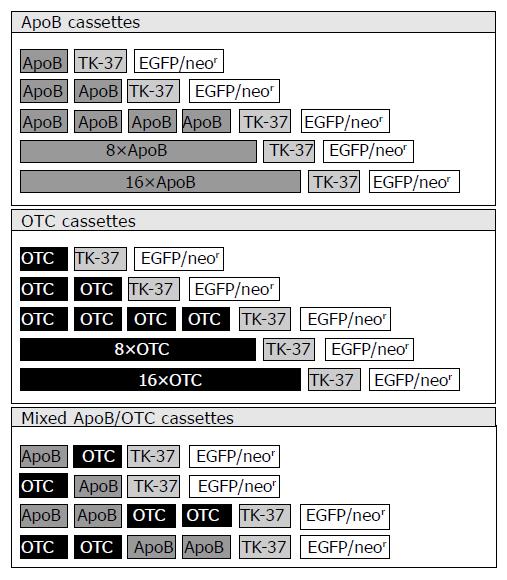
Figure 1 Schematic representation of synthetic transcriptional control unit constructs.
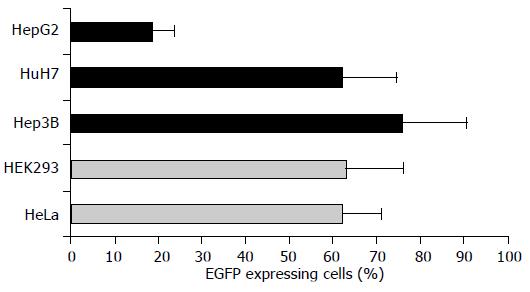
Figure 2 Transfection efficiencies of cell lines of human hepatoma and non-liver origin.
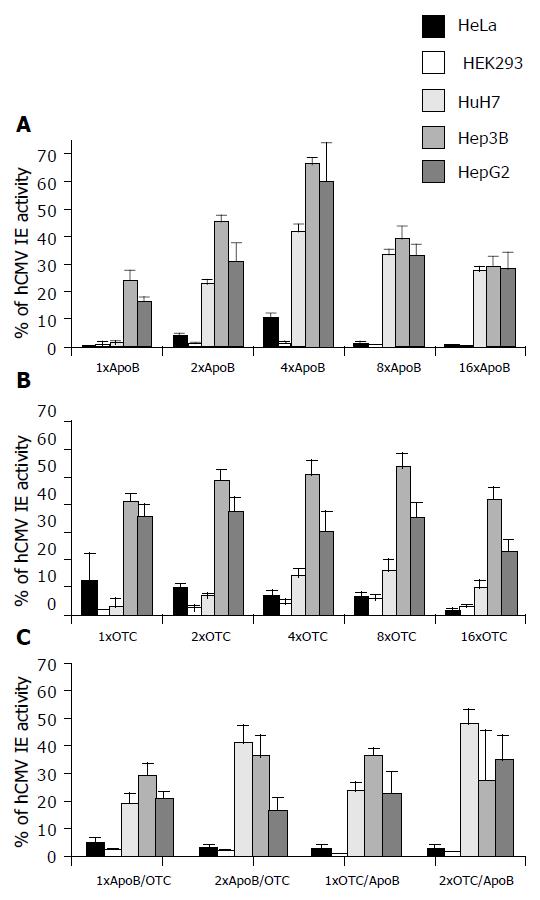
Figure 3 Transcriptional activities of synthetic transcriptional control unit constructs (A-C).
Figure 4 Transcriptional activities of synthetic ApoB transcriptional control units.
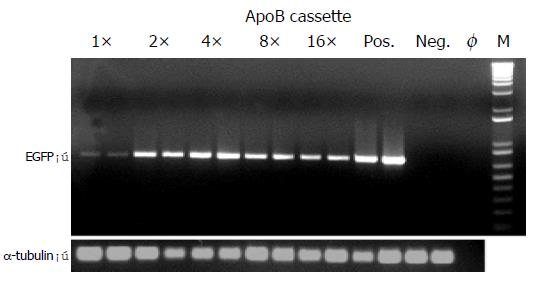
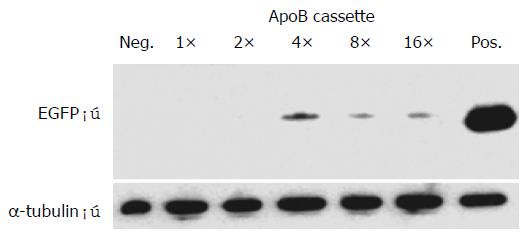
Figure 5 Western blot of EGFP expression driven by synthetic ApoB transcriptional control units.
Lane 1: untransfected Hep3B cells used as a negative control (Neg.); lanes 2-6: detection of a 27 kDa band specific for EGFP expressing Hep3B cells transiently transfected with enhancer module plasmids exhibiting single (lane 2: 1 × ) or multimeric ApoB cassettes (lane 3: 2 × ; lane 4: 4 × ; lane5: 8 × ; lane 6: 16 × ); lane 7: Hep3B cells transfected with EGFP-encoding hCMV IE promoter plasmid pEGFP-C1 used as a positive control (Pos.), and Western blot detection of á-tubulin used as an internal standard.
- Citation: Lemken ML, Wybranietz WA, Schmidt U, Graepler F, Armeanu S, Bitzer M, Lauer UM. Liver-directed gene expression employing synthetic transcriptional control units. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(34): 5295-5302
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i34/5295.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i34.5295