Copyright
©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2005; 11(29): 4490-4496
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4490
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4490
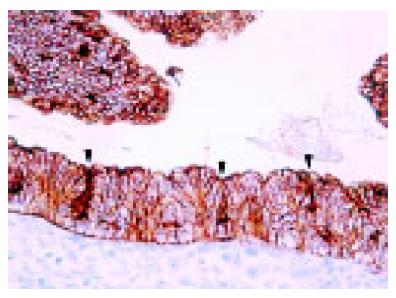
Figure 1 Foregut embryonic epithelium as seen in the esophagus and stomach at 7-wk GA.
Note the presence of depressions in the epithelial surface (arrowheads): these may be primitive pits. The immunostaining is for CK19 and shows diffuse moderate to strong positivity (original magnification, OM ×400).
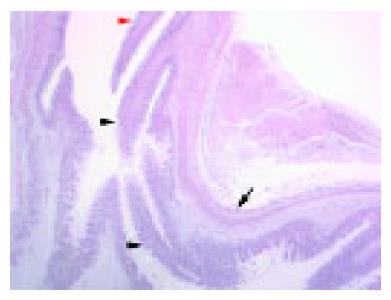
Figure 2 Overview of the fetal EGJ at 20-wk GA.
The upper border of the abdominal esophagus is indicated by a red arrowhead. The angle of His (the anatomic boundary between the tubular esophagus and the saccular stomach) is easily recognizable (arrow). The distal end of the esophagus is located at the level of the angle of His. Esophageal simple columnar epithelium is present in the distal esophagus (indicated by black arrowheads at its proximal and distal margins, H&E, OM ×125).
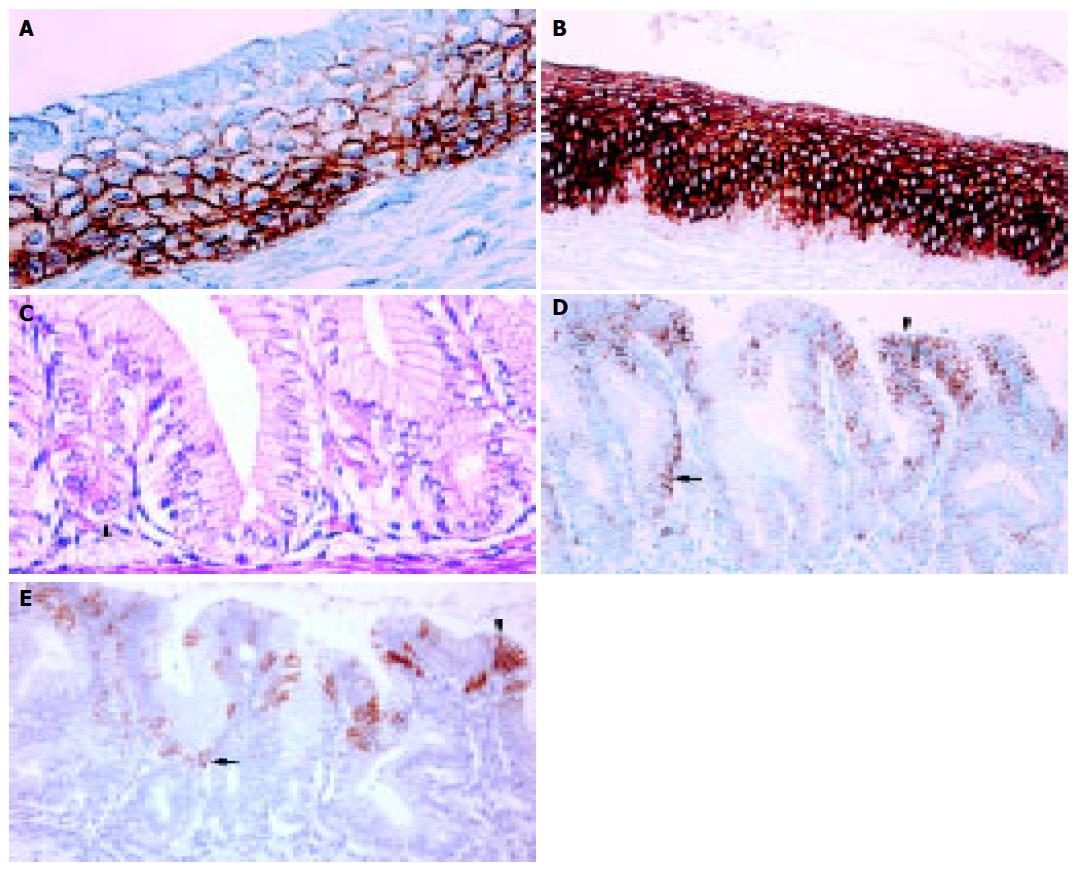
Figure 3 Tubular esophagus.
A: Esophageal ciliated epithelium at 20-wk GA. The immunostaining is for CK5 and is more intense in the basal and intermediate cell layers than in the superficial cell layer (OM ×400); B: Esophageal squamous epithelium in a 3-wk-old neonate. The immunostaining is for CK13 and is absent in the basal cell layer and diffuse moderate to strong in the intermediate and superficial cell layers (OM ×200); C: Esophageal simple columnar epithelium at 20-wk GA. To the left: parietal cells with roughly triangular shape and highly acidophilic cytoplasm (ESP, arrowhead). To the right: no discernible parietal cells are present (ESN, H&E, OM ×400); D: Esophageal simple columnar epithelium at 20-wk GA. The immunostaining is for CK7 and shows moderate positivity at the mucosal surface and deep in the glands (arrowhead and arrow, respectively, OM ×200); E: Esophageal simple columnar epithelium at 20-wk GA (same case as in Figure 3D). The immunostaining is for CK20 and shows patchy positivity of the superficial part of the mucosa (surface and pit epithelium: arrowhead and arrow, respectively, OM ×200).
- Citation: Hertogh GD, Eyken PV, Ectors N, Geboes K. On the origin of cardiac mucosa: A histological and immunohistoc-hemical study of cytokeratin expression patterns in the developing esophagogastric junction region and stomach. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(29): 4490-4496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i29/4490.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4490