Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2005; 11(30): 4703-4708
Published online Aug 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4703
Published online Aug 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4703
Figure 1 There were 16 amino acid variations between genotype B and C HBx, which were located at amino acid positions 5, 30, 31, 34, 36, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44, 47, 87, 88, 116, 118, and 119, respectively.
Four boxed amino acids, located at the positions of 127, 130, 131, 132, respectively, were to be substituted by site-directed mutagenesis.
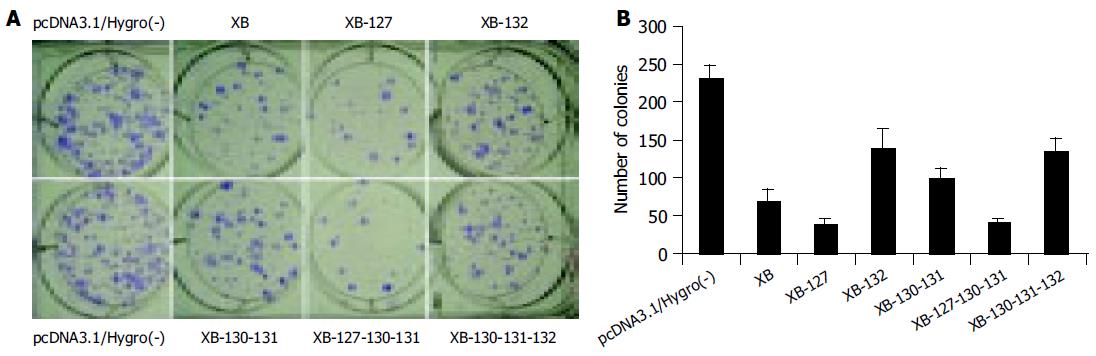
Figure 2 Chang cells were transfected by genotype B X gene expression vectors and screened by hygromycin, the drug-resistant colonies formed 14 d post-transfection were fixed by cold methanol, stained with Giemsa (A) and counted (B).
The results are shown as mean±SD of six separate experiments.
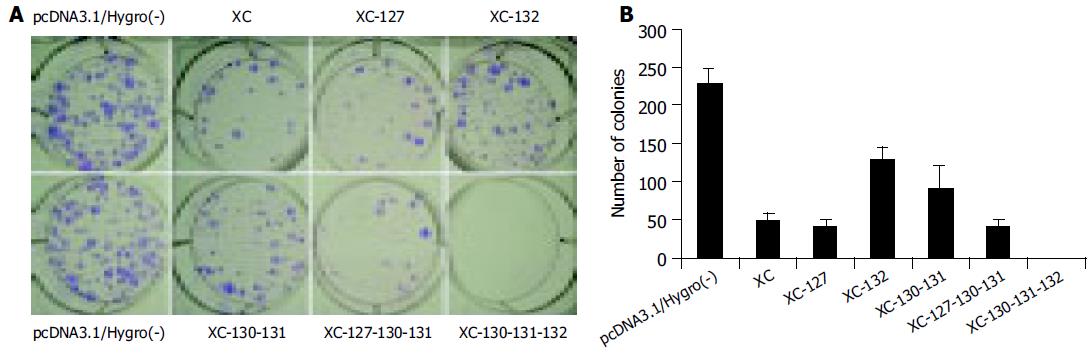
Figure 3 Chang cells were transfected by genotype C X gene expression vectors and screened by hygromycin, the drug-resistant colonies formed 14 d post-transfection were fixed by cold methanol, stained with Giemsa (A) and scored (B).
The results are shown as mean±SD of six separate experiments.
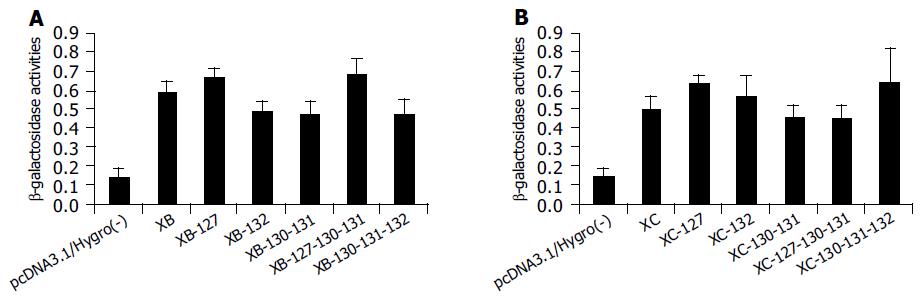
Figure 4 Chang cells were co-transfected by pCMVβ together with the X gene or related mutants with genotype B (A) or genotype C (B).
Forty-eight hours post-transfection, the cells were lysed and the intracellular β-galactosidase activities were monitored after protein normalization. The results are shown as mean±SD of six separate experiments.
- Citation: Lin X, Xu X, Huang QL, Liu YQ, Zheng DL, Chen WN, Lin JY. Biological impacts of “hot-spot” mutations of hepatitis B virus X proteins are genotype B and C differentiated. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(30): 4703-4708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i30/4703.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4703