Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2005; 11(23): 3640-3643
Published online Jun 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i23.3640
Published online Jun 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i23.3640
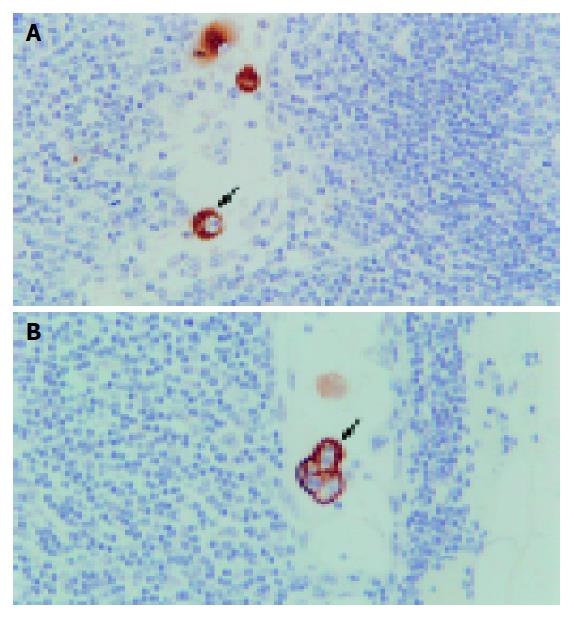
Figure 1 Representative photographs of micrometastases detected by immunohistochemistry using monoclonal cytokeratin antibody AE1/AE3.
A: arrowhead indicates a cancer cell located in the paracortical sinus showing morphological characteristics of malignant cells including a large nucleus and condensed nuclear small body; B: arrowhead points to three cancer cells located in subcapsular sinus. Original magnification: A, ×200; B, ×200.
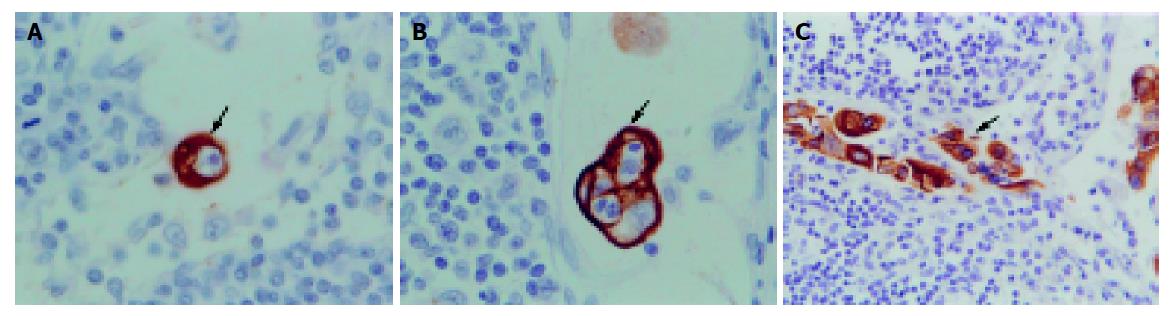
Figure 2 Representative photographs of micrometastases detected by immunohistochemistry using monoclonal cytokeratin antibody AE1/AE3.
A: arrowhead indicates a single cell in the positive node; B: arrowhead shows small groups of cells in the positive node; C: arrowhead points to large tumor deposits in the positive node. Original magnification: A, ×400; B, ×400; C, ×200.
- Citation: Zhou ZW, Rieger N, Ruszkiewicz A, Wang GQ, Wan DS. Detection of lymph nodes micrometastases in Dukes’ A and B colorectal cancer using anti-cytokeratin antibodies AE1/AE3. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(23): 3640-3643
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i23/3640.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i23.3640